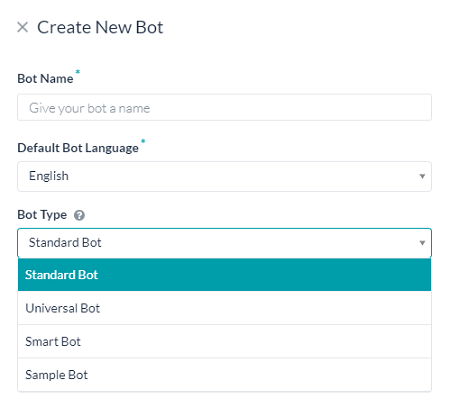
標準Botは最も一般的なタイプのBotです。ダイアログタスク、アラートタスク、アクションタスク、情報タスク、ナレッジタスクを作成したり、あるタスクを別のタスクにマッピングするフローを作成することができます。
このトピックでは、新しい標準Botを作成するのに必要な基本設定について説明します。
Botのタスクの定義
標準Botを作成したら、Botをどのように動作させるかを定義します。まずはBotのタスクの定義から始めましょう。
以下のうちどちらか1つの方法で、Botの1つ以上のタスクまたはフローを定義します。
- 「Botの概要」ページで、 [タスク] ウィジェットの [+ 新しいタスク] をクリックします。
- [Botのタスク] タブで、使用するタスクにマウスポインターを置き、 [+] アイコンをクリックします。
タスクとは、「航空券を予約する」、「天気を調べる」、「チケットをキャンセルする」などBotがエンドユーザーに対して行う動作を指します。
Kore.ai Botビルダーでは、以下のようなタスクタイプを定義することができます。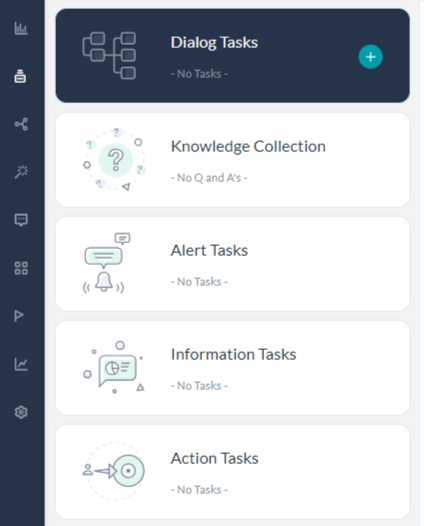
注意:[ナレッジコレクションとフロー] は「Botのタスク」ページにあります。
- ダイアログタスク − ユーザーとBotの間の複雑な会話型フローを実行するための複数のインテント、サブインテント、およびコンポーネントノードから成ります。
- アラートタスク − ウェブサービスのイベントを監視し、イベント発生時に通知メッセージを送信します。予定された投票や、Webhookを使用したほぼリアルタイムの通知にこのタスクタイプを利用できます。
- ナレッジグラフ − 静的なFAQページを、インテリジェントで、パーソナライズされた会話型体験に変換します。重要用語の優先順位を構築し、適切な順位のノードに質問を追加して「ユーザーに応答」タスクをBotに任せることで、サポートスタッフがより複雑なタスクに専念して従事できるようになります。
その他のステップ
- チャットBotが一貫してユーザーを理解し、対話することができるかどうかは、会話を強化する自然言語処理(NLP)の堅牢性によって決まります。Kore.aiプラットフォームは独自の自然言語処理戦略を採用し、ファンダメンタルミーニングと機械学習エンジンを組み合わせることで、事前のトレーニングをほとんど行わずに会話の精度を最大限に高めることができます。詳しくはこちらをご覧ください。
- いずれのタブでも、少なくとも1つのタスクが「構成済み」または「公開済み」状態にあれば、メッセージウィンドウでBotのタスクをテストすることができます。テストを実行するには、Botビルダーの右下にある [Botに話しかける] アイコンをクリックします。詳しくは、「Botに話しかける」を参照してください。
- Botのデプロイ後、エンドユーザーがBotにアクセスして対話を開始できるよう、デリバリーチャネルを追加します。詳しくは、「Botにチャネルを追加する」を参照してください。
- 開発者は、新しいまたは更新されたBotやタスクをデプロイする前に、レビュー、承認または非承認のために管理者に公開リクエストを開始することができます。また、Kore.aiのサポートに連絡してレビューと承認のプロセスを開始し、Botを公開用Botストアに公開することもできます。詳しくは、「タスクの公開」を参照してください。
- Botを公開したあとは、「分析」ページでBotがタスクを特定して実行する際のパフォーマンスについて分析情報を得ることができます。インテントに一致または一致しなかったユーザーの発話の必要な情報を確認できます。また、インテントが一致したにも関わらず実行できなかったタスクや、スクリプトやサービスノードのバックエンドのパフォーマンスを表示します。詳しくは、「Botの分析」を参照してください。