自然な会話では、ユーザーが特定のシナリオについて説明しながら、背景や関連する情報を提供することがよくあります。特性は、ユーザーが会話の中で表現する特定のエンティティ、属性、または詳細を指します。発話は、特定のインテントを直接伝えるものではないかもしれませんが、発話に存在する特性は、インテント検出やBotの会話フローを動作させるために使用することができます。
例えば、「my card is being rejected and am on a business trip」という発話は、「card decline」と「emergency」という2つの特性を表現しています。このシナリオでは、発話は、直接的な意図を伝えていない、あるいはせいぜい「unblock card」フローを動作させるために使用することができます。一方で、「emergency」の特性は、会話を人間のエージェントに直接割り当てるために使用することができます。
Botプラットフォームの特性の機能は、ユーザーの発話に存在するこれらの特徴を識別し、それらをインテント検出に使用して、特徴を使用してBotの定義をカスタマイズすることを目的としています。
ユースケース
Book a FlightBotは、選択した金額に基づいてフライトを予約するための追加要件が備わっている場合があります。
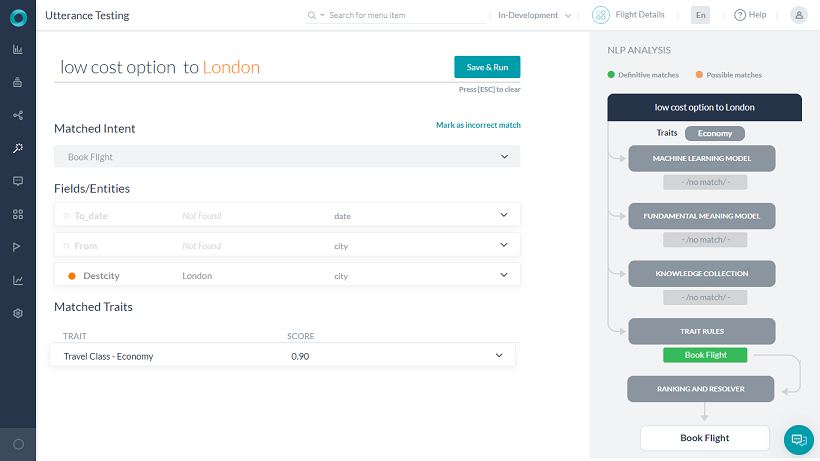
「I am looking for low-cost option to London」というユーザーの発話は、利用可能なフライトを選択し、最低価格のチケットを選ぶ結果が予想されます。
以下のように設定します。
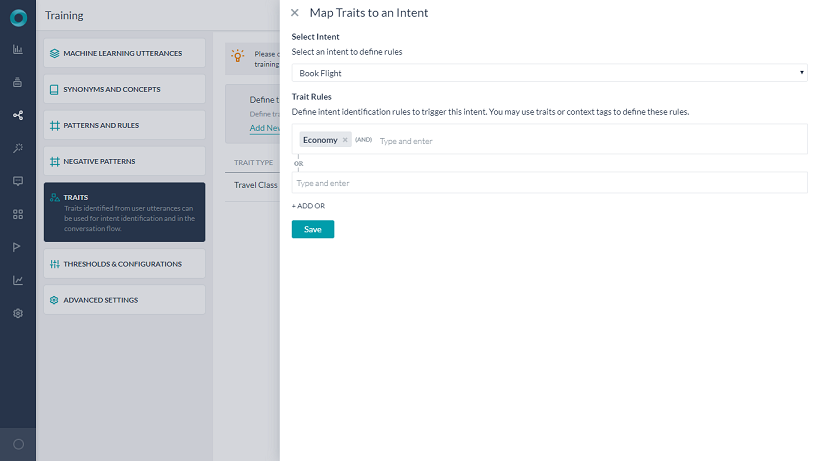
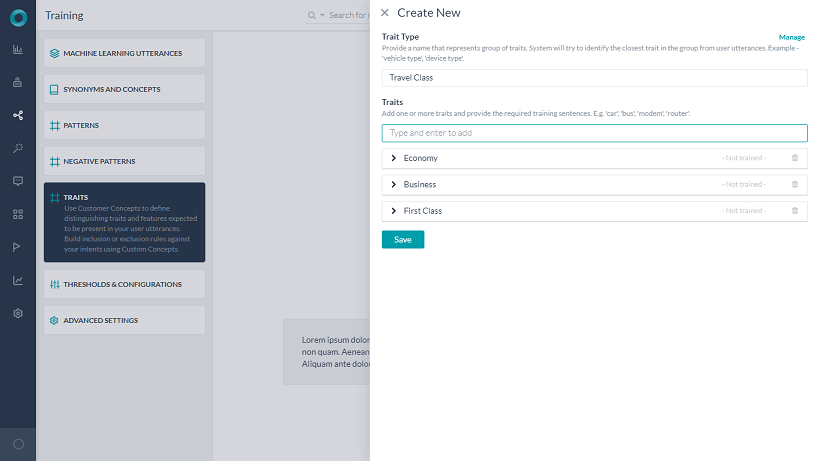
- 「low cost」という発話でトレーニングされた特性エコノミーを使用して「Travel Class」と呼ばれる特性タイプを追加します。
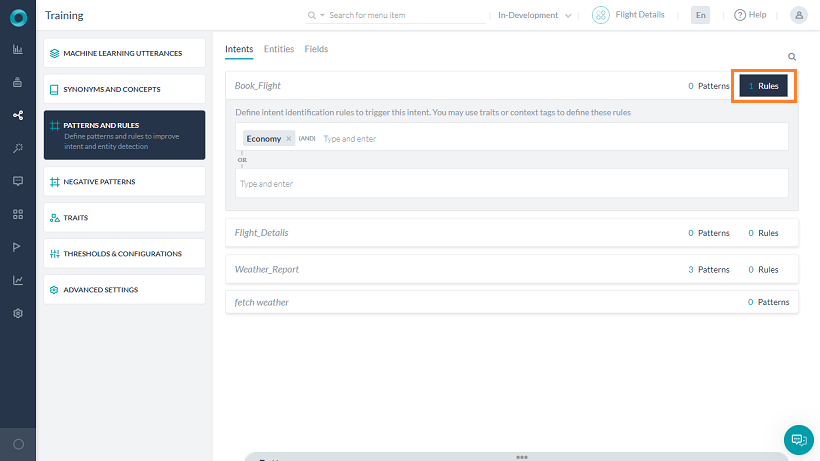
- エコノミー特性の存在によってトリガーされる「book flight」というルールを追加します。
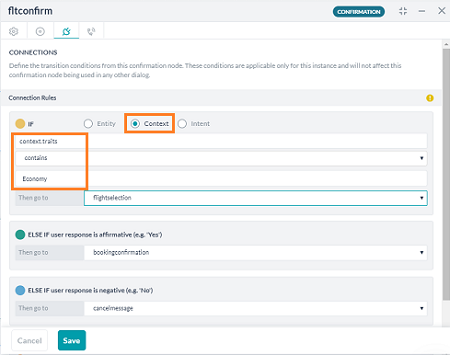
- コンテキストに特性エコノミーが存在する場合の転送条件を追加します。
設定
特性の設定には以下が含まれます。
- 特性の定義
- 特性の相関ルール
- 特性の検出
特性の定義
特性は、自然言語 > トレーニングの特性セクションから定義することができます。
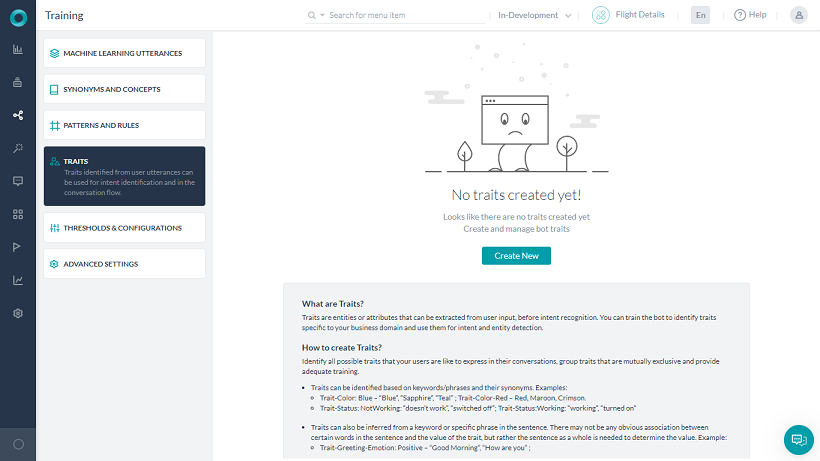
特性を定義する際に考慮すべき主な特徴は以下の通りです。
- 特性タイプは、上記の例のTravel Classのような関連する特性の集まりです。
- 特性タイプは、「MLベース」または「パターンベース」にすることが可能です。特性タイプの各特性は、そのタイプに基づいて、単語、フレーズ、発話、またはパターンを使用してトレーニングすることができます。特性タイプの管理では、トレーニングの設定を定義することができます。MLベースの特性の設定については、以下を参照してください。

- 特性タイプは、1つ以上の特性を持つことができます。
- 特性の名前はグループ内で一意のものでなければなりません。しかし、同一の名前をもつ特性は複数のグループに存在する場合があります。
- MLベースの特性については、特性を識別する単語、フレーズ、または発話を定義することができます。MLベースの特性タイプでは、特性タイプごとに1つの特性が検出されます。
- パターンベースの特性では、与えられた特性に関連するパターンを定義することができます。パターンベースの特性タイプでは、複数の特性が検出される可能性があります。特性タイプ内の特性の順序は、特性タイプ内の特性の重要性を示し、1つの特性のみを検出します。
- 追加したら、ユーザーの発話から特性を検出するためにBotをトレーニングします。
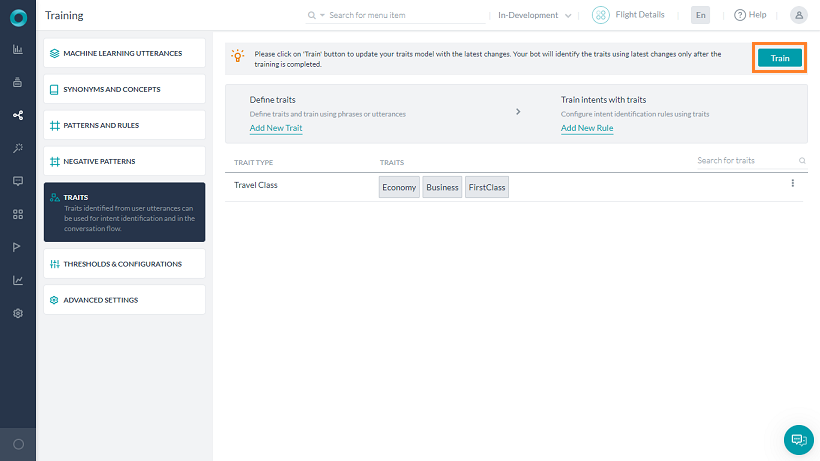
注:
- 複数言語のBotの場合、言語固有の特性を追加することができます。
- 特性名が変更された場合は、その特性を使用して定義されたすべてのルールが修正されていることを確認してください。この処理は手動で行う必要があり、プラットフォームでは行われません。
- 特性名はグループ内で一意のものでなければなりません。
- 同一の名前をもつ特性は、複数のグループに存在する可能性がありますが、特性ルールまたは特性検出結果でそれらを区別することは困難です。
特性 – MLモデル
MLモデルを用いて特性をトレーニングすることを選択する場合、デフォルトではn-gramモデルが用いられます。n-gramとは、トレーニング文の中からモデルをトレーニングするために用いる単語の連続した配列のことです。ただし、コーパスが非常に少ない場合や、一般にトレーニング文に含まれる単語が少ない場合、これは効果的ではない可能性があります。
プラットフォームのバージョン8.0から、n-gramモデルをスキップまたは使用するオプションが含まれています。さらに、「n-gram」アルゴリズムをパラメータ化するオプションが含まれています。
- n-gramオプションを選択した場合、n-gramの最大値を設定することで、n-gramのシーケンス長を設定することができます。デフォルトでは1に設定されており、1~5の任意の整数値を設定することができます。
- When skip-gram is selected, you can configure
- 連続しないシーケンスに含まれる単語の数を指定シーケンス長です。デフォルトでは2に設定されており、2~4の任意の整数値を設定することができます。
- 連続しない単語のシーケンスを形成するためにスキップできる単語数の最大スキップ距離です。この値はデフォルトでは1に設定されており、1~3の任意の整数値を設定することができます。
注:設定はすべての言語で共通しています(多言語Botの場合)が、中国語や韓国語のように、いくつかの言語では文字列がgramを作り、その他の(ラテン語ベースの)言語では単語のgramになります。
特性の相関ルール
特性ルールは、ダイアログの実行およびナレッジグラフのインテント検出を定義します。
ダイアログの実行
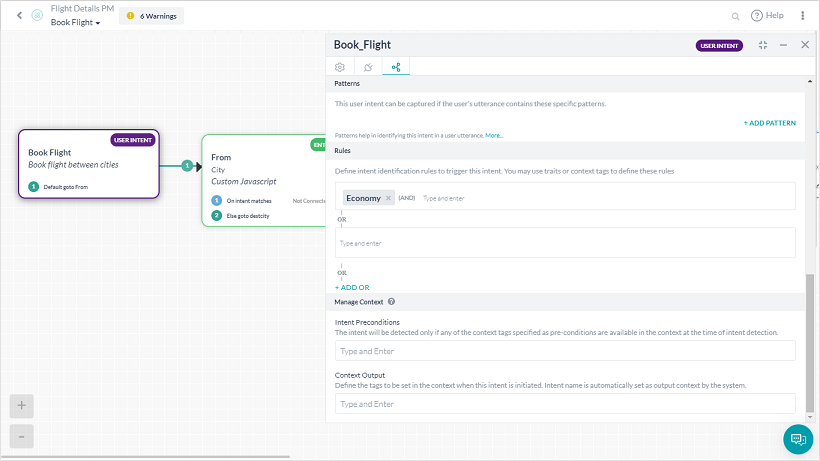
インテントの検出やダイアログの実行は、MLの発話やパターンと一緒に特性を利用して行うことができます。これらを行うには、ルールを追加して、インテントと必要な特性との関連付けを行う必要があります。
ルールの追加には複数の方法があります。
それぞれのルールは、演算子としてANDを使用して1つ以上の条件を設定することができます。与えられたインテントに対して複数の特性ルールを定義することができ、いずれかのルールが一致した場合、そのインテントは完全一致とみなされます。
ナレッジグラフインテント
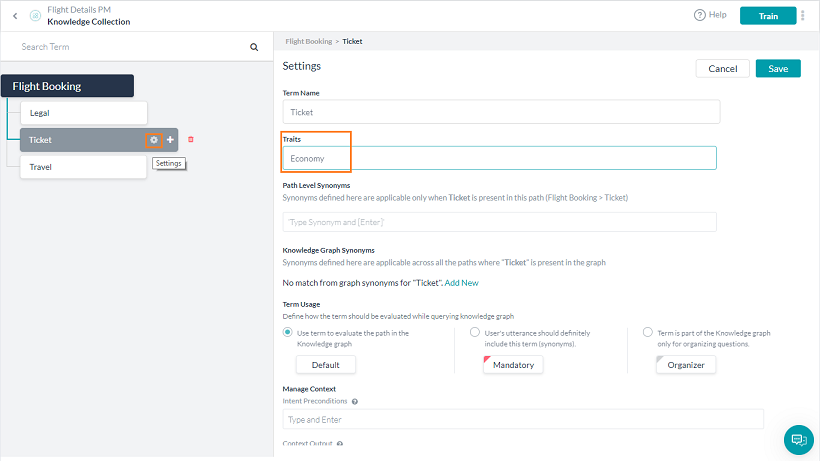
ナレッジグラフは、特性を使用して検出プロセスの一部を担うことができます。そのために、それぞれの用語またはノードを一つの特性に関連付けることができます。与えられた用語は、単一の特性に関連付けることができます。
注:特性は、リリース6.4以前のクラスに置き換わります。
特性の検出
グループ(特性タイプ)から1つの特性のみが検出され、「完全一致」とみなされます。
検出された特性はコンテキストオブジェクトに含まれます。コンテキストには、(特性タイプを参照することなく)識別された固有の特性が入力されます。この情報は以下のために使用されます。
- インテントの識別
- ダイアログの遷移
- エンティティの追加
- Botの定義
バッチテストレポートには、インテントAPIの検出と同様に、検出された特性に関する情報も含まれています。.
インテントの検出
ランキングおよび解決は、3つのNLエンジンと特性からの入力を取得し、分析し、可能性のある一致/完全一致を検出します。
- インテントは、特性ルールに存在するすべての特性(ナレッジグラフの場合は1つ)が検出された場合にのみ、「完全一致」とみなされます。
- NL分析では、検出された特性に関する情報が含まれ、NLPフローでは、検出された特性に関する情報が表示されます。
ダイアログの遷移
会話フローは特性を使用して制御することができます。ダイアログの場合、接続ルール は特性コンテキストを使用して定義することができます。これは、ダイアログのプロパティパネルの下にある接続タブから行うことができます。
特性コンテキストにはcontext.tritsを使用してアクセスすることができます。これは、インテントと一致するすべての特性の配列を返すため、使用する条件は contains となります。
ドキュメントのバージョン履歴
| 更新 日 |
プラットフォームの バージョン |
変更 |
|---|---|---|
| 2020年10月31日 | バージョン8.0 | 特性のトレーニングのためにn-gramのMLモデルを使用するかスキップするかのオプション |
| 2019年6月15日 | バージョン7.0 | プラットフォームに特性を導入 |