顧客とのやり取りを自動化する上で、組織にとってIVRシステムが上位レベルの選択肢であることが証明されています。しかし、カスタマーサービスにIVR (Interactive Voice Response) システムを使用している場合、以下の2つの問題に頻繁に直面している可能性があります。
- 非直感的なインターフェイス:IVRシステムは、顧客が必要なことを伝えるだけのものではありません。インテントを検出する前に、ユーザーは膨大な数のメニューの中から選択しなければなりません。最初にユーザーが意思表示をできるようにしたとしても、バックエンドのプログラムは限られた数のフレーズしか理解できません。
- 静的フロー:IVRシステムは静的なコールフローを使用していますが、これは人間による対話の非線形性および文脈的性質とは一致しません。次の例では、お客様が航空券を予約しようとしています。
ユーザー: NYC行きのチケットを予約してください。IVR:かしこまりました。日付を教えてください。ユーザー: 現地での今週の日曜日の天気は雨ですか? IVR: すみません、入力内容が分かりません。
従来のIVRシステムでは、ユーザーがプログラムの流れに沿って要望を伝える余地が限られていました。
Kore.ai IVRサポート
Kore.aiを使用すると、IVRシステムを会話型に変えることができます。人間味のある会話能力を持つチャットボットを構築し、既存のIVRシステムと連携させることで、組織のカスタマーサービス体験を新たなレベルに引き上げることができます。以下の機能により、お客様のKore.ai ボットと既存のIVRとのシームレスな連携が可能になります。
- VXMLのネイティブサポート:W3C準拠のVXMLファイルを解析および生成する機能を内蔵。
- ハイブリッド連携:ボットプラットフォーム上でユースケースやダイアログを構築し、IVRのダイアログと連動させることができる柔軟性があります。
- 会話アナライザー:Kore.aiの会話アナライザーは、エンタープライズが過去のチャットや通話のトランスクリプトを使用して会話フローを生成するのに役立ちます。チャットや通話のトランスクリプトをニューラルネットワークベースの機械学習モデルを用いて分析し、特定のインテントを満たすためのインテントや会話パターンを識別します。この機能はベータ版のすぐに利用できる機能です。この機能を試してみたい方は、サポートチームまでお問い合わせください。
- きめ細やかなコールフローのサポート:文法、プロンプト、リトライ、タイムアウト期間など、コールフローのすべての要素を定義する機能。Kore.aiは呼び出し終了ハンドラをサポートしており、例外が発生した場合に通話を終了したり、ダイアログを呼び出したりすることができます。
設定
IVR連携の設定は、以下の3つのステップで行います。
- ボットの設定トランスクリプションオプション、ウェルカムメッセージ、標準応答、VXMLプロパティなどのIVR設定を定義します。
- ダイアログの定義:ノード固有の文法、プロンプト、およびタイムアウトやリトライなどのコールフローの動作を設定することで、ダイアログを定義します。
- チャネルの設定:認証を設定し、IVRシステムにWebHookを設定し、チャネルを有効化します。
ボットの設定
ステップ1: ボットのIVR設定
連携の最初のステップとして、まずボットのIVR設定を有効にし、トランスクリプションオプションおよびVXMLプロパティを定義する必要があります。これらの設定は、ボットのデフォルトとして機能します。ダイアログタスクのノードレベルでカスタム値を定義することで、ボットレベルで定義されたVXMLプロパティを上書きすることができます。ボットのIVR設定を行うには
- IVRを連携したいボットを開きます。
- 左のナビゲーションパネルにカーソルを合わせてチャネルを選択します。
- IVR設定を見つけてクリックします。手順が記載されたIVRパネルが開きます。
- 設定タブから、
- ボットのテストにKore.ai IVRサンドボックスを使用することができます。詳細は以下をご確認ください。IMP:IVR設定を有効化せずにアプリを関連付けた後に設定を保存した場合、プラットフォームはサンドボックスに必要な設定を事前に入力します。
- 新しいアプリを作成するか、既存のアプリを選択して、アプリをIVRチャネルに関連付けます。
- 外部アプリケーションで提供されているWebHookのURLを使用します。
- 設定タブで各種設定を行います。
IVRサンドボックスを有効化した場合、プラットフォームで以下の設定が必要となります。IVR設定が有効になっていない場合、これらは事前に入力されています。設定を有効にしている場合は、値が以下のものと同じであることをご確認ください。異なる値を使用すると、サンドボックスが期待通りに応答しない場合があります。- トランスクリプションの有効化をはいに設定 – トランスクリプションエンジンのソースをbuiltin:speech/transcribeに設定 – IVRデータ抽出キーをuserinputに設定 – ASR確信度しきい値をuserinput.confidenceに設定 – ASRしきい値確信度を50に設定
- (オプション)外部のトランスクリプションエンジンを有効にするには、トランスクリプションの有効化ではいを選択します。
- トランスクリプションエンジンを有効にすると、トランスクリプションエンジンのソースを入力するテキストボックスが表示されます。
注意:ボットプラットフォームは、UniMRCPでエンコードされた、音声・テキスト変換サービスに対応しています。ボットにトランスクリプションの有効化オプションを選択した場合のみ、プラットフォームでは、任意のノードのIVR設定(ステップ2で説明)の際に、文法を定義する必要がなくなります。
- 詳細を入力して設定を完了します。詳細はこちらをご確認ください。
- トランスクリプションエンジンを有効にすると、トランスクリプションエンジンのソースを入力するテキストボックスが表示されます。
- IVRチャネルを有効にしたら、IVR設定の通話ウェルカムイベントを設定することをお勧めします。これは、ユーザーがIVRチャネルを介してボットに接続した際に、ウェルカムメッセージを再生するものです。以下の手順に従います。
- 自然言語 > イベントハンドラで通話ウェルカムイベントを設定します。
- 音声通話プロパティを使用ボタンをクリックして、音声設定セクションを開きます。
- 初期プロンプトテキストボックスで、ユーザーがボットに接続する際に再生するメッセージを入力します。
- その他の設定フィールドの詳細については、ノードの音声通話プロパティの設定セクションを参照してください。
サンドボックスの設定
注意:このオプションは、プラットフォームのバージョン7.1で導入されました。オンプレミスのインストールではご利用いただけません。Kore.aiは、IVRサンドボックス環境を提供しており、ボットを即座に起動して音声通話でやり取りをすることができます。これは、動作中のIVRシステムが実行不能である、あるいは音声チャネルを介したボットのテストに利用できない場合に特に有効です。IVRサンドボックスはオプションの連携であり、お客様のカスタムIVR連携と共存することができます。このオプションを有効にすると、電話番号、PIN、シークレットが表示されます。ボットに割り当てられた電話番号とPINを使用してボットを呼び出し、チームでボットの開発やテストを行うことができます。有効なPINとシークレットを受け取ると、やり取りを行うためにボットに接続されます。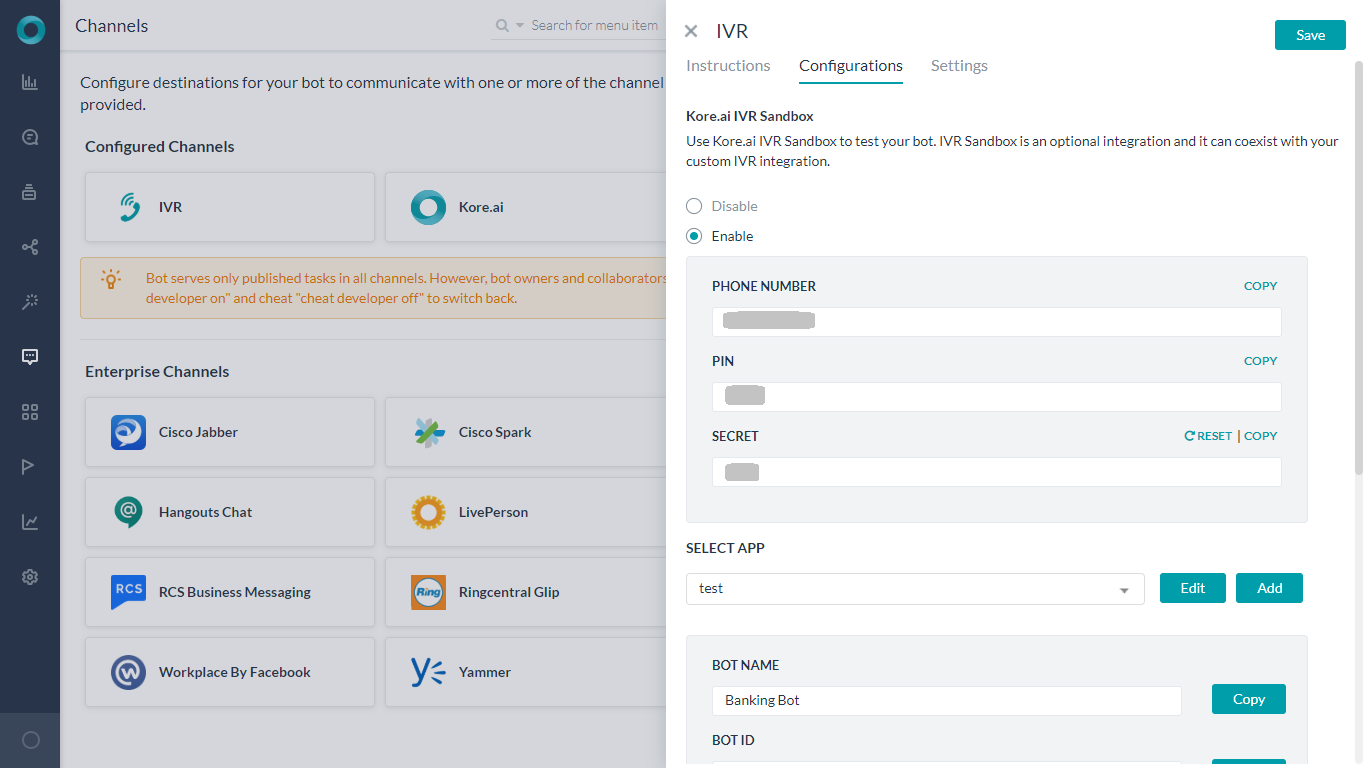 有効化されると、チャネルページのIVRアイコンにカーソルを合わせてテストボタンを選択することで、IVRサンドボックスの対話の詳細にアクセスできるようになります。制限事項
有効化されると、チャネルページのIVRアイコンにカーソルを合わせてテストボタンを選択することで、IVRサンドボックスの対話の詳細にアクセスできるようになります。制限事項
- このプラットフォームは限られた数の同時回線しかサポートしていないため、IVRサンドボックスを介したボットへの呼び出しに応答できない場合があります。
- IVRサンドボックスは、機能制限がある場合があるため、社内でのテスト目的のみに使用し、ボットのエンドユーザーには使用しないことを強くお勧めします。
チャネル設定
ステップ3: ボット用IVRチャネルの設定
ボットとダイアログの両方のレベルでIVR設定を行った後、ボットにIVRチャネルを設定する必要があります。IVRチャネルは、基本的な連携によってボットとIVRシステムを接続します。Kore.aiプラットフォームは、IVRシステムを介したエンドユーザーとのボットのやり取りの一環として、必要なVXMLファイルを生成します。
IVRチャネルの有効化とアプリの関連付け
Kore.ai ボットは、IVRからの受信リクエストを認証するためにJWTトークンを必要とします。JWTトークンを生成するには、アプリをボットに関連付ける必要があります。Kore.aiのアカウントで利用可能な既存のアプリを選択するか、新しいアプリを作成することができます。
-
- ボットのサイドナビゲーションパネルにカーソルを合わせてチャネルをクリックします。
<liチャネルページでIVRをクリックします。IVRチャネルの手順のページが開きます。
- 設定タブをクリックします。
- アプリを選択ドロップダウンリストから、既存のアプリを選択します。ボットを関連付けるアプリがない場合は、追加をクリックします。
- 以下をコピーします。
- WebhookのURL:IVRからボットを呼び出す場合。
- クライアントシークレット: WebHook URLに付加されるJWTトークンを生成します。
- チャネルの有効化ではいを選択します。
JWTトークンの生成
- JWTトークンの取得について参照するには、こちらをクリックしてください。
- JWTは、クエリパラメータ「トークン」の値としてIVRフックURLで渡す必要があります。
https://bots.kore.ai/ivr/hooks/{{botId}}?token={{JWT}}
The token can also be passed as the body parameter.
IVRコールフローからのボットの呼び出し 下図のように、VXML を使用して、IVRコールフローからボットにデータを渡すことができます。サブダイアログのソースは、以下のパラメーターを入力として受け取るJWTトークンを含むWebhook URLです。
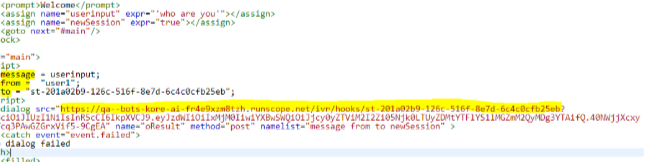
- メッセージ:ユーザーからのメッセージ
- From:ユニークなユーザーIDの例:電話番号
- To:ボットのストリームID
endOfConversation変数は、サブダイアログから返ってきたデータをもとに処理する必要があります。この値が「true」に設定されると、ダイアログの実行(会話)が完了したことを示します。ユーザーとの通話を終了させるトリガーにもなります。


