개발자는 기계 학습 모델을 학습시키려면 봇이 식별해야 하는 각 의도(작업)의 샘플 발화를 입력해야 합니다. 플랫폼 ML 엔진은 사용자 발언을 봇 의도 중 하나에 매핑하려고 시도하는 모델을 구축할 것입니다. Kore.ai의 봇 플랫폼은 완전한 비지도 기계 학습을 통해 사람의 개입 없이 챗봇의 언어 기능을 지속적으로 확장할 수 있습니다. 챗봇이 좋든 나쁘든 어떠한 입력이건 학습하는 비지도 모델과 달리, Kore.ai 봇 플랫폼은 챗봇이 의도를 성공적으로 인식하고 인간의 작업 완료 요청 엔티티를 추출할 때만 챗봇이 자동으로 어휘를 늘릴 수 있도록 합니다. 그러나 봇 성능을 모니터링하고 필요에 따라 수동으로 조정하도록 지도 학습을 하는 것이 좋습니다. 봇 플랫폼을 통해, 개발자는 인터렉션 로그를 평가하고 실패한 시나리오의 NL 설정을 쉽게 변경하며 학습한 내용을 토대로 더 나은 대화를 위해 봇을 재교육할 수 있습니다.
다중 의도 모델
다른 목적을 가진 “유사한 의도”를 학습시키는 일은 그 의도에 대한 학습이 다른 의도에 대한 학습에 잡음을 일으키거나 서로 충돌할 수 있기 때문에 일반적으로 어려운 일입니다. 이는 의도가 문맥상 다른 의미나 목적을 갖는 경우에 더욱 두드러지게 됩니다. 이런 경우를 생각해보세요. 사용자가 주문 작업을 할 때, 환불 정책 또는 배송 옵션과 관련된 모든 질의에는 설정된 주문 컨텍스트로 답변해야 합니다. 그러나 포괄적으로 반품 FAQ의 질의가 트리거됩니다.

고급 NLP 구성에서 다중 의도 모델을 활성화하면(방법은 여기 참조) 기본 의도에 대해서만 전용 ML 모델을 갖게 하고 각 대화의 ML 모델을 관련 하위 의도와 분리하여 하위 의도의 의도 탐지가 우선적으로 처리되도록 할 수 있습니다. 위의 예를 계속 가져와보면, 다중 의도 모델을 통해 별도의 컨텍스트 기반 FAQ를 정의하고 사용자에게 적절한 응답을 하도록 할 수 있습니다.

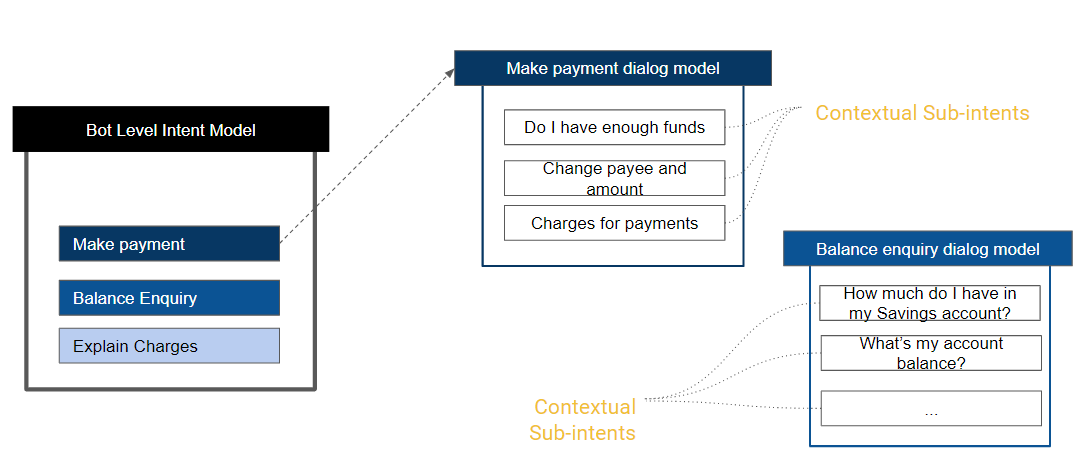
봇의 모든 기본 의도는 봇 수준 의도 모델의 일부가 됩니다. 각 대화 작업에는 추가된 모든 하위 의도로 구성된 자체 ML 모델을 가질 것입니다. 임계값 및 구성은 각 모델에 대해 개별적으로 구성될 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 봇 수준 의도 모델은 ‘표준’ 네트워크 유형을 사용할 수 있고 특정 대화의 의도 모델은 ‘LSTM’ 네트워크 유형을 사용할 수 있습니다.
기계 학습 발언 추가
- 샘플 사용자 발언을 추가하기를 원하는 봇을 엽니다.
- 상단 메뉴에서 빌드 탭을 선택합니다.
- 왼쪽 메뉴에서, 자연어 -> 학습 옵션을 선택합니다.
- 기본적으로, 모든 의도의 항목이 있는 탭이 표시됩니다.
- 필터 옵션을 사용하여 표시 항목을 대화, 하위 대화, 하위 의도 또는 조치 작업으로 제한할 수 있습니다.
- 동의어를 추가하려는 의도의 발화/+ 발화를 클릭합니다

- 사용자 발화 페이지가 열립니다.
- 거기에 발화를 입력합니다. 길이가 3,000자를 초과하는 발화는 허용되지 않습니다.

참고: 추가된 발화는 독자적인 것이어야 하지만, 다중 의도 모델의 경우 동일한 발화를 다른 모델에서 사용할 수 있습니다. 학습된 의도의 부정은 플랫폼에서 무시됩니다. 예를 들어, 송금이라는 학습된 발화가 있는 뱅킹 봇을 고려하세요. “송금을 하지 않아도 내 계좌에서 인출이 됩니다”라는 사용자 발화는 “자금 이체” 작업을 트리거하지 않습니다.
개체명 인식
의도와는 별개로, 봇이 사용자 발화에서 엔티티(존재하는 경우)를 인식하도록 학습할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 사용자가 의도를 “항공편 예약”으로 인식하는 것과 별도로 “하이데라바드에서 뭄바이까지 항공편 예약”이라고 말하면 항공편의 출발지와 목적지도 인식되어야 합니다. 이는 학습 중 사용자 발화의 엔티티를 표시하는 것으로 가능합니다. 엔티티 값을 선택하고 상응하는 엔티티를 클릭하여 발화에서 엔티티를 표시할 수 있습니다. 
또한 플랫폼에서 엔티티를 식별하고 표시하려고 할 것입니다. 이를 수락하거나 취소할 수 있는 옵션이 있습니다. 플랫폼은 다음을 기반으로 엔티티를 식별합니다.
- 시스템 엔티티;
- 열거되거나 조회된 항목의 정적 목록;
- 개체명 인식이 학습된 엔티티(위에서부터).
이렇게 표시된 각 엔티티에 대해 ML 엔진에서 식별한 신뢰도 점수가 표시됩니다. 이 점수는 개체명 인식 모델로 조건부 임의 필드를 선택한 경우에만 사용할 수 있습니다. 
또한, 엔티티 플레이스 홀더를 활성화한 경우 플랫폼은 학습 발화의 엔티티 값을 ML 모델 학습의 개체명 플레이스 홀더로 대체합니다. 실제 엔티티 값 사용뿐만 아니라 엔티티 값만 변경하여 여러 개의 발화를 추가하면 ML 학습 모델에 좋지 않은 영향을 미칩니다. 개체명도 의도 탐지 모델에 크게 영향을 미치게 됩니다.
봇 학습시키기
사용자 발화를 추가한 후에는, 발화 및 관련된 사용자 의도를 인식하도록 Kore.ai 인터프리터를 학습시켜야 합니다. 봇에 학습되지 않은 발언이 있는 경우 다음 메시지가 표시됩니다. "ML 모델에 학습되지 않은 발화가 있습니다. 모든 발화로 업데이트하도록 봇을 학습시키세요." 학습을 클릭합니다. 발화 학습의 진행 상황을 표시하는 상태 표시줄이 표시됩니다. 완료되면 발화가 성공적으로 학습됨이라는 메시지가 표시됩니다. 사용자 발화가 기계 학습 데이터베이스에 추가됩니다. ML 엔진을 추가로 설정하고, 사용자 발화에 봇 학습, 즉 봇 어휘에 사용하지 않는 단어가 포함된 경우, 더미 의도를 식별할 수 있으며, 자세한 내용은 여기를 참조하세요. 봇을 학습시키는 방법 알아보기.
자동 – 학습
기본적으로, 기계 학습은 다음과 같은 작업이 있을 때마다 정의된 사용자 발화에 자동으로 학습됩니다.
- 진행 중인 상태에서 설정된 상태로 변경.
- 새 작업명
- 또는 의도명,
- 개체명 또는 매개 변수명,
- 엔티티 유형,
- 봇명으로 업데이트.
- 게시됨.
- 봇 관리자에 의해 중단됨.
- 봇 관리자에 의해 삭제됨.
봇 빌더에서 자동 학습이 진행 중일 때 자동 학습이 완료되기 전에 봇을 테스트하려고 하면, 학습되지 않은 사용자 발화를 식별할 수 없습니다라는 경고 메시지가 표시됩니다. 자동 학습 옵션은 다음과 같이 설정할 수 있습니다.
- 설정을 수정하려는 봇을 엽니다.
- 상단 메뉴에서 빌드 옵션을 선택합니다.
- 왼쪽 탐색 메뉴에서, 자연어 ->고급 설정을 선택합니다.
- 요구 사항에 따라 자동 학습 옵션을 활성화 또는 비활성화합니다.
네거티브 패턴
네거티브 패턴을 사용하여 Fundamental meaning 또는 기계 학습 모델을 통해 탐지된 의도를 제거할 수 있습니다. 자세히 알아보려면 여기를 참조하세요.
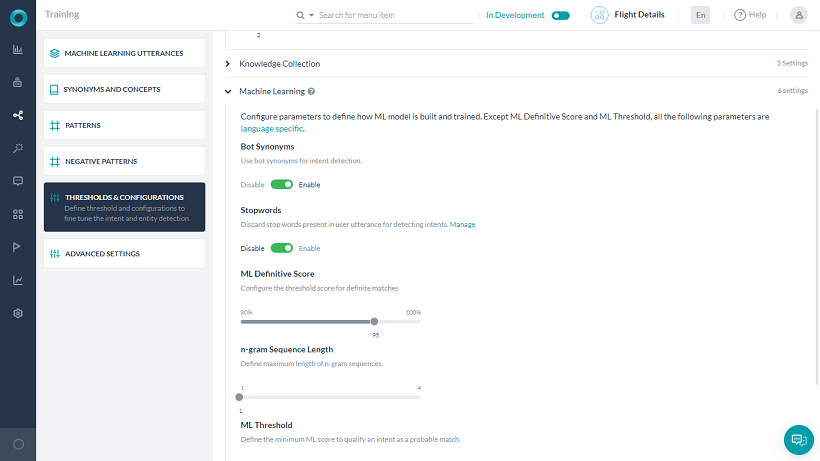
임곗값 & 설정
학습 및 성능 향상을 위해 세 가지 NLP 엔진(FM, KG, ML)의 임곗값 및 설정을 지정할 수 있습니다. 빌드 > 자연어 >임곗값 및 설정에서 이러한 설정에 액세스할 수 있습니다. 참고: 봇이 다국어인 경우 다른 언어에 다른 임곗값을 설정할 수 있습니다. 설정하지 않으면, 모든 언어에 기본 설정이 적용됩니다. ML 엔진 설정에 대해서는 다음 섹션에 자세하게 설명되어 있습니다.
기계 학습
봇 플랫폼 버전 6.3에서는 기계 학습(ML) 모델을 v3으로 업그레이드했습니다. 많은 개선이 이루어졌으며 개발자가 비즈니스 요구 사항에 맞게 매개 변수를 통해 모델을 미세 조정할 수 있습니다. 개발자는 불용어 사용, 동의어 사용, 임곗값, n-그램과 같은 매개 변수를 변경할 수 있을 뿐만 아니라, 개체명 인식(NER) 모델로의 경우 Deep Neural Network 또는 조건부 임의 필드 기반 알고리즘 중에서 선택할 수 있습니다. 플랫폼 v8.0에서는 ML 의도 모델의 v5 사용 및 하이퍼 매개 변수를 외부화할 수 있게 되었습니다. 이는 고급 NLP 설정을 통해 가능하며 자세한 내용은 여기를 참조하세요. '다중 의도 모델' 옵션이 활성화되면 ML 엔진은 봇에 대한 다음과 같은 다중 의도 모델을 유지하게 됩니다.
- 기본 대화 의도 및 경고 작업 의도 등 봇의 모든 기본 의도를 포함하는 봇 수준 의도 모델입니다.
- 대화 의도 모델 – 대화 정의에 추가된 하위 의도 노드, 그룹 노드의 일부로 범위가 지정된 하위 의도, 대화 정의에 추가된 중단 예외 사항 등 모든 기본 대화 의도 및 하위 대화 의도를 위한 모델.
임곗값 및 설정은 각 의도 모델에 개별적으로 설정할 수 있습니다. 여기에는 다음 사항이 포함됩니다.
- 임곗값 및 설정의 모든 설정 – 아래 섹션에 설명되어 있는 ML 엔진;
- 고급 NLP 설정의 모든 ML 엔진 설정은 여기에서 자세히 다루고 있습니다.
기계 학습 매개 변수 설정
봇 플랫폼은 봇의 ML 성능과 관련된 다음 매개 변수에 언어별 기본값을 제공합니다. 특정 요구 사항에 맞게 사용자가 지정을 할 수 있습니다.  ML 설정에서 참고할 점:
ML 설정에서 참고할 점:
- 다음은 전체 설정 목록이며 단일 및 다중 의도 모델 모두에 사용할 수 있습니다.
- 다중 의도 모델이 활성화되면, 모델에 대한 설정 링크를 선택하여 개별 모델을 설정할 수 있습니다.
- 봇 수준 의도 모델은 하나뿐이지만, 새로 추가 버튼을 사용하여 다중 대화 의도 모델을 추가하고 각각 요구 사항에 따라 설정할 수 있습니다.
- 고급 ML 설정은 여기서 적용하거나 고급 NLP 설정 섹션에서 적용할 수 있으며 자세한 내용은 여기를 참조하세요.
네트워크 유형
의도 모델을 학습시키는 데 사용할 신경망을 선택할 수 있습니다. 이 설정은 v8.1의 고급 NLP 구성에서 기계 학습으로 이동되었습니다. 다음 유형 중에서 선택할 수 있습니다. 선택에 따라 고급 NLP 설정 섹션에서 추가 설정을 수행할 수 있으며 자세한 내용은 여기를 참조하세요.
- 표준:
- MLP-BOW – 단어 주머니(bag-of-words) 모델은 자연어 처리 및 정보 검색에 사용하는 단순화된 표현입니다. 이 모델에서 문법과 어순은 무시되지만 다중성은 유지하는 단어 주머니로 텍스트가 나타납니다.
- MLP-워드 임베딩(WordEmbeddings) – 워드 임베딩은 어휘의 단어나 구가 실수 벡터에 매핑되는 자연어 처리에서 언어 모델링 및 기능 학습 기술 세트의 집합적 명칭입니다.
- LSTM(Long Short-Term Memory)은 딥 러닝 분야에서 사용하는 인공 순환 신경망(RNN) 아키텍처입니다. LSTM에는 피드백 연결이 있으므로 어떤 길이의 텍스트든 장기 의존성을 캡쳐할 수 있으며 보다 긴 텍스트에 적합합니다.
- CNN(convolutional neural networks)은 시각 이미지 분석에 가장 일반적으로 적용되는 딥 러닝의 deep neural networks 클래스입니다. 특정 영역 크기의 어순을 활용하여 다양한 텍스트 분류 작업에서 놀라운 결과를 얻었습니다.
- 트랜스포머는 학습 파이프라인의 벡터화 단계에서 Universal Sentence 인코더를 사용합니다. 학습을 위한 다층 퍼셉트론 네트워크에 문장 인코더 출력을 공급합니다. 문장 인코더에는 같은 문장의 동의어 및 다양한 사용 패턴을 고려하여 문장 간의 의미 유사도를 이해하는 기능이 내장되어 있습니다. Universal Sentence 인코더는 텍스트를 텍스트 분류, 의미 유사도, 클러스터링, 기타 자연어 작업에 사용할 수 있는 고차원 벡터로 인코딩합니다. 이 모델은 문장, 구 또는 짧은 단락과 같이 단어 단위보다 긴 텍스트를 학습하며 이에 최적화되어 있습니다. 다양한 자연어 이해 작업을 동적인 방식으로 제공할 목적으로 다양한 데이터 소스와 다양한 작업을 학습합니다. 입력은 가변 길이 영어 텍스트, 출력은 512차원 벡터입니다.
- KAEN (Kore Advanced Embeddings Network) – 문장 임베딩만으로 학습된 모델은 특히 학습 단어가 사전에 있는 단어가 아닌 경우 도메인별 용어를 이해할 수 없습니다. Kore.ai는 문장의 의미를 이해함과 동시에 도메인별 용어에 중요성을 부여할 수 있는 모델을 제공합니다. 이 모델에는 두 가지 병렬 층이 있습니다. 하나는 문장 임베딩에 대한 가중치를 최적화하는 층과 주어진 문장의 단어 중요성을 최적화하는 층입니다. 이 두 층에서 사용되는 활성화 기능은 RReLU(Randomized Leaky Rectified Linear Unit)이며 자세한 내용은 여기를 참조하세요)
ML 임곗값
ML 임곗값은 가능한 일치 또는 확실한 일치가 될 의도의 확률 점수를 선별하기 위한 기준을 정의합니다. 기본값은 0.3으로 설정됩니다. 즉, 0.3을 초과하는 점수를 얻은 의도는 자격을 갖춘 의도로 간주됩니다. 점수가 0.3 미만인 의도는 거부됩니다.
ML 확정 스코어링
다음 분류를 사용하여 80-100% 사이의 값으로 설정할 수 있는 확실한 일치에 대한 임곗값 스코어링을 설정합니다.
- 확률 스코어링 – 분류 엔진에 의한 확률 스코어링이 0.95("ML 확실한 스코어링"을 100으로 나눈 값을 사용하여 조정 가능한 기본값)를 초과하는 경우, 의도는 확실한 일치/완벽한 일치로 간주됩니다.
- 퍼지 논리는 주어진 의도의 각 발화를 거쳐 사용자 입력과 발화가 일치하는 정도를 확인하기 위해 사용자 입력과 비교합니다(점수는 일반적으로 0에서 100 사이입니다). 점수가 95%(“ML 확실한 점수”를 사용하여 조정 가능한 기본값)를 초과하는 경우, 의도는 확실한 일치/완벽한 일치로 간주됩니다.
봇 동의어
이 설정은 기본적으로 비활성화되어 있습니다. ML 모델을 구축할 때 의도 동의어를 염두에 두려면 이 옵션을 활성화하세요. 동의어를 활성화하면 ML 모델을 학습시키는 동안 고려해야 할 "동의어 및 개념"에 정의된 동의어를 ML 모델이 사용할 수 있습니다. 중복 발화 준비를 피하는 데 도움이 됩니다. 예: “I want to transfer funds”. “send”, “give”, “move”를 “transfer” 및 “money”의 동의어로 정의하고, “dollars”를 “funds”의 동의어로 정의했다면 “I want to send money” 또는 “I want to give dollars” 등의 학습 발화를 추가할 필요가 없습니다.
개체명 인식 모델
엔티티 탐지에 사용될 개체명 인식 모델 선택. Kore.ai는 다음과 같은 동일한 접근 방법을 따르는 NER을 사용한 학습을 위한 두 가지 엔티티 인식 모델을 제공합니다
- 조건부 임의 필드: 경량이며 모든 크기의 데이터 세트에 사용하기 쉽습니다
- 신경망: 중대형 데이터 세트와 잘 작동하지만 학습 시간이 매우 깁니다
불용어
이 설정은 기본적으로 비활성화되어 있습니다. ML 모델을 구축할 때 발화 학습에서 불용어를 제거하려면 이 옵션을 활성화하세요. 활성화되면 불용어를 사용하여 ML 모델을 학습시키기 전에 학습 발화에서 단어/구문을 필터링하는 데 사용되며 예측 전에 사용자 발화에서 제거됩니다. 네트워크 유형이 트랜스포머로 설정된 경우에는 유효하지 않습니다.
특징 추출
이 옵션(ver8.0에 도입됨)으로 ML 의도 모델을 선호하는 알고리즘과 연결할 수 있습니다. 네트워크 유형이 MLP 워드 임베딩, LSTM, CNN, 트랜스포머로 설정된 경우에는 유효하지 않습니다. 옵션은 다음과 같습니다.
- n-그램 – 기본 설정이며 모델을 학습시키기 위해 학습 문장에서 사용할 연속적인 단어 시퀀스를 정의할 수 있습니다. 예를 들어, 세일즈 예측 보고서 생성이 사용자 발화이고 n-그램을 2로 설정한 경우 세일즈, 세일즈 예측 및 예측 보고서 생성을 모델 학습에 사용합니다. n-그램을 3으로 설정한 경우, 세일즈 예측 생성 및 세일즈 예측 보고서를 모델 학습에 사용합니다. n-그램 시퀀스 길이로 n-그램을 설정할 수 있습니다. 최소 n-그램 제한은 기본적으로 1입니다. 최대 한도를 4까지 설정할 수 있습니다.
- 스킵-그램 – 말뭉치가 매우 제한적이거나 일반적으로 학습 문장이 더 적은 단어를 포함하는 경우 스킵-그램이 더 나은 옵션일 것입니다. 이를 위해 다음 사항을 정의해야 합니다.
- 시퀀스 길이 – 스킵-그램 시퀀스의 길이로 최소 2개, 최대 4개
- 최대 스킵 거리 – 그램을 형성하기 위해 스킵할 수 있는 최대 단어는 최소 1에서 최대 3.
엔티티 플레이스 홀더
학습 발화에 있는 엔티티 값을 학습 모델의 해당 엔티티 플레이스 홀더로의 변경을 사용하세요. 엔티티 플레이스 홀더는 의도 감지에서 실제 엔티티 값의 기여도를 제거합니다. 이것은 엔티티 학습(NER)이 ML을 통해 수행되는 경우에만 작동합니다. 이 플래그를 활성화하면 엔티티 값에 의해 기여된 점수가 줄어듭니다. 예: I want to transfer $500 to John Doe의 예에서, 엔진이 $500와 “John Doe”가 중요한 특징이라는 것을 학습하도록 하고 싶지 않습니다. 따라서 NER이 수행되고 엔티티 플레이스 홀더 플래그가 활성화되면 이것은 플레이스 홀더로 대체됩니다. 학습 발화는 “I want to transfer <Amount> to <Payee>”가 됩니다. 네트워크 유형이 트랜스포머로 설정된 경우에는 유효하지 않습니다.
ML 모델 업그레이드
생성된 새 봇은 기본적으로 새 ML 모델을 사용합니다. 개발자는 이전 봇의 ML 모델을 업그레이드하거나 새 모델로 봇의 모델을 다운그레이드할 수 있습니다. 봇 플랫폼에서 ML의 이전 모델을 사용하는 경우, 다음과 같이 업그레이드할 수 있습니다.
- ML 모델을 업그레이드하려는 봇을 열고 자연어 > 임곗값 및 설정으로 이동합니다.
- 기계 학습을 확장합니다. ML 업그레이드 섹션에서, 지금 업그레이드하기 버튼을 클릭합니다. 설정 창이 열립니다.
- 업그레이드 및 학습을 클릭하세요. 기계 학습 섹션에서 새 사용자 지정 가능 옵션을 볼 수 있습니다.
참고: 이전 모델(V2)로 봇을 내보내고 새 봇으로 가져온 경우, 업그레이드가 이루어질 때까지 봇은 V2 모델에 있게 됩니다.
Exporting and Importing Machine Learning Utterances
You can import and export ML utterances of a bot into another in CSV and JSON formats. You can choose between ‘In-Development’ or ‘Published’ tasks to export, whereas importing utterances always replace the latest copy of the task in the bot.
How to Export or Import ML Utterances
- On the bot’s Build menu, click Natural Language -> Training.
- The ‘In-Development’ version of the bot’s ML utterances open by default. If you want to see the utterances in the ‘Published’ version, toggle on the top right side of the window to Published.
Note: The export of ML utterances varies based on this selection as explained in the Versioning and Behavior of the Exported Utterances section below.
- Click the options icon and select an option:
- Click Import Utterances and upload a CSV or JSON file with the utterances to import. Read the Versioning and Behavior of the Imported Utterances section below for more information.-OR-
- Click Export Utterances and select CSV or JSON formats to export the utterances. Read Versioning and Behavior or the Exported Utterances section below for more information.
Versioning and Behavior of Imported Utterances
- The imported utterances in CSV/JSON entirely replace the utterances present in the latest copy of the tasks.
- If the task is in the Configured status, the utterances in the task get entirely replaced with the new utterances for the task present in the imported file.
- If the task is in Upgrade in Progress status, the utterances related to the task get entirely replaced with the task utterances present in the imported file. The utterances in the Published copy of the task aren’t affected.
- If the task is in the Published status, an Upgrade in Progress copy of the task gets created by default and the new utterances present in the imported file will be added to the upgraded copy. The utterances in the Published copy of the task aren’t affected.
Versioning and Behavior of Exported Utterances
- When you export a bot’s utterances, all the utterances related to every task type – alert, action, information, dialog – get exported.
- When you export an In Development copy of the bot, the utterances of all tasks in the latest available copy get exported.
- When you export a Published copy of the bot, all the utterances in the published state get exported.
- In the case of multi-language bots, the export of utterances includes utterances added in all of the bot languages.
- Export of utterances to JSON includes NER tagging present in the tasks, whereas CSV export doesn’t include them.
ML 학습 권장 사항
- 봇이 탐지해야 할 어떠한 의도에 대해서든 균형 잡힌 학습을 제공하도록 하고 대략 같은 수의 샘플 발화를 추가하도록 합니다. 편향된 모델은 편향된 결과를 초래할 수 있습니다.
- 각 의도에 최소 8-10개의 샘플 발화를 제공하도록 합니다. 1-2개의 발화만 있는 모델로는 기계 학습의 이점이 없습니다. 발화가 다양한지 확인하고 같은 단어를 다른 순서로 바꿔서 제공하지 마세요.
- 어떤 의도에나 적용될 수 있는 일반적인 문구(예: "나는 ~을 하고 싶다")를 학습시키지 마세요. 다양성과 학습을 위해 다양한 발화를 제공하세요.
- 변경 후에는 항상 모델을 학습시키고 모델을 확인하세요. ML 모델에 있는 모든 점들이 대각선(참양성 및 참음성) 사분면인지, 다른 사분면에 흩어져 있는 발화가 없는지 확인하세요. 그런 모양이 될 때까지 모델을 학습시키세요.
- 새로운 발화를 사용하여 봇을 정기적으로 학습시키세요.
- 실패하거나 포기한 발화를 정기적으로 검토하고 유효한 작업 또는 의도의 발화 목록에 추가합니다.
NLP 의도 탐지 학습 권장 사항
- 샘플 발화가 많은 경우, 기본 의미 모델을 학습시키기 전에 먼저 기계 학습 접근 방법으로 봇을 학습시키세요.
- 비밀번호를 나타내는 pwd, 저축 은행 계좌를 나타내는 SB>와 같은 도메인 사전을 구축하기 위해서 봇 동의어를 정의합니다.
- 모델 학습이 변경될 때마다, 배치 테스트 모듈을 실행합니다. 테스트 스위트는 봇의 ML 모델에 회귀 테스트를 하는 방법입니다.
NLP 엔티티 탐지 학습 권장 사항
엔티티를 학습시키는 가장 좋은 접근 방법은 아래에 설명된 엔티티 유형을 기반으로 하는 것입니다.
- 항목 목록(열거, 조회), 도시, 날짜, 국가 같은 항목 유형은 동일한 항목 유형이 동일한 작업에서 여러 유형을 사용하지 않는 한 학습시킬 필요가 없습니다. 봇 작업에 동일한 엔티티 유형을 사용한 경우, 학습 모델 중 하나로 사용자 발화 내에서 엔티티를 찾습니다.
- 엔티티 유형이 문자열 또는 설명인 경우에 권장하는 접근 방법은 엔티티 패턴 및 동의어를 사용하는 것입니다.
- 기타 엔터티 유형은 개체명 인식 및 패턴을 함께 사용할 수 있습니다.
엔티티 학습 권장 사항
- 가능한 한 개체명 인식 학습을 사용하세요. 개체명 인식 적용 범위가 패턴보다 넓습니다.
- 개체명 인식 접근 방법은 무서식 데이터 정보 엔티티를 탐지하는 데 가장 적합합니다. 날짜 및 시간 같은 엔티티의 경우 대규모 데이터 세트로 플랫폼을 학습시켰습니다.
- 개체명 인식 모델은 neural network 기반 모델이며 효과적인 작동을 위해서는 최소 8-10개의 샘플로 학습시켜야 합니다.
추천 자료 ML 모델에 대해 읽어보고 싶으면, 여기를 참조하세요.
開発者は、機械学習モデルをトレーニングするためにBotによる識別を必要とするそれぞれのインテント(タスク)に対して、サンプルの発話を提供する必要があります。プラットフォームのMLエンジンは、Botのインテントの1つにユーザーの発話をマッピングしようとするモデルを構築します。
Kore.aiのBotプラットフォームは、完全に教師なしの機械学習によって、人間が介入することなく継続的にチャットBotの言語能力を拡張することができます。Kore.aiのBotプラットフォームでは、チャットBotがあらゆる入力(善悪を問わず)から学習する教師なしモデルとは異なり、チャットBotが正常にインテントを認識し、人間がタスクを完了させるために要求した内容を抽出した場合にのみ、チャットBotは自動的に語彙を増やすことができます。
ただし、Botのパフォーマンスを監視し、必要に応じて手動で調整を行えるよう、教師あり学習を有効にしておくことをお勧めします。Botプラットフォームを使用することで、開発者はすべての対話ログを評価し、失敗したシナリオのNL設定を簡単に変更し、会話の精度を上げるために学習を使用してBotを再度トレーニングすることができます。
複数インテント モデル
(v8.1で導入) 目的が異なる「類似インテント」のトレーニングは、多くの場合難しいものです。一つのインテントに与えられるトレーニングが、ノイズや他のインテントのトレーニングとの矛盾を含む場合があるからです。 これは、インテントが文脈上異なる意味や目的を持っている場合にはより顕著になります。
次のようなケースを考えてみましょう。ユーザーが注文タスクにいるときの返品条件や配送オプションに関する問い合わせは、注文コンテキスト内で回答されなければなりません。 ところが、一般的な商品返品の FAQ の質問がトリガーされてしまいます。

詳細 NLP 設定 (設定方法についてはこちらをご覧ください) で複数インテント モデルを有効にすると、プライマリ インテント専用の機械学習モデルを作成して、サブインテントのインテント検出が優先されるよう、関連サブインテントを持つダイアログごとに機械学習モデルを分けることができます。
上記の例では、複数インテント モデルを使用してコンテキスト ベースの FAQ を個別に定義し、ユーザーに適切な応答を返すことができます。

ボットのすべてのプライマリ インテントは、ボット レベルのインテント モデルの一部となります。 それぞれのダイアログ タスクは、追加されたすべてのサブインテントからなる独自の機械学習モデルを持ちます。しきい値および設定は、モデルごとに個別に設定できます。
たとえば、ボット レベルのインテント モデルは「標準」ネットワーク タイプを、特定のダイアログのインテント モデルは「LSTM」ネットワーク タイプを使用することができます。

機械学習の発話の追加
体験向上のために、プラットフォームのバージョン8.1ではUIが再設計されています。
- サンプルのユーザー発言を追加するBotを開きます。
- 左ペインから、自然言語 > トレーニングをクリックします。
- 機械学習の発話タブを選択します。
- すべてのインテント一覧が提供され、フィルタオプションを使用して表示項目をダイアログ、サブダイアログ、サブインテントに制限することができます。

- 発話を追加するインテントを選択すると、ユーザーの発話ページが開きます。
- こちらに発話を入力します。
プラットフォームは、トレーニングされたインテントのネゲーションを無視します。
例えば、「Funds Transfer」というトレーニングされた発話を含むバンキングBotを例に考えてみましょう。その場合、「My account is debited even without doing funds transfer」というユーザーの発言は、「funds transfer」タスクのトリガーにはなりません。
名前付きエンティティの認識
インテントとは別に、ユーザーの発話の中にエンティティが存在する場合には、それを認識するようBotをトレーニングすることができます。例えば、ユーザーが「Book Flight from Hyderabad to Mumbai」と言った場合、「Book Flight」というインテントを認識するだけでなく、フライトの出発地と目的地も認識する必要があります。これは、ユーザーの発話内のエンティティをトレーニング中にマークすることで行われます。
エンティティ値を選択し、ドロップダウンリストから対応するエンティティをクリックすることで、発話の中にエンティティをマークすることができます。

さらに、プラットフォームはエンティティを識別してマークを付けようとしますが、お客様はこれらの提案を受け入れるか破棄するかを選択することができます。プラットフォームは、以下に基づいてエンティティを識別します。
- システムエンティティ
- 列挙またはルックアップのいずれかの項目の静的リスト
- NERのトレーニング済みエンティティ(上から)
このようにしてマークされたそれぞれのエンティティについて、MLエンジンによって識別された信頼度スコアが表示されます。これはプラットフォームのリリース8.0で導入されたもので、NERモデルとして条件付きランダムフィールドが選択されている場合にのみ利用可能です。

さらに、エンティティプレースホルダを有効にしている場合、トレーニング用の発話のエンティティ値をエンティティ名プレースホルダに置き換えてMLモデルをトレーニングします。エンティティ値を変更しただけの発話を複数回追加した場合と同様に、実際のエンティティ値を使用すると、MLのトレーニングモデルに悪影響を与えます。また、エンティティ名もインテント検出モデルに大きな影響を与えます。
Botのトレーニング
ユーザーの発言を追加した後、Kore.aiインタプリタをトレーニングして発話と関連するユーザーインテントを認識させる必要があります。Botにトレーニングされていないの発話がある場合、以下のようなメッセージが表示されます。
「機械学習モデルにはトレーニングされていない発話があります。エンジンがトレーニングされない限り、トレーニングされていない発話に基づき、Botはインテントおよびエンティティを識別しません。すべての発話でBotを更新するには、[トレーニング]ボタンをクリックしてください。」
ユーザーの言葉セクションのトレーニングをクリックします。発話トレーニングの進捗状況を示すステータスバーが表示されます。完了すると、発話は正常にトレーニングされましたというメッセージが表示されます。ユーザーの発話が機械学習データベースに追加されます。さらに、MLエンジン(リリース8.0以降)を設定したり、ユーザーの発話にBotのトレーニングで使用されていない単語、つまりBotの語彙が含まれている場合にダミーのインテントを識別したりすることができます。詳細についてはこちらを参照してください。
自動トレーニング
デフォルトでは、タスクが以下の場合に、定義済みのユーザーの発話に対して機械学習が自動的にトレーニングされます。
- 進行中 から 設定済み に変更された。
- 以下の項目が更新された。
- タスク名またはインテント名
- エンティティ名またはパラメータ名
- エンティティタイプ
- Bot名
- 公開された。
- Bot管理者によって一時停止された。
- Bot管理者によって削除された。
自動トレーニング中のBotビルダーでは、自動トレーニングが完了する前にBotのテストを実行しようとした場合、トレーニングされていないユーザーの発話を識別することはできませんという警告メッセージが表示されます。
自動トレーニングオプションは以下のように設定することができます。
- 設定を変更するBotを開きます。
- サイドナビゲーションパネルにカーソルを合わせ、自然言語 > トレーニングをクリックします。
- 詳細設定タブを選択します。
- 要件に応じて自動トレーニングオプションを有効または無効にします。
ネガティブパターンs
ネガティブパターンは、ファンダメンタルミーニングや機械学習モデルによって検出されたインテントを排除するために使用することができます。詳細はこちらを参照してください。[/vc_column_text][us_separator size="small" show_line="1"][vc_column_text]
しきい値および設定
ファンダメンタル ミーニング、ナレッジ グラフ、機械学習の 3 つの NLP エンジンにしきい値および設定を指定して、トレーニングとパフォーマンスの向上を図ることができます。 これらは [自然言語] > [トレーニング] > [しきい値および設定] で設定できます。
メモ:: ボットが多言語に対応している場合は、言語ごとにしきい値を設定することができます。 設定しない場合は、すべての言語にデフォルトの設定が適用されます。
機械学習エンジンの設定については、以下のセクションで詳しく解説しています。
機械学習
ボット プラットフォーム バージョン 6.3 では、機械学習モデルが v3 にアップグレードされています。 これには改良点が多数含まれており、開発者はパラメーターを使用して、ビジネス要件に合わせてモデルを微調整することができます。開発者はストップ ワードや同義語の使用、しきい値、N グラムのパラメーターを変更したり、固有表現認識 (NER) モデルにディープ ニューラル ネットワークまたは条件付きランダム フィールド ベースのアルゴリズムを選択したりすることができます。
プラットフォームの v8.0 では、機械学習インテント モデルの v5 を使用して、いくつかのハイパーパラメーターを外部化できるようになりました。 これは詳細 NLP 設定で実現できます。詳細については、こちらを参照してください.
プラットフォームの v8.1 では、複数インテント モデル機能が導入されました。 「複数インテント モデル」オプションが有効になっている場合、機械学習エンジンはボットの複数インテント モデルを次のように管理します。
- プライマリ ダイアログ インテントや通知タスク インテントなどのボットのすべてのプライマリ インテントを含む、ボット レベルのインテント モデルです。
- ダイアログ インテント モデル – ダイアログの定義に追加されたサブインテント ノード、グループ ノードの一部としてスコーピングされたサブインテント、ダイアログの定義に追加された割り込みの例外を含む、すべてのプライマリ ダイアログ インテントとサブダイアログ インテントに一つずつ指定します。
しきい値および設定で、インテント モデルごとに個別に設定できます。 これは、以下を含みます。
- しきい値および設定以下の設定 – 次のセクションで解説されている機械学習エンジン
- こちらで詳しく説明されている、詳細 NLP エンジン設定以下のすべての機械学習エンジン設定 .
しきい値と設定
トレーニングを行い、パフォーマンスを向上させるために、FM、KG、MLの3つのNLPエンジンすべてに対して、しきい値と設定値を指定することができます。これらの設定は、自然言語 > トレーニング > しきい値と設定からアクセスすることができます。
注:Botが多言語の場合、言語ごとに異なるしきい値を設定することができます。設定されていない場合、すべての言語でデフォルト設定が使用されます。
MLエンジンの設定については、以下のセクションで詳述します。
機械学習
Botプラットフォームのバージョン6.3では、機械学習(ML)モデルがバージョン3にアップグレードされました。これには多くの改善点が含まれており、開発者はビジネス要件に合わせてパラメータを使用してモデルを微調整することができるようになりました。開発者は、ストップワードの使用、同義語の使用、しきい値、n-gramsなどのパラメータを変更できるだけでなく、名前付きエンティティ認識(NER)モデルの深層ニューラルネットワークまたは条件付きランダムフィールドベースのアルゴリズムを選択することができます。
プラットフォームのバージョン8.0では、MLインテントモデルのバージョン5を使用し、いくつかのハイパーパラメータを外部化するためのプロビジョニングが有効になっています。これは、NLPの詳細設定から行えます。
機械学習パラメータの設定
Botプラットフォームは、お客様のBotのMLパフォーマンスに関連する以下のパラメータの、言語ごとのデフォルト値を適用します。特定のニーズに合わせてカスタマイズすることが可能です。
Botの同義語
デフォルトではこの設定は無効になっています。MLモデルを構築する際にインテントの同義語を考慮したい場合には、このオプションを有効にしてください.
ストップワード
デフォルトではこの設定は無効になっています。MLモデルを構築する際にトレーニングしている発話内のストップワードを削除したい場合は、このオプションを有効にしてください。
ML確定スコア
完全一致のしきい値スコアを設定します。80〜100%の値に設定できます。
特徴抽出
このオプション(バージョン8.0で導入)を使用すると、MLインテントモデルを優先するアルゴリズムと関連付けることができます。
- n-gram – これはデフォルトの設定であり、モデルをトレーニングするためにトレーニング文から使用される単語の連続シーケンスを定義するために使用することができます。
例えば、ユーザ発話がGenerate sales forecast reportで、n-gramを2に設定した場合、Generate sales、Sales forecast、Forecast reportがモデルの学習に使用されます。n-gramを3に設定した場合には、Generate sales forecastおよびSales forecast reportがモデルの学習に使用されます。
n-gramシーケンス長を使用してn-gramを設定することができます。n-gramの最小値はデフォルトで1になっています。 最大4まで設定することができます。 - Skip-gram – コーパスが非常に限られている場合や、トレーニング文の単語数が少ない場合は、一般的にSkip-gramの方が適しています。このためには、以下を定義する必要があります。
- シーケンス長 – Skip-gramシーケンスの長さで、最小値は2、最大値は4です。
- 最大スキップディスタンス – グラムを形成するためにスキップする最大単語数で、最小値は1、最大値は3です。
MLしきい値
インテントを一致の可能性のあるものとして認定するための最小MLスコアを定義します。MLスコアリングについての詳細をご確認ください。
NERモデル
エンティティ検出に使用するNERモデルを選択します。
エンティティのプレースホルダ
トレーニング音声内に存在するエンティティ値を、学習モデルの対応するエンティティプレースホルダに置き換えることを可能にします。
MLモデルのアップグレード
新しく作成されたBotはすべて、新しいMLモデルをデフォルトで使用します。開発者は、古いBotのMLモデルをアップグレードしたり、新しいモデルを使用してBotのモデルをダウングレードしたりすることができます。
Botプラットフォームで以前のモデルのMLを使用している場合は、以下の方法でアップグレードすることができます。
- MLモデルをアップグレードするBotを開き、自然言語 > 詳細設定に進みます。
- 機械学習を展開します。MLのアップグレードセクションで今すぐアップグレードボタンをクリックします。確認ウィンドウが開きます。
- アップグレードとトレーニングをクリックします。機械学習セクションの下に新しいカスタマイズ可能なオプションが表示されます。
また、古いバージョンに置き換えるをクリックすると、MLモデルをダウングレードすることができます。ただし、古いバージョンのMLモデルはサポート終了となる可能性があることにご注意ください。継続的なサポートおよび今後の機能強化を受けるためには、最新版をご利用いただくことを強くお勧めします。
注:旧モデル(バージョン2)を使用してBotをエクスポートし、新しいBotとしてインポートした場合、アップグレードするまではバージョン2モデルのままです。[/vc_column_text][us_separator show_line="1"][vc_column_text]
機械学習の発話のエクスポートとインポート
BotのML発話をCSVやJSON形式で別のBotにインポートしたり、エクスポートしたりすることができます。エクスポートするタスクは「開発中」と「公開済み」のどちらかを選択することができますが、発話をインポートすると、Bot内のタスクの最新のコピーが常に置き換えられます。
ML発話のエクスポートまたはインポート方法
- Botのメニューで自然言語 > 機械学習の発話をクリックします。
- デフォルトではBotのML発話の「開発中」バージョンが表示されます。「公開済み」バージョンの発話を確認したい場合は、ウィンドウの右上にある公開済みに切り替えてください。
注:ML発話のエクスポートは、以下の「エクスポート済みの発話のバージョニングと動作」で説明されているように、この選択によって異なります。 - オプションアイコンをクリックして、オプションを選択します。
- インポートをクリックして、インポートする発話を含むCSVファイルまたはJSONファイルをアップロードします。詳細については、インポート済みの発話のバージョニングと動作のセクションを参照してください。
- エクスポートをクリックし、CSV形式またはJSON形式を選択して発話をエクスポートします。詳細については、以下のエクスポート済みの発話のバージョニングと動作のセクションを参照してください。
インポート済みの発話のバージョニングと動作
- インポートされたCSV/JSON形式の発話は、タスクの最新のコピーに存在する発話に、完全に置き換えられます。
- タスクが設定済みステータスになっている場合、タスク内の発話は、インポートされたファイルに存在するタスクの新しい発話に、完全に置き換えられます。
- タスクが進行中のアップグレードのステータスになっている場合、タスクに関連する発話は、インポートされたファイルに存在するタスクの発話に完全に置き換えられます。タスクの公開済みコピーの発話は影響を受けません。
- タスクが公開済みのステータスになっている場合、タスクの進行中のアップグレードのコピーがデフォルトで作成され、インポート済みファイルに存在する新しい発話がアップグレードされたコピーに追加されます。タスクの公開済みのコピーの発話は影響を受けません。
エクスポート済みの発話のバージョニングと動作
- Botの発話をエクスポートすると、アラート、アクション、情報、ダイアログなど、すべてのタスクタイプに関連するすべての発話がエクスポートされます。
- Botの開発中コピーをエクスポートすると、最新の利用可能なコピー内にあるすべてのタスクの発話がエクスポートされます。
- Botの公開済みのコピーをエクスポートすると、公開済みになっているすべての発話がエクスポートされます。
- 多言語Botの場合、発話のエクスポートは選択したBotの言語に対してのみ行われます。
- 発話のJSONへのエクスポートにはタスクに存在するNERタグが含まれていますが、CSVエクスポートには含まれていません。
MLトレーニングの推奨事項
- ボットが検出する必要があるすべての意図に対して、バランスのとれた訓練を与え、ほぼ同じ数のサンプル発言を追加します。偏向したモデルは偏向した結果をもたらす可能性があります。
- それぞれのインテントに対して少なくとも8~10のサンプル発話を提供します。発話の数が1~2しかないモデルでは、機械学習の効果は得られません。発話は多様なものにし、同じ単語を異なる順序で使用するような発話は提供しないようにします。
- 例えば「I want to」など、すべてのインテントに適用される可能性のある一般的なフレーズはトレーニングしないようにします。より多くの多様性と学習のために、発話を変化させるようにします。
- 変更のたびに、モデルをトレーニングし、モデルのチェックを行います。MLモデルのすべてのドットが対角(真正および真負)象限であり、他の象限に散在する発話がないようにします。これが達成されるまでモデルをトレーニングします。
- 新しい発話でBotを定期的にトレーニングします。
- 失敗した発話または放棄された発話を定期的に見直し、有効なタスクやインテントに照らし合わせて発話リストに追加します。
NLPインテント検出トレーニングの推奨事項
- 発話のサンプル数が多い場合は、ファンダメンタルミーニングモデルをトレーニングしようとする前に、まず機械学習のアプローチを使用してBotをトレーニングしてみます。
- Botの同義語を定義して、パスワード用のpwd 、普通預金口座用のSBなどのドメイン辞書を作成します。
- モデルのトレーニングを変更するたびに、バッチテストモジュールを実行します。テストスイートは、BotのMLモデルの回帰テストを実行するための手段です。
NLPエンティティ検出トレーニングの推奨事項
エンティティをトレーニングするための最良のアプローチは、以下に説明するように、エンティティの種類によって異なります。
- List of Items(列挙、ルックアップ)、City、Date、Countryのようなエンティティタイプは、同じエンティティタイプが同一タスク内において複数のタイプで使用されない限り、トレーニングの必要はありません。Botタスクで同一のエンティティタイプが使用されている場合は、トレーニングモデルのいずれかを使用して、ユーザーの発話の中からエンティティを見つけます。
- エンティティのタイプがStringまたはDescriptionの場合、エンティティパターンおよび同義語を使用することが推奨されます。
- その他すべてのエンティティタイプについては、NERとパターン両方を組み合わせて使用することができます。
エンティティトレーニングの推奨事項
- 可能な限りNERトレーニングを使用する – NERはパターンよりもバレッジが高くなります。
- NERアプローチは、情報がフォーマットされていないデータとして提供されるエンティティの検出に最適です。日付や時刻のようなエンティティについては、プラットフォームは大規模なデータセットを用いてトレーニングされています。
- NERはニューラルネットワークベースのモデルであり、効果的に動作させるためには少なくとも8~10のサンプルを用いてトレーニングする必要があります。
Developers need to provide sample utterances for each intent (task) the bot needs to identify to train the machine learning model. The platform ML engine will build a model that will try to map a user utterance to one of the bot intents.
Kore.ai’s Bots Platform allows fully unsupervised machine learning to constantly expand the language capabilities of your chatbot – without human intervention. Unlike unsupervised models in which chatbots learn from any input – good or bad – the Kore.ai Bots Platform enables chatbots to automatically increase their vocabulary only when the chatbot successfully recognizes the intent and extracts the entities of a human’s request to complete a task.
However, we recommend keeping Supervised learning enabled to monitor the bot performance and manually tune where required. Using the bots platform, developers can evaluate all interaction logs, easily change NL settings for failed scenarios, and use the learnings to retrain the bot for better conversations.
Multiple Intent Model
Training of “similar intents” with different purposes is usually difficult as the training given for an intent can add noise or conflict with the training given to the other intent. This is more evident in cases where the intents have a contextually different meaning or purpose.
Consider the following case, here when the user is in the Place Order task, any query pertaining to returns policy or delivery options should be answered in the placed order context. But the query from the generic Return a product FAQ would be triggered.

Enabling the Multiple Intent Models from the Advanced NLP Configurations (see here for how) allows you to have a dedicated ML model only for the primary intents and separate ML Models for each of the dialogs with their associated sub-intents so that the intent detection of sub-intents gets preferential treatment.
Continuing with the above example, with a Multiple Intent Model, you can define a separate context-based FAQ and ensure a proper response to the user.

All the primary intents of the bot will be part of the Bot Level Intent Model. Each of the Dialog tasks will have its own ML Model consisting of all the sub-intents added to it. The Thresholds and Configurations can be individually configured for each of the models.
For example, the Bot Level Intent Model can use ‘Standard’ Network Type and a specific Dialog’s intent model can use ‘LSTM’ Network Type.

Adding Machine Learning Utterances
- Open the bot for which you want to add sample user utterances.
- Select the Build tab from the top menu.
- From the left menu, select the Natural Language -> Training option.
- By default, the tab with a list of all Intents would be displayed.
- You can use the filter option to restrict the display items to Dialog, Sub-dialog, Sub-intents, or Action tasks.
- Click the Utterances/+ Utterance against the Intent for which you want to add the utterances

- The user utterance page would open.
- Here enter the utterances. Note that utterances greater than 3,000 characters in length are not allowed.

Note: Utterances added should be unique, but in the case of multiple intent models, the same utterance can be used across different models.
The negation of trained intents will be ignored by the platform.
For example, consider a Banking Bot with trained utterance – Funds Transfer. Then a user utterance “My account is debited even without doing funds transfer” will not trigger the “funds transfer” task.
Named Entity Recognition
Apart from the intent, you can train your Bot to recognize the entities, if present, in the user utterance. For example, if the user says “Book Flight from Hyderabad to Mumbai” apart from recognizing the intent as “Book Flight” the source and destination of the flight should also be recognized. This can be achieved by marking the entities in the user utterance during training.
You can mark entities in your utterances, by selecting the entity value and clicking the corresponding entity name.

The platform will also try to identify and mark the entities, you have the option to accept or discard these suggestions. The platform will identify the entities based upon:
- System entities;
- Static List of items either enumerated or lookup;
- NER trained entities (from above).
For each of the entities thus marked, the confidence scores identified by the ML engine are displayed. This score is available only when Conditional Random Field is selected as the NER model.
Further, if you have enabled Entity Placeholders the platform will replace the entity values in the training utterance with entity name placeholders for training the ML model. Using actual entity values as well as multiple additions of an utterance with just a change in the entity value will have an adverse impact on the ML training model. The name of entities also starts contributing highly to the intent detection model.
Training your Bot
After you add user utterances, you should train the Kore.ai interpreter to recognize the utterances and the associated user intent. When you have untrained utterances in your bot, the following message is displayed:
“You have untrained utterances in your ML model. Train your bot to update with all your utterances.”
Click Train. A status bar is displayed to show progress for utterance training. When complete, the Utterances trained successfully message is displayed. The user utterances are added to the Machine Learning Database. You can further configure the ML engine, identify the dummy intents when a user utterance contains the words that are not used in the bot’s training i.e. bot vocabulary, refer here for more details.
Auto-Train
By default, machine learning is automatically trained for any defined user utterances whenever a task is:
- changed from a status of In-Progress to Configured.
- updated with a new
- task name or intent name,
- entity name or parameter name,
- entity type,
- bot name.
- published.
- suspended by the Bots Admin.
- deleted by the Bots Admin.
In Bot Builder when auto-train is in progress, a warning message that untrained user utterances cannot be identified is displayed if you try to test the bot before auto-train is complete.
You can set the Auto Train option as follows:
- Open the bot for which you want to modify the settings.
- Select the Build option from the top menu.
- From the left navigation menu, Natural Language -> Advanced Settings.
- Enable or Disable the Auto Training option as per your requirements.
Negative Patterns
Negative patterns can be used to eliminate intents detected by the Fundamental Meaning or Machine Learning models. Refer here to know more.
Threshold & Configurations
To train and improve the performance Threshold and Configurations can be specified for all three NLP engines – FM, KG, and ML. You can access these settings under Build > Natural Language > Thresholds & Configurations.
NOTE: If your Bot is multilingual, you can set the Thresholds differently for different languages. If not set, the Default Settings will be used for all languages.
The settings for the ML engine are discussed in detail in the following sections.
Machine Learning
The Bots Platform ver 6.3 upgraded its Machine Learning (ML) model to v3. This includes a host of improvements and also allows developers to fine-tune the model using parameters to suit business requirements. The developers can change parameters like stopword usage, synonym usage, thresholds, and n-grams, as well as opt between Deep Neural Network or Conditional Random Field-based algorithm for the Named-Entity Recognition (NER) model.
In v8.0 of the platform, provision has been enabled to use the v5 of the ML intent model and externalize several hyperparameters. This can be achieved through the Advanced NLP Configuration, refer here for details.
When the ‘multiple intents model’ option is enabled, the ML Engine maintains multiple intent models for the bot as follows:
- Bot level Intent Model containing all the Primary Intents of the bot which includes Primary Dialog Intents, and Alert Task Intents.
- Dialog Intent Models – one for every primary dialog intent and sub-dialog intent which includes the Sub-intent nodes added to the dialog definition, Sub-intents scoped as part of the Group nodes and Interruption exceptions added to the dialog definition.
You can configure the Thresholds and Configurations separately for each of the intent models. This includes
- All the configurations under Thresholds and Configurations – ML Engine as discussed in the below section;
- All the ML Engine configurations under the Advanced NLP Configurations discussed in detail here.
Configuring the Machine Learning Parameters
The Bots Platform provides language-wise defaults for the following parameters related to the ML performance of your bot. You can customize them to suit your particular needs.
Points to note in ML configurations:
- The following is the list of all possible configurations and these are available for both single and multiple intent models.
- When the multiple intent model is enabled, you can configure the individual models by selecting the Configure link against the model.
- While there is only one Bot level intent model, you can add multiple dialog intent models using the Add New button and configure each as per your requirements.
- Advanced ML Configurations can be applied from here or from the Advanced NLP Configurations section refer here for details.
Network Type
You can choose the Neural Network that you would like to use to train the intent models. This setting has been moved to Machine Learning from Advanced NLP Configurations in v8.1.
You can choose between the following types. Based on the selection additional configurations can be done from the Advanced NLP Configurations section, refer here for details.
- Standard;
- MLP-BOW – The bag-of-words model is a simplifying representation used in natural language processing and information retrieval. In this model, a text is represented as the bag of its words, disregarding grammar and even word order but keeping multiplicity.
- MLP-WordEmbeddings – Word embedding is the collective name for a set of language modeling and feature learning techniques in natural language processing where words or phrases from the vocabulary are mapped to vectors of real numbers.
- LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) is an artificial recurrent neural network (RNN) architecture used in the field of deep learning. LSTM has feedback connections and hence has the ability to capture long-term dependencies for texts of any length and is well suited for longer texts.
- CNN (convolutional neural networks) is a class of deep neural networks in deep learning most commonly applied to analyzing visual imagery. It makes use of the word order for a specific region size and has achieved remarkable results on various text classification tasks.
- Transformers use a Universal Sentence encoder in the vectorization stage of the Training pipeline. The output of the sentence encoder is fed to a Multi-Layer perceptron network for training. SentenceEncoder has an inbuilt capability of understanding the semantic similarity between sentences taking into account the synonyms and various usage patterns of the same sentence.
The Universal Sentence Encoder encodes text into high-dimensional vectors that can be used for text classification, semantic similarity, clustering, and other natural language tasks. The model is trained and optimized for greater-than-word length text, such as sentences, phrases, or short paragraphs. It is trained on a variety of data sources and a variety of tasks with the aim of dynamically accommodating a wide variety of natural language understanding tasks. The input is the variable-length English text and the output is a 512-dimensional vector. - KAEN (Kore Advanced Embeddings Network) – Models trained with Sentence Embeddings alone can not understand the domain-specific terminology especially if the words from training are non-dictionary words. Kore.ai provides a model which can understand the meaning of the sentence and at the same time give importance to the domain-specific terminology. There are two parallel layers in work in this model – one to optimize the weights against the sentence embeddings and the other to optimize the word importance for a given sentence. The activation function used for these two layers is RReLU (Randomized Leaky Rectified Linear Unit, refer here for details)
ML Threshold
ML Threshold defines the criteria for qualifying a probability score of an intent to be a possible or definite match. The default value is set to 0.3. This means that any intent which scores >0.3 is considered as qualified Intent. Intents scoring < 0.3 are rejected
ML Definitive Score
Configure the threshold score for definite matches, which can be set to a value between 80-100%, with the following classification:
- Probability Score – If the probability score by the classification Engine is >0.95 (default which is adjustable using “ML Definitive Score” divided by 100) Intent is considered as a Definite Match/Perfect Match.
- Fuzzy logic goes through each utterance of a given Intent and compares it against the user input to see how close the user input and the utterance are (scores are usually from 0-100). If the score is above 95% (default which is adjustable using “ML Definitive Score”) Intent is considered as a Definite Match/Perfect Match.
Bot Synonyms
This setting is Disabled by default. Enable this option if you would like to consider intent synonyms in building the ML model.
Enabling Synonyms allows the ML model to take the synonyms defined under “Synonyms and Concepts” to be considered while training the ML model. It helps in avoiding preparing duplicate utterances.
For example: “I want to transfer funds”.
If we had defined “send”, “give”, “move” as synonyms of “transfer” and “money”, “dollars” as synonyms of “funds”, then we need not add training utterances like “I want to send money” or “I want to give dollars” etc.
NER Model
Choose the NER model to be used for entity detection. Kore.ai provides two entity recognition models for training using NER that follow the same approach with
- Conditional Random Fields: lightweight and is easy to use for all sizes of datasets
- Neural network: works well with medium to large datasets but training time is very high
Stop Words
This setting is Disabled by default. Enable this option if you would like to remove the stop words in the training utterances in building the ML model. Once enabled, stop words are used to filter out the words/phrases from the Training utterances before training the ML model and removed from the user utterance before prediction.
Not valid when Network Type is set to Transformer.
Feature Extraction
Using this option (introduced in ver8.0) you can associate the ML intent model with the preferred algorithm. Not valid when Network Type is set to MLP WordEmbeddings, LSTM, CNN, and Transformer.
The options being:
- n-gram – this is the default setting and can be used to define the contiguous sequence of words to be used from training sentences to train the model.
For example, if Generate sales forecast report is the user utterance and if the n-gram is set to 2, then Generate sales, Sales forecast, and Forecast report are used in training the model. If n-gram is set to 3, then Generate sales forecast, and Sales forecast report will be used in training the model.
You can set the n-gram using the n-gram Sequence Length – The minimum n-gram limit is 1 by default. You can set the maximum limit up to 4. - skip-gram – when the corpus is very limited or when the training sentences, in general, contain fewer words then skip-gram would be a better option. For this you need to define:
- Sequence Length – the length for skip-gram sequences, with a minimum of 2 and a maximum of 4
- Maximum Skip Distance – the maximum words to skip to form the grams, with a minimum of 1 and a maximum of 3.
Entity Placeholders
Enable to replace entity values present in the training utterances with the corresponding entity placeholders in the training model. Entity placeholders remove the contribution of real entity values in Intent detection. This works only when the entity training(NER) is done via ML. Enabling this flag reduces scores contributed by entity values.
Ex: I want to transfer $500 to John Doe
In the above example, we don’t want the engine to learn that $500 and “John Doe” are important features. Hence they are replaced with their Placeholders once NER is done and the Entity Placeholders flag is enabled. Training utterance becomes “I want to transfer <Amount> to <Payee>”
Not valid when Network Type is set to Transformer.
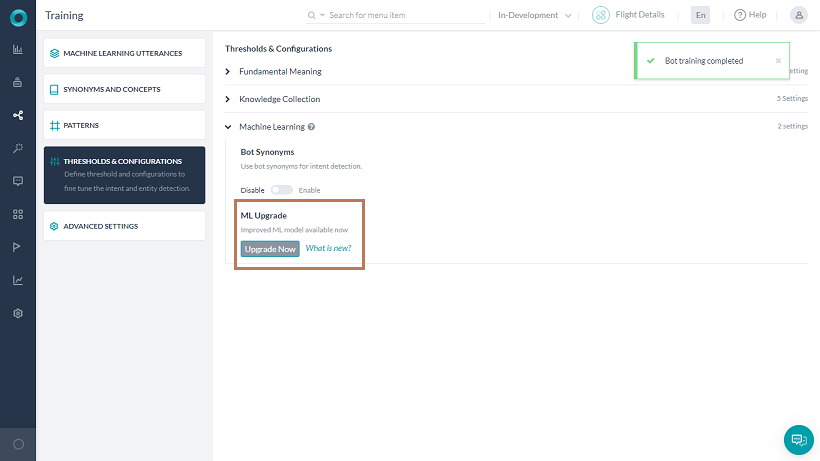
Upgrading the ML Model
All new bots that are created use the new ML model by default. Developers can upgrade the ML model for old bots or downgrade the model for the bots using the new model.
If you are using a previous model of ML in the bots platform, you can upgrade it as follows:
- Open the bot for which you want to upgrade the ML model and go to Natural Language > Thresholds & Configurations.
- Expand Machine Learning. Under the ML Upgrade section, click the Upgrade Now button. It opens a confirmation window.
- Click Upgrade and Train. You can see new customizable options under the Machine Learning section.
Note: If a bot is exported using the older model (V2) and imported as a new bot, it continues to be in the V2 model until you upgrade it.
Exporting and Importing Machine Learning Utterances
You can import and export ML utterances of a bot into another in CSV and JSON formats. You can choose between ‘In-Development’ or ‘Published’ tasks to export, whereas importing utterances always replace the latest copy of the task in the bot.
How to Export or Import ML Utterances
- On the bot’s Build menu, click Natural Language -> Training.
- The ‘In-Development’ version of the bot’s ML utterances open by default. If you want to see the utterances in the ‘Published’ version, toggle on the top right side of the window to Published.
Note: The export of ML utterances varies based on this selection as explained in the Versioning and Behavior of the Exported Utterances section below.
- Click the options icon and select an option:
- Click Import Utterances and upload a CSV or JSON file with the utterances to import. Read the Versioning and Behavior of the Imported Utterances section below for more information.-OR-
- Click Export Utterances and select CSV or JSON formats to export the utterances. Read Versioning and Behavior or the Exported Utterances section below for more information.
Versioning and Behavior of Imported Utterances
- The imported utterances in CSV/JSON entirely replace the utterances present in the latest copy of the tasks.
- If the task is in the Configured status, the utterances in the task get entirely replaced with the new utterances for the task present in the imported file.
- If the task is in Upgrade in Progress status, the utterances related to the task get entirely replaced with the task utterances present in the imported file. The utterances in the Published copy of the task aren’t affected.
- If the task is in the Published status, an Upgrade in Progress copy of the task gets created by default and the new utterances present in the imported file will be added to the upgraded copy. The utterances in the Published copy of the task aren’t affected.
Versioning and Behavior of Exported Utterances
- When you export a bot’s utterances, all the utterances related to every task type – alert, action, information, dialog – get exported.
- When you export an In Development copy of the bot, the utterances of all tasks in the latest available copy get exported.
- When you export a Published copy of the bot, all the utterances in the published state get exported.
- In the case of multi-language bots, the export of utterances includes utterances added in all of the bot languages.
- Export of utterances to JSON includes NER tagging present in the tasks, whereas CSV export doesn’t include them.
Goal Driven Training Validations
The ML engine enables you to identify issues proactively in the training phase itself with the following set of recommendations:
- Untrained Intents – notifies about intents that are not trained with any utterances so that you can add the required training.
- Inadequate training utterances – notifies the intents that have insufficient training utterances so that you can add more utterances to them.
- Utterance does not qualify any intent (false negative) – notifies about a utterance for which the NLP model cannot predict any intent. For example, an utterance added to Intent A is expected to predict Intent A. Whereas in some cases the model won’t be able to predict neither the trained Intent A nor any other Intents within the model. Identifying such cases proactively helps you to rectify the utterance and enhance the model for prediction.
- Utterance predicts wrong intent (false positive) – Identifies utterances that predict intents other than the trained intent. For example, when you add an utterance that is similar to utterances from another intent, the model could predict a different intent rather than the intent to which it is trained to. Knowing this would help you to rectify the utterance and improve the model prediction
- Utterance predicts intent with low confidence – notifies about the utterances that have low confidence scores. With this recommendation, you can identify and fix such utterances to improve the confidence score during the virtual assistant creation phase itself.
How to View NLU Training Validations
- On the virtual assistant’s Build menu, click Natural Language -> Training.
- In the Intents tab, you can see the set of recommendations for the Intents and ML utterances.

Note: The errors and warnings in this screen are examples. The ML validations vary based on the error or waning recommendation as explained in the Goal-Based NLU Training Validations section above. - Hover over the validation options and view the following recommendations:
- Hover on the
 Error icon to view the recommendations to resolve the error.
Error icon to view the recommendations to resolve the error.  Note: An Error is displayed when the intent has a definite problem that impacts the virtual assistant’s accuracy or intent score. Errors are high severity problems.
Note: An Error is displayed when the intent has a definite problem that impacts the virtual assistant’s accuracy or intent score. Errors are high severity problems. - Hover on the
 Warning icon and follow the instructions in the warning to enhance the training for ML utterances.
Warning icon and follow the instructions in the warning to enhance the training for ML utterances. Note: A warning is displayed when the issue impacts the VA’s accuracy and it can be resolved. Warnings are less severe problems when compared to errors.
Note: A warning is displayed when the issue impacts the VA’s accuracy and it can be resolved. Warnings are less severe problems when compared to errors.
- Hover on the
- Once you click on the Intent with error or warning, hover over the
 Bulb icon to view the summary of error or warning messages as illustrated below:
Bulb icon to view the summary of error or warning messages as illustrated below:
ML Training Recommendations
- Give a balanced training for all the intents that the bot needs to detect, add approximately the same number of sample utterances. A skewed model may result in skewed results.
- Provide at least 8-10 sample utterances against each intent. The model with just 1-2 utterances will not yield any machine learning benefits. Ensure that the utterances are varied and you do not provide variations that use the same words in a different order.
- Avoid training common phrases that could be applied to every intent, for example, “I want to”. Ensure that the utterances are varied for larger variety and learning.
- After every change, train the model and check the model. Ensure that all the dots in the ML model are diagonal (in the True-positive and True-negative) quadrant and you do not have scattered utterances in other quadrants. Train the model until you achieve this.
- Regularly train the bot with new utterances.
- Regularly review the failed or abandoned utterances and add them to utterance list against a valid task or intent.
NLP Intent Detection Training Recommendations
- If there are a good number of sample utterances, try training the bot using Machine Learning approach first, before trying to train the fundamental meaning model.
- Define bot synonyms to build a domain dictionary such as pwd for a password; SB for a savings bank account.
- After every change to the model training, run the batch testing modules. Test suites are a means to perform regression testing of your bot’s ML model.
NLP Entity Detection Training Recommendations
The best approach to train entities is based on the type of entity as explained below:
- Entity type like List of Items (enumerated, lookup), City, Date, Country do not need any training unless the same entity type is used multiple types in the same task. If the same entity type is used in a bot task, use either of the training models to find the entity within the user utterances.
- When the entity type is String or Description, the recommended approach is to use Entity patterns and synonyms.
- For all other entity types, both NER and Patterns can be used in combination.
Entity Training Recommendations
- Use NER training where possible – NER coverage is higher than patterns.
- NER approach best suits detecting an entity where information is provided as unformatted data. For entities like Date and Time, the platform has been trained with a large set of data.
- NER is a neural network-based model and will need to be trained with at least 8-10 samples to work effectively.
ML Training Recommendations
- Give a balanced training for all the intents that the bot needs to detect, add approximately the same number of sample utterances. A skewed model may result in skewed results.
- Provide at least 8-10 sample utterances against each intent. The model with just 1-2 utterances will not yield any machine learning benefits. Ensure that the utterances are varied and you do not provide variations that use the same words in a different order.
- Avoid training common phrases that could be applied to every intent, for example, “I want to”. Ensure that the utterances are varied for larger variety and learning.
- After every change, train the model and check the model. Ensure that all the dots in the ML model are diagonal (in the True-positive and True-negative) quadrant and you do not have scattered utterances in other quadrants. Train the model until you achieve this.
- Regularly train the bot with new utterances.
- Regularly review the failed or abandoned utterances and add them to utterance list against a valid task or intent.
NLP Intent Detection Training Recommendations
- If there are a good number of sample utterances, try training the bot using Machine Learning approach first, before trying to train the fundamental meaning model.
- Define bot synonyms to build a domain dictionary such as pwd for a password; SB for a savings bank account.
- After every change to the model training, run the batch testing modules. Test suites are a means to perform regression testing of your bot’s ML model.
NLP Entity Detection Training Recommendations
The best approach to train entities is based on the type of entity as explained below:
- Entity type like List of Items (enumerated, lookup), City, Date, Country do not need any training unless the same entity type is used multiple types in the same task. If the same entity type is used in a bot task, use either of the training models to find the entity within the user utterances.
- When the entity type is String or Description, the recommended approach is to use Entity patterns and synonyms.
- For all other entity types, both NER and Patterns can be used in combination.
Entity Training Recommendations
- Use NER training where possible – NER coverage is higher than patterns.
- NER approach best suits detecting an entity where information is provided as unformatted data. For entities like Date and Time, the platform has been trained with a large set of data.
- NER is a neural network-based model and will need to be trained with at least 8-10 samples to work effectively.
Suggested Reading
You might want to read on ML Model, refer here.