Kore.aiのナレッジグラフは、FAQの静的テキストをインテリジェントでパーソナライズされた会話体験に変えるのに役立ちます。FAQを質問と回答の組み合わせの形で収集するというこれまでの慣行以上のものです。代わりに、ナレッジグラフを使用すると、主要なドメイン用語のオントロジー構造を作成し、それらをコンテキスト固有の質問やその代替品、同義語、機械学習が可能な特性と関連付けることができます。プラットフォームによってトレーニングされた場合、このグラフはインテリジェントなFAQ体験を可能にします。
この文書ではナレッジグラフの概念、用語、実装について説明しています。ナレッジグラフに対するユースケースによるアプローチについては、こちらを参照してください。
ナレッジグラフが選ばれる理由
ユーザーは複数の方法で質問を投げかけることができます。すべての代替質問を手動で可視化および追加するのは大変な作業です。
Kore.aiはノード、タグ、同義語を使ってナレッジグラフを設計しました。これにより、考えられるすべての一致をカバーする作業が容易になります。ナレッジグラフは、ノード、タグ、同義語を使ったトレーニングにより、様々な代替質問を処理することができます。
ユーザーが質問をするたびに、ナレッジグラフのノード名はチェックされ、ユーザーの発言から得たキーワードと照合されます。ノード名、タグ、および同義語がチェックされ、質問が一致の可能性があるまたはインテントとしてリストアップされます。リストアップされた質問は、実際のユーザーの発話と比較され、ユーザーに提示されるであろう、考えられる最良のインテントを考え出します。応答は単純な応答またはダイアログタスクの実行のいずれかの形をとります。
このように、FAQに全く異なる代替質問をいくつか追加し、適切にタグ、同義語、およびノード名を提供することで、トレーニングを受けていない質問にも一致させることができます。ナレッジグラフのパフォーマンスおよびインテリジェンスは、適切なノード名、タグ、および同義語を使用したトレーニング方法に依存します。
専門用語
この文書は、ナレッジグラフを構築する際に使用される用語に慣れることを目的としています。
用語またはノード
用語またはノードはオントロジーの構成要素であり、ビジネス領域の基本的な概念やカテゴリを定義するために使用することができます。
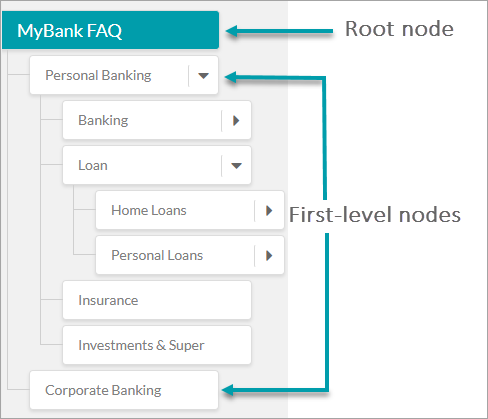
以下の画像で示されるように、Botオントロジーウィンドウの左側のパネルにある用語を階層的に整理することで、組織内の情報の流れを表すことができ、そこから用語の作成、整理、編集、削除などを行うことができます。ノード数は最大20,000、FAQ数は最大50,000というプラットフォーム上の制限があります。
表現を容易にするために、以下の名前を使用して特殊なノードを識別します。
ルートノード
ルートノードはBotオントロジーの最上位の用語を形成します。ナレッジグラフは1つのルートノードのみで構成されており、オントロジー内のその他すべてのノードはルートノードの子ノードになります。ルートノードにはBotの名前がデフォルトで使用されますが、必要に応じて変更することができます。このノードはノードの適格化や処理には使用されません。パスの適格化は第1レベルノードから始まります。ルートノードの直下にFAQを置くことはお勧めできませんが、必要に応じてルートノードでのFAQの数を最大100に制限してください。
第1レベルノード
ルートノードのすぐ次のレベルのノードを第1レベルノードと呼びます。1つのコレクション内に第1レベルノードをいくつでも持つことができます。第1レベルノードは、部門名や機能などの高レベルの用語を表すために残しておくことをお勧めします(例:パーソナルバンキング、オンラインバンキング、コーポレートバンキングなど)。
リーフノード
質問と回答の組み合わせやダイアログタスクが追加されたノードは、どのレベルのものでもリーフノードと呼ばれます。
ノードの関係
ノードは、オントロジー内での位置によって第1レベルノード、第2レベルノードなどと呼ばれることがあります。簡単に言えば、第1レベルノードとは下に1つ以上の第2レベルノードと呼ばれるサブカテゴリを持つことができるカテゴリです。
例:ローンとは、住宅ローンおよび個人ローンの第1レベルノードです。個人ローンはレートと手数料、ヘルプとサポートなど、さらに2つのサブカテゴリノードを持つことができます。
タグ
同義語
ユーザーは、オントロジーの用語に対してさまざまな代替を使用します。ナレッジグラフでは、用語に同義語を追加して、用語のあらゆる代替形式を含めることができます。また、同義語を追加することで、代替質問を使用してBotをトレーニングする必要性を減らすことができます。
例えば、インターネットバンキングノードには、オンラインバンキング、e-バンキング、サイバーバンキング、ウェブバンキングなどの同義語が追加されている可能性があります。
ナレッジグラフに用語の同義語を追加する場合は、ローカル同義語またはグローバル同義語として追加することができます。ローカル同義語(またはパスレベルの同義語)は、その特定のパス内の用語にのみ適用され、グローバル同義語(またはナレッジグラフの同義語)は、その用語がオントロジー内のその他のパスに表示されている場合でも適用されます。
リリース7.2以降では、ナレッジグラフエンジン内でBotの同義語を使用してパスの適格化および質問の照合を行うことができます。この設定では、Botの同義語とKGの同義語で同じ同義語を再作成する必要はありません。
特性
注:バージョン7.0以降は、バージョン6.4以前のクラスを特性に置き換えています。
特性とは、特定のインテントに関連した情報を求める際に質問の性質を定義する、一般的なエンドユーザーによる発話の集まりです。特性についての詳細はこちらを参照してください。
特性は、Botオントロジーの複数の用語に適用することができます。
インテント
Botはユーザーからの質問に対して、ダイアログタスクやFAQを実行して応答することができます。
パフォーマンスの向上
ナレッジグラフエンジンはデフォルト設定でも動作しますが、Bot開発者であるお客様は、KGエンジンのパフォーマンスを様々な方法で微調整することができます。
- 用語、同義語、一次質問と代替質問、またはユーザーの発言を定義することにより、ナレッジグラフの適切な設定を行います。階層化はKGエンジンのパフォーマンスには影響しませんが、KGエンジンの動作を整理および誘導するのに役立ちます。
- 以下のパラメータを設定します。
- パス範囲 – ユーザーの発話に含まれる用語のうち、パス内に存在する用語の最低パーセンテージを定義して、さらにスコアリングの対象となるようにします。
- KGの明確なスコア – 完全一致と見なされるKGのインテント一致の最小スコアを定義して、検出されたその他のインテント一致を破棄します。
- ナレッジタスクの最小レベルおよび確定レベル – ナレッジタスクの場合に識別および応答するための最小かつ明確なしきい値を定義します。
- KGの提案数 – 明確なKGのインテント一致が利用できない場合に表示されるKG/FAQの提案の最大数を定義します。
- 提案された一致の近接性 – トップスコアおよびすぐ次の提案された質問間に許容される差の最大値を定義して、それらを平等に重要なものと見なします。
プラットフォームには上記のしきい値のデフォルト値が設定されていますが、これらは自然言語 -> トレーニング -> しきい値および設定から変更することができます。
- コンテキストに応じたパスの適格化 – これにより、Botのコンテキストには一致したインテントの用語/ノードが入力され、保持されるようになり、ユーザー体験がさらにスムーズになります。
- 特性 – 前述したように、特性はユーザーの発話に用語/ノードが含まれていなくても、ノード/用語を適格化するために使用することができます。さらに、提案されたインテントリストをフィルタリングするのにも役立ちます。
KGエンジンの動作
ナレッジグラフエンジンは、ユーザーの発話に対して正しい応答を抽出しつつ、2段階のアプローチを行っています。これは、検索駆動型のインテント検出プロセスとルールベースのフィルタリングを組み合わせたものです。パスの範囲(必要とされる用語の割合)とユーザーの発話における用語の使用(必須または任意)に関する設定は、FAQのインテントの初期フィルタリングに役立ちます。トークン化およびn-gramベースのコサインスコアリングモデルは、最終的な検索基準の達成に役立ちます。
ナレッジグラフのトレーニングには以下の手順が含まれます。
- すべての用語/ノードと同義語が検出され、インデックスが付けられます。
- これらのインデックスを使用して、各KGインテントに対してフラットパスが作成されます。
ナレッジグラフエンジンがユーザーの発話を受信した場合:
- ユーザの発話とKGノード/用語をトークン化し、n-gramを抽出します(ナレッジグラフエンジンでは最大4-gramまで対応)。
- トークンはKGノード/用語とマッピングされ、それぞれのインデックスが取得されます。
- ユーザーの発話とKGノード/用語との間のパス比較により、その発話用の適格パスが作成されます。このステップでは、上述したパス範囲と用語の使用法を考慮します。
- 適格パスの質問リストの中から、コサインスコアに基づいて最適なものが選ばれます。