開発者が詳細なコードを書かなくても、プラットフォームがユーザーの発話に応答できる場面がいくつかあります。たとえば、:
- ユーザー インテントが検出されない場合やボットが理解できない場合の、デフォルトのダイアログ
- 特定の質問やあいさつ、エラーおよび警告のシナリオなどへの標準応答
- イベント ハンドラで特定の共通ボット イベントを定義することができます。詳細については、こちらをご覧ください。
これらはプラットフォームによりデフォルトで設定されていますが、ビジネス要件に応じてカスタマイズすることができます。このドキュメントでは、そのようなカスタマイズについて説明しています。
デフォルト ダイアログ
Kore.ai の自然言語処理がユーザーのインテントを決定できない場合、ダイアログ タスクを実行するか標準のエラー メッセージを表示するかを選択することができます。デフォルトでは、エラー メッセージを表示するように設定されています。[自然言語] > [デフォルトの会話] セクションで、[デフォルト ダイアログ] タブを選択してデフォルトのダイアログ タスクを定義します。たとえば、ボットからライブ エージェントへ会話を切り替えたり、ボットとの会話でユーザー インテントが決定できない場合は、メイン メニューのような汎用ダイアログを実行したりすることができます。デフォルト ダイアログ タスクが定義されていない場合は、標準エラー メッセージや「標準応答」セクションで定義されているカスタマイズが使用されます。以下の図は、銀行ポータル ボットで、ユーザー インテントが決定できない場合にアカウント ヘルプの取得ダイアログ タスクを実行するように設定されたボットビルダーの、「デフォルト ダイアログ」セクションの例です。 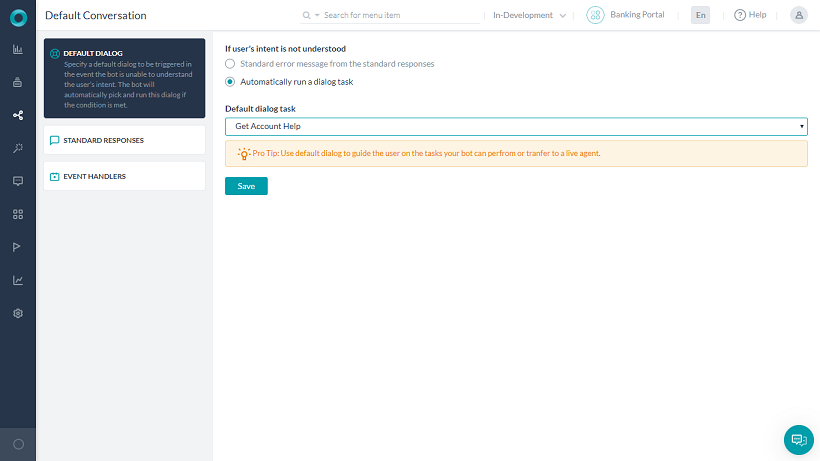
デフォルト ダイアログの定義
以下の手順を完了するには、デフォルト ダイアログとして選択できる 1 つのダイアログがあらかじめ定義されている必要があります。
- [自然言語] > [デフォルトの会話] タブで、「デフォルト ダイアログ」セクションを選択します
- 「ユーザーのインテントを理解できない場合」のセクションで、[ダイアログ タスクを自動的に実行] を選択します。
- 表示されている [デフォルト ダイアログ タスク] フィールドで、リストからデフォルトのダイアログを選択して [保存] をクリックします。
「設定が正常に保存されました」のメッセージが表示されます。
標準応答
Kore.ai ボットビルダー ツールでは、デフォルトの自然言語処理や、ユーザー入力やイベントに対する NLP インタープリタの応答を確認することができます。たとえば、ユーザーの「やあ!」という入力に対し、ボットは実行時に以下の応答のうち 1 つをランダムに選択して返答します。
- やあ
- こんにちは
- こんにちは!
- どうも 🙂
NLP インタープリタは、イベントや条件、トリガーまたはユーザー入力に基づいて事前定義されたテキストの応答をユーザーに表示します。カスタム ボットやボットのユーザーに応じて、イベントや入力の要求に対してユーザーに表示されるデフォルトの応答を変更したい場合があります。たとえば、:
- ユーザー入力 - 生年月日は?
- イベント - 認証エラーです。
- トリガー - タスクがキャンセルされました。
両方の標準ボット応答を定義することができますが、必要に応じてユーザーがいる指定されたチャネルにのみ表示する、チャネル オーバーライド応答を追加することもできます。デフォルトの標準応答の一覧についてはこちらをご覧ください。たとえば SMS チャネルでは、データ量を節約するために短いボット応答のみを使用したい場合があります。
デフォルトの応答
ボットビルダーのデフォルトの応答を管理するには、
- 左側のナビゲーション メニューにマウス ポインターを置き、[自然言語] > [デフォルトの会話] を選択します
- [標準応答] セクションを選択して、下記の図のように [ステートメント] タブを表示します。
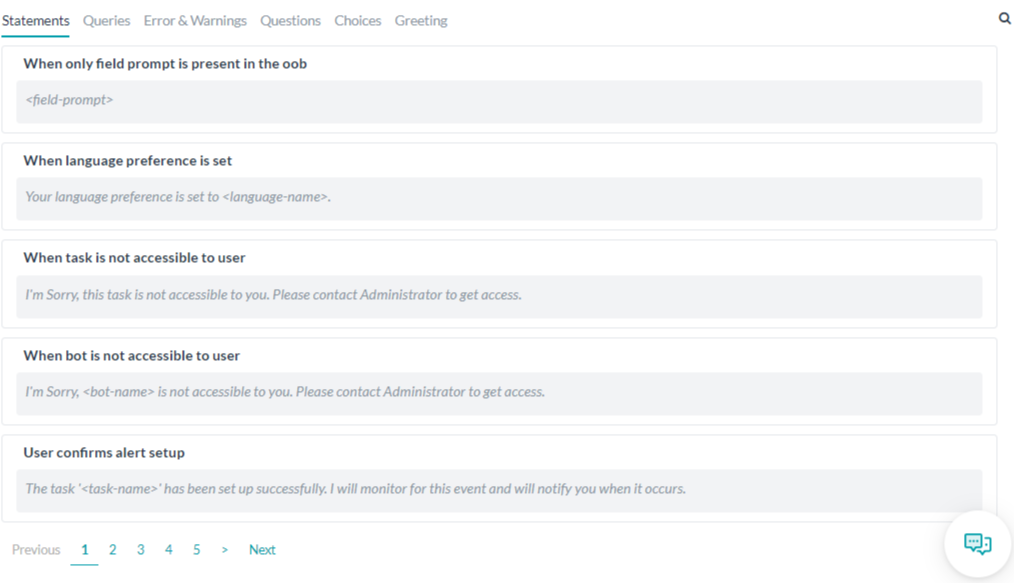
それぞれの標準応答のタブでは、イベントやユーザー入力に 1 つ以上の NLP インタープリタの標準応答がリスト化されています。デフォルトの応答を変更したり、必要に応じて NLP インタープリタがランダムに選んだ応答を、ユーザー入力やシステム イベントの応答として追加したりすることができます。「標準応答」セクションでは、標準のボット応答が以下のタブでカテゴリ分けされています。
- ステートメント - ボットまたはユーザーの動作に応じて表示される応答です。たとえば、ユーザーがタスクをキャンセルしたり、ユーザーがボットの要求に対して有効でない応答を返した場合に表示されます。
- 問い合わせ - 「どのフィールドを変更しますか?」のような、ボットからユーザーにさらなる情報を求めるためのステートメントです。
- エラーと警告 - シナリオ内でエラーが発生した場合の、ボットからユーザーに向けたステートメントです。たとえば、「終了日を開始日以前に設定することはできません。」のようなものです。
- 質問 - ボットがユーザーに尋ねる可能性のある、他のどのカテゴリにも該当しない質問です。
- 選択肢 - ボットは「はい」または「いいえ」の入力を求めます。たとえば、「このタスクが発生するたびにプッシュ通知を受け取りますか?」のようなものです。
- あいさつ - ボットがインストールされたとき、およびその他の初接触の際のボットの最初の応答です。たとえば、ユーザーがしばらくの非アクティブの状態から戻った場合など。
上記の図は、ボットの [自然言語] タブの「標準応答」セクションの [ステートメント] タブを示しています。
応答の追加および編集
新しい標準応答の追加 注意: あいまいさが提示されるような条件で標準応答が更新されている場合、ボットの応答はあいまいな選択肢を表示しないため、あいまいさのリストを提示するには “getChoices()“ 関数を使用する必要があります(以下のポイント 6 をご覧ください)。
- あいさつなどの標準応答のタブ カテゴリを選択して、応答を追加したい状況の上にマウス ポインターを置きます。 [応答を追加] をクリックします
- [チャネル オーバーライド を追加] ダイアログが表示されます。
- チャネル固有の応答を作成するには、[チャネルを選択] のドロップダウン リストでチャネルを選択します。[すべてのチャネル] オプションで、すべてのチャネルに応答を有効化できます。
- チャネル固有の応答の場合、[タスク] ドロップダウン リストから [すべてのタスク] を選択してこのチャネル固有の応答をすべてのタスクに適用するか、または特定のタスクを選択します。
- 特定のタスクが選択されている場合、[フィールドを選択] ドロップダウンが表示されます。[すべてのフィールド] またはこのチャネル固有の応答のための特定のフィールドを選択します。
- [ボット応答エディタ] では、[簡易モード] タブのベーシック エディタ コントロールを使用してこのチャネルのデフォルトのボット応答をオーバーライドできます。もしくは、[詳細設定モード] タブで応答のためのカスタム JavaScript を記述します。
- [簡易モード] タブ - 「おかえりなさい、お待ちしていました。」のような、デフォルトの標準応答のテキストを入力します。必要に応じて、太字、イタリック、見出し、ハイパーリンク、番号付き/記号付きリストや、ラインの挿入などのボタンで書式を設定することもできます。詳しくは、「プロンプト エディタの使用」をご覧ください。
- [詳細設定モード] タブ - 以下のコード例のように JavaScript を記述して、チャネル メッセージをオーバーライドします。
注意:デフォルトの値を返すには、以下のキーを使用します。response.message - デフォルトのメッセージを文字列として返します。response.choices - オプションの選択肢または確認メッセージのタイプを配列として返します。
- Slack チャネル オーバーライドの例
var message = {}; var attachments = []; var attachment = { 'text': "Exception occurred during API execution", 'color': '#FFCC00', 'attachment_type': 'default' }; attachments.push(attachment); message.attachments = attachments; print(JSON.stringify(message)); - Facebook チャネル オーバーライドの例
var message = { text: response.message }; var buttons = []; for (var i = 0; i < response.choices.length; i++) { var choiceItem = response.choices[i]; if (choiceItem.length > 20) { choiceItem = choiceItem.substring( 0, 18) + '..'; } var element = { content_type: 'text', title: choiceItem, payload: choiceItem }; buttons.push(element); } message.quick_replies = buttons; print(JSON.stringify(message)); - メール チャネル オーバーライドの例
var message = {}; var text = response.message + ' <br> '; for (var i = 0; i < response.choices.length; i++) { text = text.concat( '<u> + response.choices[i] + ' < /u> <br>'); } message.text = text; print(JSON.stringify(message)); - SMS チャネル オーバーライドの例
var message = {}; var indexArray = ['a', 'b', 'c', 'd', 'e', 'f', 'g', 'h', 'i', 'j', 'k', 'l', 'm', 'n', 'o', 'p', 'q', 'r', 's', 't', 'u', 'v', 'w', 'x', 'y', 'z' ]; var text = response.message + '\\n'; for (var i = 0; i < response.choices .length; i++) { text = text.concat(indexArray[i] + ') ' + response.choices[ i] + '\\n'); } message.text = text; print(JSON.stringify(message));
- Slack チャネル オーバーライドの例
- getChoices() 関数を使用すると、メッセージ書式テンプレートを使用して応答の表示形式をカスタマイズすることができます。getChoices() 関数が呼び出され、あいまいさが存在する場合、プラットフォームはあいまいな選択肢の情報をエンドユーザーに対してオプションとして提示できる配列として返します。たとえば、「もしかして」の標準応答をボタン形式で表示するには、以下のコードを使用します。
var info =getChoices() ; var message = { "type": "template", "payload": { "template_type": "button", "text": "Did you mean", "subText": "You can now customize response for did you mean", "buttons": [] } }; for (i = 0; i < info.length; i++) { var button = { "type": "postback", "title": info[i], "payload": "payload1" }; message.payload.buttons.push(button); } print(JSON.stringify(message)); - [完了] をクリックして [応答の編集] ダイアログを保存して終了し、新しい標準応答を適用します。


