Kore.ai NLP 엔진은 기계 학습, 기초 의미 및 지식 그래프(있는 경우) 모델을 사용하여 의도를 일치시킵니다. 세 가지 Kore.ai 엔진 모두 최종적으로 결과를 Kore.ai 순위 및 결정 구성 요소에 정확한 일치 또는 가능한 일치로 전송합니다. 순위 및 해결은 전체 NLP 계산을 통해 최종 승자를 결정합니다.
작동 방식
NLP 엔진은 기계 학습, 기초 의미 및 지식 그래프(봇에 있는 경우) 모델을 통한 하이브리드 접근 방식으로 관련성에 대한 일치 의도의 점수를 매깁니다. 모델은 사용자 발화를 가능한 일치 또는 확실한 일치로 분류합니다. 확실한 일치는 높은 신뢰도 점수를 얻은, 사용자 발화와 완벽하게 일치하는 것으로 간주합니다. 게시된 봇에서 사용자 입력이 단일한 확실한 일치와 일치하면 봇이 작업을 직접 실행합니다. 발화가 여러 개의 확실한 일치와 일치하는 경우, 최종 사용자가 하나를 선택할 수 있는 옵션으로 전송합니다. 반면에, 가능한 일치는 사용자 입력에 대해 꽤 좋은 점수를 받지만 정확한 일치라고 부를 만큼 확실하다는 생각이 들지 않는 의도입니다. 내부적으로 시스템은 점수에 따라 가능한 일치를 좋은 일치와 확실하지 않은 일치로 추가 분류합니다. 게시된 봇에서 최종 사용자의 발화가 가능한 일치를 생성한 경우, 봇은 이러한 일치를 이런 뜻이 맞습니까?라고 보냅니다. 최종 사용자를 위한 제안. 순위 및 해결에 따라 엔진 간의 최적 의도를 파악합니다. 플랫폼이 모호한 점을 발견하면 모호함 대화가 시작됩니다. 플랫폼은 사용자 발화에 대한 하나의 최상의 의도를 확인할 수 없을 때 다음 두 시스템 대화 중 하나를 시작합니다.
- 모호성 해소 대화: 엔진에서 둘 이상의 확실한 일치가 반환될 때 시작됩니다. 이 시나리오에서, 봇은 사용자에게 실행할 확실한 일치 항목을 선택하도록 요청합니다. NLP 표준 응답에서 사용자에게 표시되는 메시지를 사용자 정의할 수 있습니다.
- 대화를 의미한 것입니까: 순위 및 해결이 둘 이상의 최종 결과를 반환하거나 유일한 최상의 의도가 KG 엔진 점수가 하한 임곗값과 상한 임곗값 사이에 있는 FAQ인 경우 시작됩니다. 이 대화를 통해 사용자는 봇이 완전히 확실하지는 않은 의도와 일치하는 항목을 찾았고 사용자가 계속하기를 선택하기를 원한다는 사실을 알 수 있습니다. 이 시나리오에서, 개발자는 이러한 발화를 식별하고 봇을 추가로 학습시켜야 합니다. NLP 표준 응답에서 사용자에게 표시되는 메시지를 사용자 정의할 수 있습니다.
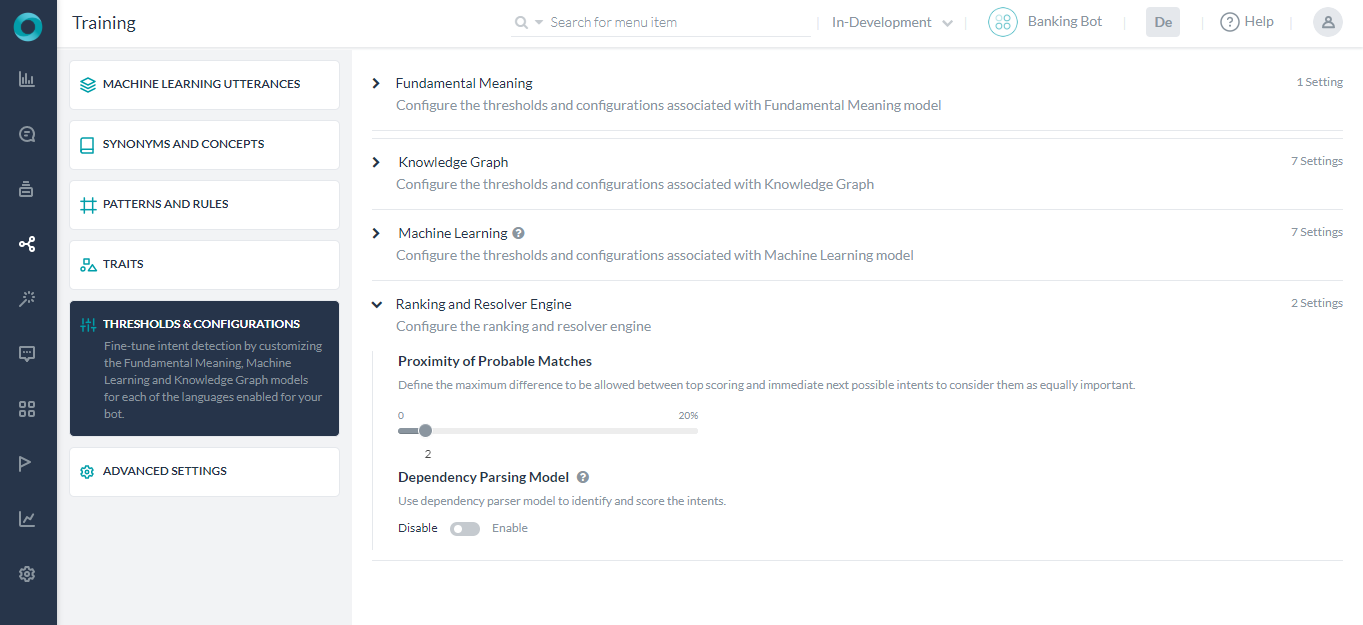
임곗값 및 설정
순위 및 해결 엔진을 설정하려면, 다음 단계를 따르세요.
- 임곗값을 설정하고 싶은 봇을 엽니다.
- 상단 메뉴에서 빌드 탭을 선택합니다.
- 왼쪽 탐색 메뉴에서 자연어 > 임곗값 및 설정을 클릭합니다.
- 순위 및 해결 엔진 섹션에서는 임곗값을 설정할 수 있습니다.
- 선호하는 확실한 일치는 가능한 일치보다 확실한 일치의 우선 순위를 지정하는 데 사용할 수 있으므로, 재채점을 위해 모든 일치를 염두에 두고 모호한 경우 최종 사용자가 올바른 의도를 선택할 수 있습니다. 이 설정은 기본적으로 활성화되어 있으며 비활성화할 수 있습니다. 활성화된 경우(기본 동작), 확실한 일치가 선택되고 가능한 일치는 삭제됩니다. 최종 일치가 없는 경우 가능한 일치를 재채점합니다. 비활성화된 경우 모든 일치(확실한 및 가능한)를 재채점합니다.
- 다른 의도 엔진에서 조건에 맞는 모든 의도가 최상의 의도로 간주되고 최종 사용자에게 전송하여 필요한 의도를 선택할 수 있도록, 의도 재채점하기를 끌 수 있습니다. 하나의 의도만 조건에 맞는 경우 최종 결과로 간주되고, 둘 이상의 의도가 조건에 맞으면 사용자에게 모호성 해소를 위한 결과가 나타납니다.
- 최고 스코어링 및 그와 동등하게 중요하다고 여겨지는 바로 그 다음의 가능한 의도 사이에 허용되는 최대 차이를 정의하는 가능한 일치의 근접함. 플랫폼 v7.3 이전에는, 이 설정이 기초 의미 섹션에 있었습니다.
- 종속성 파싱 모델은 기초 의미 모델로 의도 인식이 가능할 뿐만 아니라 순위 및 해결 엔진으로 의도의 재채점도 활성화할 수 있습니다. 이 설정은 기본적으로 비활성화되어 있으며 무조건 설정해야 합니다. 자세한 내용은 아래를 참조하세요.
종속성 파싱 모델
플랫폼에는 Fundamental Meaning Engine, 순위 및 해석 엔진을 통한 의도 채점 모델 두 개가 있습니다.
- 첫 번째 모델은 주로 단어의 존재, 발화에서 단어의 위치 등에 의존하여 의도를 결정하며 Fundamental Meaning Engine으로만 점수를 매깁니다. 이는 기본 설정입니다.
- 두 번째 모델은 의도 탐지가 단어, 단어의 상대적 위치 및 가장 중요하게는 문장의 키워드 간 종속성을 기반으로 하는 종속성 매트릭스를 기반으로 합니다. 이 모델에서 Fundamental Meaning Engine으로 의도의 점수를 매긴 다음 순위 및 해석 엔진에서 다시 점수를 매깁니다.
종속성 파싱 모델은 학습 > 임곗값 & 설정의 순위 및 해결 섹션에서 활성화하고 설정할 수 있습니다. 참고: 이 기능은 선택 언어에 대해서만 지원됩니다. 지원되는 언어는 여기를 참조하세요. 종속성 파싱 모델은 다음과 같이 설정할 수 있습니다.
NLP 탐지
자연어 분석의 결과는 다음과 같은 시나리오입니다.
- FM 또는 ML 또는 KG 엔진과의 확실한 일치를 식별하는 NLP 분석.
- 여러 엔진이 가능한 일치를 반환하고 단일 일치를 선택하는 NLP 분석.
- 여러 엔진이 가능한 일치를 반환하고 해결이 여러 결과를 반환하는 NLP 분석.
- 일치 항목이 없는 NLP 분석.
위의 각 경우에 대해 이 섹션에서 설명합니다. NLP 탐지를 이해하기 위해, 다음 세부 정보가 포함된 뱅킹 봇의 예를 사용하겠습니다.
시나리오 3 – 확실한 일치를 식별하는 KG
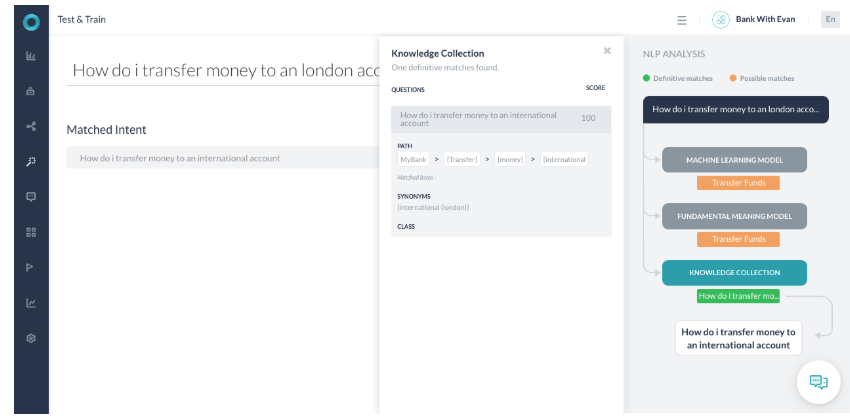
- 사용자 발화가 런던 계좌로 이체하려면 어떻게 해야 하나요?(How do I make transfer money to a London account?인 경우입니다.
- 사용자 발화에는 이 지식 그래프 의도 경로 이체(Transfer), 돈(Money), 국제(International)와 일치하는 데 필요한 모든 용어가 포함되어 있습니다.
- 국제(International)라는 용어는 사용자가 발화에서 사용한 런던의 동의어로 식별됩니다.
- 경로 용어가 100% 일치하므로 경로는 조건에 맞습니다. 신뢰도 스코어링의 일부로 사용자 질의의 용어는 실제 지식 그래프 질문의 용어와 유사합니다. 따라서 100점을 반환합니다.
- 반환된 점수가 100 이상이면 확실한 일치로 의도를 표시하고 선택합니다.
- FM 엔진은 핵심 용어 전송(Transfer)이 사용자 발화에 있으므로 가능한 일치로 찾았습니다.
- ML 엔진은 해당 발화가 학습된 발화와 완전히 일치하지 않았기 때문에 해당 발화를 가능한 일치로 찾았습니다.
시나리오 4 – 가능한 일치를 반환하는 여러 엔진
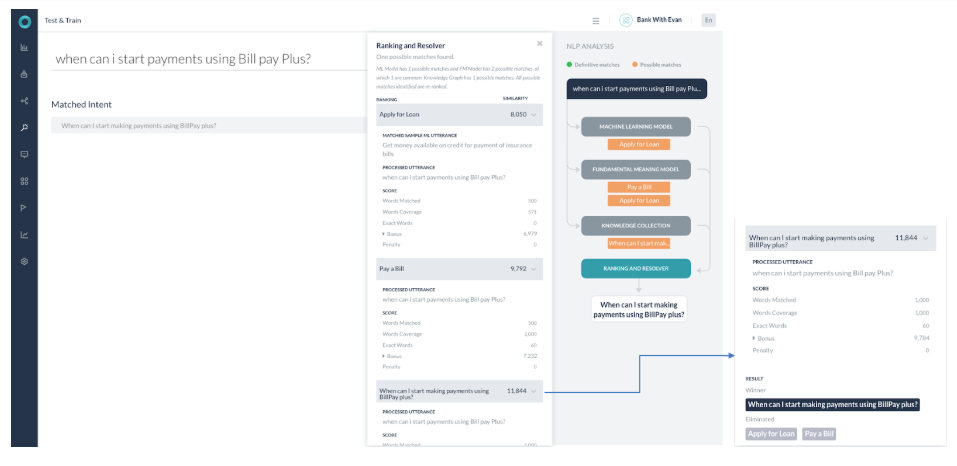
- 3개의 엔진 모두 가능한 일치를 반환했으며 확실한 일치는 반환하지 않았던 경우입니다.
- ML 모델에는 1개의 가능한 일치가 있고 FM 모델에는 2개의 가능한 일치가 있는데, 그 중 1개는 공통입니다. 지식 그래프에는 1개의 가능한 일치가 있습니다. 식별된 가능한 일치는 모두 순위 및 해결에서 다시 순위를 매깁니다.
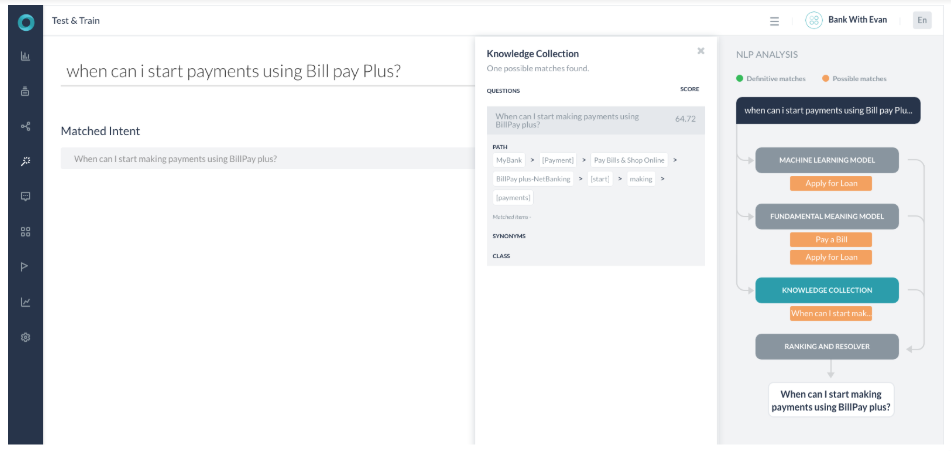
- 순위 및 해결 구성 요소는 지식 그래프 엔진의 단일 일치(작업 이름 – BillPay plus로 언제부터 결제를 시작할 수 있습니까?(When can I start making payments using BillPay plus?))에서 가장 높은 점수를 반환했습니다. 다른 가능한 일치의 점수는 최고 점수의 2백분위수보다 낮으므로 무시됩니다. 이 경우 최종 결과는 'KG' 반환 질의이며 사용자에게 나타나게 됩니다.
- 사용자 발화에 있는 대부분의 키워드가 KG 쿼리에 있는 키워드에 매핑되지만 여전히 이것이 확실한 일치는 아닙니다.
- 일치하는 경로 용어의 수가 100%가 아니기 때문입니다.
- KG 엔진은 64.72%의 확률로 점수를 반환했습니다. Billpay 대신 bill pay라는 단어를 사용했다면 점수는 87.71%였을 것입니다. (여전히 100% 일치는 아닙니다)
- 이제 점수가 60%-80% 사이에 있으므로 질의 임곗값이 완전한 최종 결과가 아니라 이런 뜻이 맞습니까 대화의 일부로 나타납니다. 점수가 80% 이상인 경우 플랫폼은 이런 뜻이 맞습니까 대화를 다시 확인하지 않고 응답을 제공했을 것입니다.
Kore.aiのNLPエンジンは、機械学習、ファンダメンタルミーニング、ナレッジグラフ(あれば)モデルを使用してインテントを一致させます。3つのKore.aiエンジンは最終的に完全一致または可能性のある一致のどちらかとしてKore.aiランキングおよび解決コンポーネントに結果を提供します。ランキングおよび解決はNLP計算全体の最終的な結果を決定します。
動作
NLPエンジンは、機械学習、ファンダメンタルミーニング、ナレッジグラフ(Botに含まれる場合)モデルを使用したハイブリッドアプローチによって、関連性に関する一致するインテントをスコア化します。モデルは、ユーザーの発話を可能性のある一致または完全一致のいずれかに分類します。 完全一致は、高い信頼度スコアを取得し、ユーザーの発話に完全に一致すると見なされます。公開済みのBotでは、ユーザー入力が単一の完全一致と一致する場合、Botは直接タスクを実行します。発話が複数の完全一致と一致する場合、エンドユーザーが選択できるようにオプションとして送信されます。 一方、可能性のある一致とは、ユーザー入力に対してある程度スコアが高いインテントを指しますが、完全一致と呼ぶには十分でないインテントのことです。内部的には、システムは、スコアに基づいて、可能な一致をさらに通常の一致と不正確な一致に分類します。公開済みのBotでエンドユーザーの発話が可能性のある一致を生成していた場合、Botはこれらの一致をエンドユーザーに「Did you mean?」として送信します。 ランキングおよび解決に基づいて、エンジン間の上位インテントを確認します。プラットフォームがあいまいさを検出した場合、あいまいさのダイアログが開始されます。プラットフォームは、ユーザーの発話に対する単一の上位インテントを確認できない場合、これら2つのシステムダイアログのいずれかを開始します。
- あいまい性解消ダイアログ:エンジン間で返された完全一致が複数ある場合に開始されます。このシナリオでは、Botは実行する完全一致を選択するようユーザーに求めます。NLP標準応答から、ユーザーに表示されるメッセージをカスタマイズすることができます。
- 「Did You Mean」ダイアログ:ランキングおよび解決が複数の上位インテントを返した場合、あるいは唯一の上位インテントが、KGエンジンのスコアがしきい値の下限と上限の間にあるFAQである場合に開始されます。このダイアログは、完全であるか不明なインテントと一致するものを検出したことをBotがユーザーに知らせるものであり、ユーザーに先へ進んための選択を促します。このシナリオでは、開発者はこれらの発話を識別し、Botをさらにトレーニングする必要があります。ユーザーに表示されるメッセージは、NLPの標準応答からカスタマイズすることができます。
しきい値および設定
ランキングおよび解決エンジンは以下の手順で設定することができます。
- しきい値を設定するBotを開きます。
- サイドナビゲーションパネルにカーソルを合わせ、自然言語 > トレーニングをクリックします。
- しきい値および設定タブをクリックします。
- ランキングおよび解決エンジンセクションでしきい値を設定することができます。
- 可能性のある一致の近似度は、スコアの高い上位インテントとその次の可能性のあるインテントを同じように重要なものとみなすために許容される最大差を定義します。プラットフォームのバージョン7.3以前では、この設定はファンダメンタルミーニングセクションで行うことができました。
- 依存構造解析モデルは、ファンダメンタルミーニングモデルによるインテント認識と同様に、ランキングおよび解決エンジンによるインテントの再スコアリングを有効にするためのものです。この設定はデフォルトでは無効になっており、設定を行う必要があります。詳細は以下を参照してください。
依存構造解析モデル
このプラットフォームには、ファンダメンタルミーニングエンジンとランキングおよび解決エンジンによる、2つのインテントのスコアリングモデルがあります。
- 最初のモデルは、主に単語の存在、発話の中での単語の位置などに依存してインテントを判断し、ファンダメンタルミーニングエンジンのみによってスコア化されます。こちらがデフォルト設定になっています。
- 2つ目のモデルは、依存マトリックスに基づいており、インテントの検出は、単語やその相対的な位置、そして最も重要とされる、文中のキーワード間の依存関係に基づいて行われます。このモデルでは、インテントはファンダメンタルミーニングエンジンによってスコアリングされ、その後、ランキングおよび解決エンジンによって再ドスコアリングされます。
依存構造解析モデルは、自然言語 > トレーニング > しきい値および設定のランキングおよび解決セクションから有効化や設定を行うことができます。 注:この機能はプラットフォームのバージョン7.3で導入され、一部の言語でのみサポートされています。対応言語についてはこちらを参照してください。 依存構造解析モデルは、以下のように設定することができます。
NLP検出
自然言語分析の結果、以下のようなシナリオになります。
- FM、ML、またはKGエンジンで完全一致を識別するNLP分析
- 可能性のある一致を返し、単一の一致を選択する、複数のエンジンを用いたNLP分析
- 可能性のある一致を返す複数のエンジンと複数の結果を返す解決を用いたNLP分析
- 一致しないNLP分析
ここでは、上記のそれぞれのケースについて説明します。 NLP検出を理解するために、以下の詳細を含む銀行Botを例として見てみましょう。
シナリオ3 – 完全一致を識別するKG 
- ユーザーの発話は「How do I make transfer money to a London account?」です。
- ユーザーの発話には、このナレッジグラフのインテントパスである「Transfer」、「Money」、「International」に一致するために必要なすべての用語が含まれています。
- 「international」という用語は、ユーザーが発話の中で使用した「London」の同義語として識別されます。
- 100%のパス用語が一致したため、パスが修飾されました。信頼度スコアリングの一部として、ユーザークエリの用語は実際のナレッジグラフの質問の用語と似ており、そのため100のスコアが返されます。
- 返されたスコアが100以上の場合、インテントは完全一致とマークされ、選択されます。
- FMエンジンは、キー用語であるTransferがユーザーの発話の中に存在するため、可能性のある一致と判断しました。
- MLエンジンは、発話がトレーニングされた発話と完全に一致しなかったため、可能性のある一致と判断しました。
シナリオ4 – 可能性のある一致を返す複数のエンジン 
- 3つのエンジンはすべて可能性のある一致を返し、完全一致を返しませんでした。。
- MLモデルには可能性のある一致が1件あり、FMモデルには可能性のある一致が2件あり、そのうち1件は共通しています。ナレッジグラフには可能性のある一致が1件あります。識別された可能性のある一致はすべて、ランキングおよび解決で再ドランク付けされます。
- ランキングおよび解決コンポーネントは、ナレッジグラフエンジンから単一の一致(タスク名 – 「When can I start making payments using BillPay plus?」)の最高スコアを返しました。他の可能性のある一致のスコアは、上位スコアの2パーセンタイルよりも低いため、無視されます。この場合、上位は「KG」に返されたクエリであり、ユーザーに提示されます。
- ユーザーの発話のほとんどのキーワードはKGクエリのキーワードをマッピングしますが、これらは完全一致ではありません。理由は以下のとおりです。
- パス用語の一致数は100%ではありません。
- KGエンジンは64.72%の可能性を示すスコアを返しました。「bill pay」の代わりに「Billpay」という単語を使用していた場合、スコアは87.71%になっていたはずです。(それでも100%ではありません)
- スコアが60%~80%の場合、クエリは「Did-you-mean」ダイアログの一部として表示され、完全な一致として表示されません。スコアが80%を超えていた場合、プラットフォームは「Did-you-mean」ダイアログを使用して再度確認することなく回答を表示していたはずです。
The Kore.ai NLP engine uses Machine Learning, Fundamental Meaning, and Knowledge Graph (if any) models to match intents. All the three Kore.ai engines finally deliver their findings to the Kore.ai Ranking and Resolver component as either exact matches or probable matches. Ranking and Resolver determines the final winner of the entire NLP computation.
Working
The NLP engine uses a hybrid approach using Machine Learning, Fundamental Meaning, and Knowledge Graph (if the bot has one) models to score the matching intents on relevance. The model classifies user utterances as either being Possible Matches or Definitive Matches.
Definitive Matches get high confidence scores and are assumed to be perfect matches for the user utterance. In published bots, if user input matches with a single Definitive Match, the bot directly executes the task. If the utterances match with multiple Definitive Matches, they are sent as options for the end-user to choose one.
On the other hand, Possible Matches are intents that score reasonably well against the user input but do not inspire enough confidence to be termed as exact matches. Internally the system further classifies possible matches into good and unsure matches based on their scores. If the end-user utterances were generating possible matches in a published bot, the bot sends these matches as Did you mean? suggestions for the end-user.
Based on the ranking and resolver, the winning intent between the engines is ascertained. If the platform finds ambiguity, then an ambiguity dialog is initiated. The platform initiates one of these two system dialogs when it cannot ascertain a single winning intent for a user utterance:
- Disambiguation Dialog: Initiated when there are more than one Definitive matches returned across engines. In this scenario, the bot asks the user to choose a Definitive match to execute. You can customize the message shown to the user from the NLP Standard Responses.
- Did You Mean Dialog: Initiated if the Ranking and Resolver returns more than one winner or the only winning intent is an FAQ whose KG engine score is between lower and upper thresholds. This dialog lets the user know that the bot found a match to an intent that it is not entirely sure about and would like the user to select to proceed further. In this scenario, the developer should identify these utterances and train the bot further. You can customize the message shown to the user from the NLP Standard Responses.
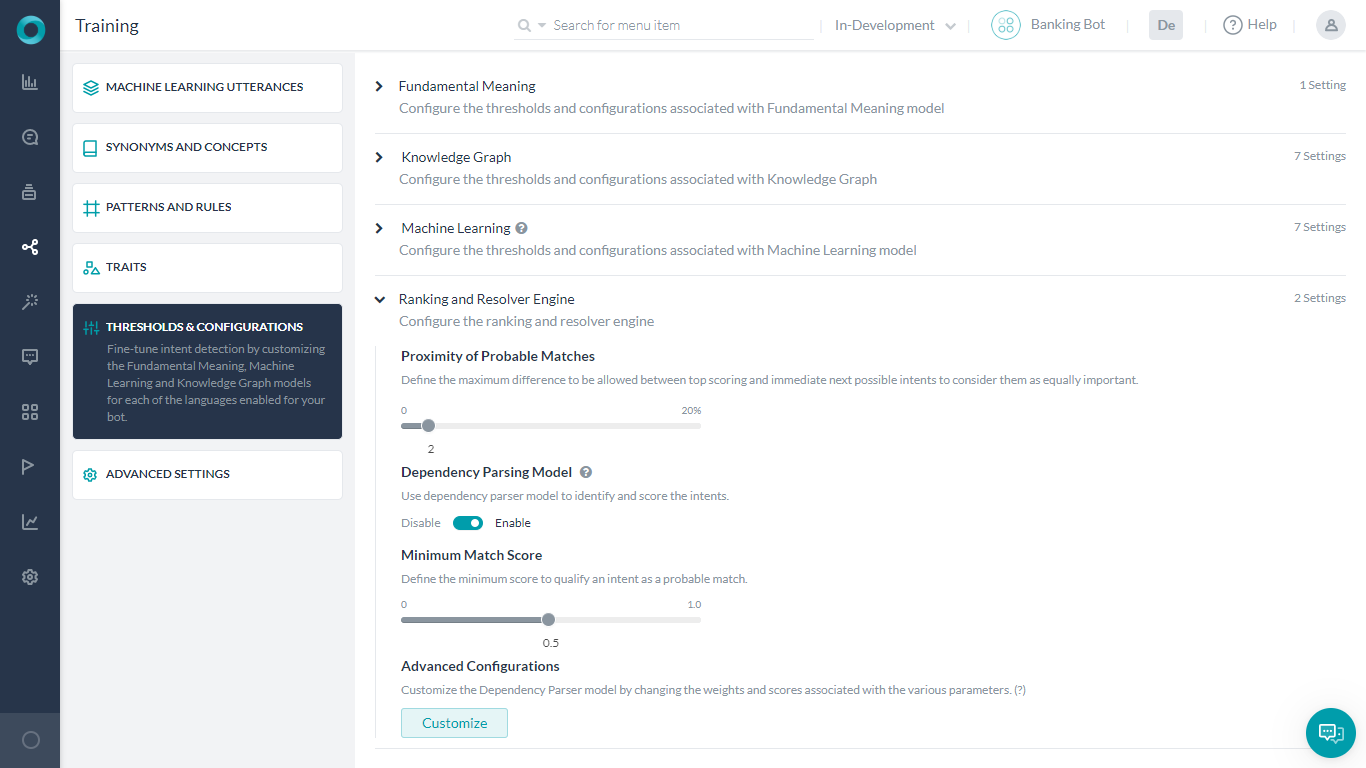
Thresholds & Configuration
To configure a Ranking and Resolver Engine, follow the below steps:
- Open the bot for which you want to configure thresholds.
- Select the Build tab from the top menu.
- From the left navigation click Natural Language > Thresholds & Configurations.
- The Ranking & Resolver Engine section allows you to set the threshold:
- Prefer Definitive Matches can be used to prioritize definitive matches over probable matches so that all the matches are considered for rescoring and the end-user gets to choose the right intent in case of any ambiguity. This setting is enabled by default and you can disable it. If enabled (default behavior), definitive matches will win and the probable matches would be discarded, in case of no definitive match, then probable matches would get rescored. If disabled, all the matches – definitive and probable, would be rescored.
- Rescoring of Intents can be turned off so that all the qualified intents from the different intent engines are assumed winning intents and are sent to the end-users to choose the required intent. If only one intent is qualified, then it is considered a winner, if more than one is qualified then the user will be presented with results for disambiguation.
- Proximity of Probable Matches which defines the maximum difference to be allowed between top-scoring and immediate next possible intents to consider them as equally important. Before v7.3 of the platform, this setting was under the Fundamental Meaning section.
- Dependency Parsing Model for enabling rescoring the intents by the Ranking and Resolver engine as well as for the intent recognition by the Fundamental Meaning model. This configuration is disabled by default and needs to be set implicitly. See below for details.
Dependency Parsing Model
The platform has two models for scoring intents by the Fundamental Meaning Engine and the Ranking & Resolver Engine:
- The first model predominantly relies on the presence of words, the position of words in the utterance, etc. to determine the intents and is scored solely by the Fundamental Meaning Engine. This is the default setting.
- The second model is based on the dependency matrix where the intent detection is based on the words, their relative position, and most importantly the dependency between the keywords in the sentence. Under this model, intents are scored by the Fundamental Meaning Engine and then rescored by the Ranking and Resolver Engine.
Dependency Parsing Model can be enabled and configured from the Ranking and Resolver section under Training > Thresholds & Configurations.
Note: This feature is supported only for select languages, see here for supported languages.
Dependency Parsing Model can be configured as follows:
- Minimum Match Score to define the minimum score to qualify an intent as a probable match. It can be set to a value between 0.0 to 1.0 with the default set to 0.5.
- Advanced Configurations are used to customize the model by changing the weights and scores associated with various parameters. This opens a JSON editor where you can enter the valid code. You can click the restore to default configurations to get the default threshold settings in a JSON structure, you can change the settings provided you are aware of the consequences.

NLP Detection
The Natural Language Analysis will result in the following scenarios:
- NLP Analysis identifying a Definitive match with FM or ML or KG engines.
- NLP Analysis with multiple engines returning probable match and selecting a single match.
- NLP Analysis with multiple engines returning probable match and resolver returning multiple results.
- NLP Analysis with no match.
Each of the above cases is discussed in this section.
To understand NLP detection, let us use the example of a Bank bot with the following details:
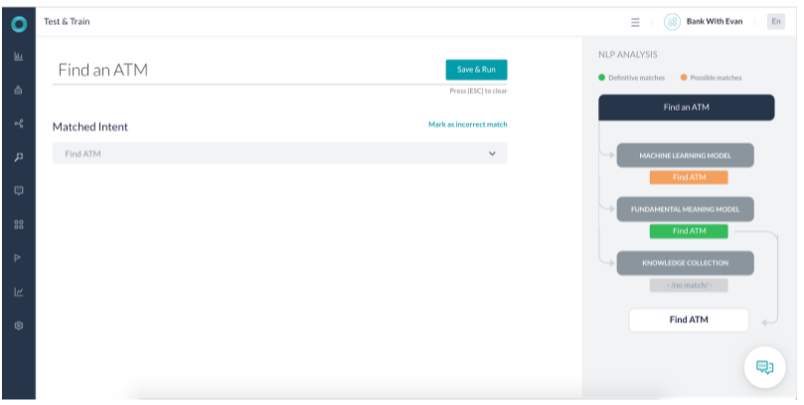
Scenario 1 – FM Identifying a Definitive Match
- The Fundamental Meaning (FM) model identified the utterance as a Definitive match.
- The Machine Learning (ML) model also identified it as a Possible match.
- The score returned for the task identified is 6 times more than other intent scores. Also, all the words in the intent name are present in the user utterance. Thus the FM model termed it a Definitive match.
- The ML model matches the Find ATM intent as a Probable match.
Scenario 3 – KG Identifying a Definitive Match

- The user utterance is How do I make transfer money to a London account?
- The user utterance contains all the terms required to match this Knowledge Graph intent path Transfer, Money, International.
- The term international is identified as a synonym of London that the user used in the utterance.
- As 100% path term matched the path was qualified. As part of confidence scoring, the terms in the user query are similar to that of the actual Knowledge Graph question. Thus, it returns a score of 100.
- As the score returned is above 100, the intent is marked as a Definitive match and selected.
- FM engine found it a Probable match as the key term Transfer is present in the user utterance
- ML engine found the utterance as a Probable match as the utterance did not fully match any trained utterance.
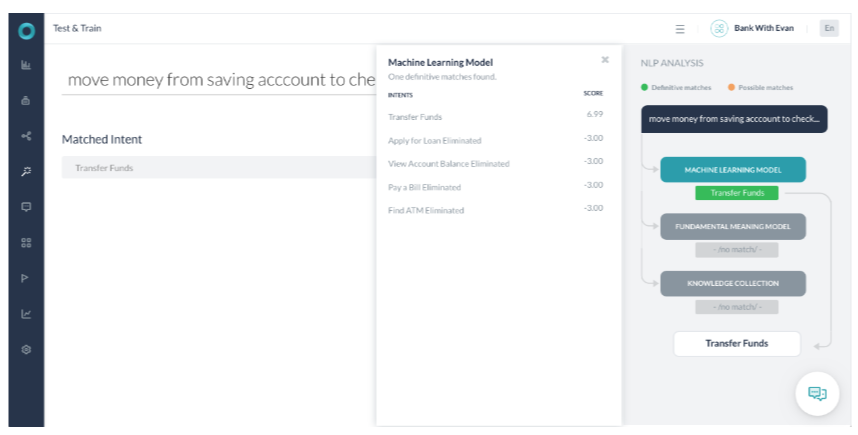
Scenario 4 – Multiple Engines Returning Probable Match

- All the 3 engines returned a possible match and no definitive match.
- ML Model has 1 possible match and FM Model has 2 possible matches, of which 1 is common. Knowledge Graph has 1 possible match. All possible matches identified are re-ranked in the Ranking and Resolver.
- The Ranking and Resolver component returned the highest score for the single match (Task name – When can I start making payments using BillPay plus?) from the Knowledge graph engine. The scores for other probable match come out to be lower than 2 percentile of the top score and are thus ignored. The winner, in this case, is the ‘KG’ returned query and is presented to the user.
- Though most of the keywords in the user utterance map to the keywords in the KG query, still this is not a definitive match because
- The number of path terms matched is not 100%.
- The KG engine returned the score with a 64.72% probability. Had we used the word Billpay instead of bill pay the score must have been 87.71%. (still not a 100% match)
- Now as the score is between the 60%-80%, a threshold of the Query is presented as part of the Did-you-mean dialog and not as a complete winner. If the score was above 80%, the platform would have given out the response without re-confirming with the Did-you-mean dialog.
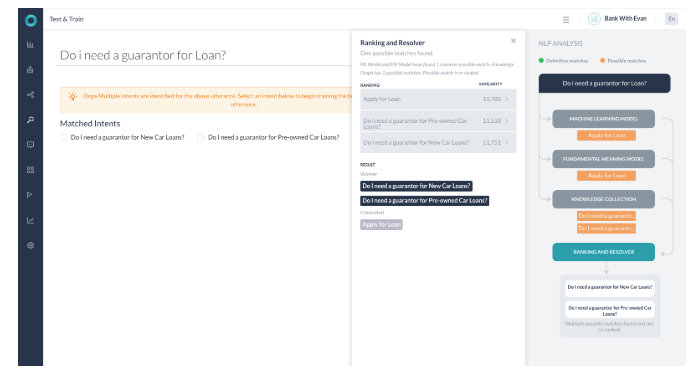
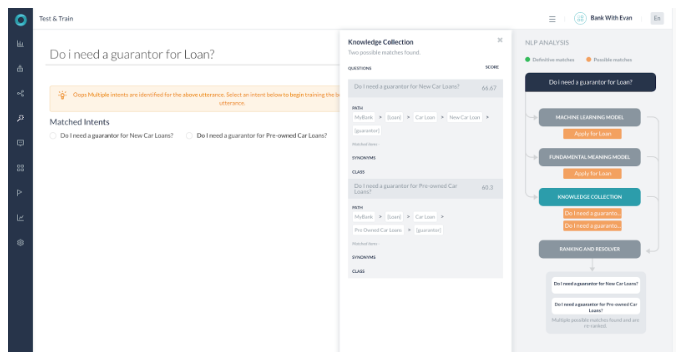
Scenario 5 – Resolver Returning Multiple Results
- All the engines detected probable matches.
- KG returned with 2 possible paths.
- Ranking and resolver found the 2 queries with a score of less than 2% apart.
- Both the Knowledge Graph intents are selected and presented to the user as Did-you-mean.
- Both the paths were selected as terms in both matches and the score for both the paths is more than 60%.