양식 필드 추가
기본 사용자 이름과 암호 필드가 권한 부여 입력의 요구 사항을 충족하지 않는 경우 권한 부여 IDP 양식 필드를 추가하여 최종 사용자에게 표시할 사용자 정의 필드를 추가할 수 있습니다. 이러한 양식 필드를 사용할 수 있습니다. 예를 들면, PIN 코드가 권한 부여 프로세스, 추가로 사용자 이름 및 암호 양식 필드에 필요한 경우입니다.

다음 표에서는 권한 부여 IDP 양식 필드를 정의하는 데 사용되는 필드를 설명합니다.
| 필드 이름 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| 필드 제목 | 권한 부여 대화 상자에서 최종 사용자에게 표시되는 필드 이름을 지정합니다. |
| 필드 키 | 이 값은 권한 부여 서비스에 대한 최종 사용자 입력을 나타냅니다. |
| 도움말 힌트 | 필드에 표시되는 도움말 텍스트로서 필드에 입력해야 하는 내용을 설명합니다. |
| 필드 유형 |
고급 옵션을 선택하면 최종 사용자 인터페이스에서 표시되는 필드의 유형을 지정하여 다음 중 하나의 필드 키 값으로 할당된 사용자 입력을 수집합니다.
|
| 필수 | 고급 옵션을 선택하면 최종 사용자가 권한 부여를 완료하려면 이 필드를 정의해야 하는지 여부를 선택합니다. |
| 데이터 유형 | 고급 옵션을 선택하면 최종 사용자의 입력으로 예상되는 데이터 유형(예: 문자열)을 지정합니다. |
| 가시성 | 고급 옵션을 선택하면 권한 부여 필드의 속성을 표시, 숨김 또는 읽기 전용으로 표시할지 여부를 지정합니다. |
권한 부여 필드 추가
기본적으로 권한 부여 필드는 봇 요청 메시지의 헤더 일부로 구성됩니다. 봇 요청에 추가 권한 부여 필드가 필요하거나 예상되는 권한 부여(예: 사회 보장 번호 또는 PIN)가 헤더의 일부가 아닌 경우 권한 부여 필드 섹션에서 추가를 클릭한 후 필수 필드를 정의합니다.
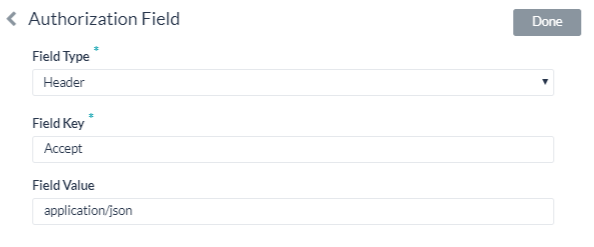
- 필드 유형 필드에서 봇 요청 메시지 및 필요한 권한 부여 필드 유형에서 위치에 따라 다음 중 하나를 선택할 수 있습니다.
- 헤더 – 봇이 요청 헤더에서 권한 부여 필드를 찾습니다.
- 페이로드 – 봇이 요청 본문 콘텐츠에서 권한 부여 필드를 찾습니다.
- 쿼리 문자열 – 봇이 요청 본문에서 쿼리로 권한 부여 필드를 찾습니다.
- 경로 매개 변수 – 봇이 요청 URL 경로에서 권한 부여 필드를 찾습니다.
- 필드 키 필드에서 선택한 필드 유형에 대한 필드 이름을 입력합니다.
- 필드 값 필드에 지정된 필드 키의 값을 입력합니다.
- 추가를 클릭합니다. 새 권한 부여 필드가 권한 부여 필드 섹션에 추가됩니다.
추가 인증 권한 필드를 추가하려면 권한 부여 필드 섹션에서 추가를 클릭합니다.
권한 부여 확인 URL
권한 부여 확인 URL 필드에서 권한 부여 메커니즘으로 봇을 배포하기 전에 봇 빌더에서 권한 부여 설정 테스트에 사용할 수 있는 URL을 선택적으로 정의하세요. 동적 필드와 경로 매개 변수 필드, 쿼리 필드 등을 사용하여 URL 테스트를 정의할 수 있습니다. 예: https://kore.someCompany.com/sap/opu/odata/sap/{{authfield1}}?$format=json 또는 https://{tenant}.service-now.com/api/now/v1/table/incident 더 자세한 내용은 작업에서 세션 및 컨텍스트 변수 사용하기를 참조하세요.
커넥터를 사용한 액세스
커넥터를 사용한 액세스 섹션에서 Kore.ai 커넥터 에이전트를 사용하여 Kore.ai 봇의 액세스를 활성화하려면 예를 선택합니다. Kore.ai 커넥터 에이전트를 사용하여 클라우드 기반 Kore.ai 봇과 온프레미스 봇 애플리케이션 간의 보안 데이터 연결을 설정하고 유지할 수 있습니다. 온프레미스 봇 애플리케이션을 사용하여 회사 인트라넷 내에서 사용자와 시스템을 제한하거나 특정 데이터 교환을 위한 특정 채널을 구성하여 통신 보안을 유지합니다. 도메인에 활성 Kore.ai 커넥터가 정의되지 않으면 봇 관리자 콘솔 시스템 관리자에게 문의하라는 경고 메시지가 표시됩니다. 자세한 내용은 봇 관리 콘솔 설명서에서 Kore.ai 커넥터 사용을 참조하세요. 저장을 클릭하여 권한 부여 설정을 저장하고 새 권한 부여 메커니즘 대화 상자를 닫습니다.
권한 부여 테스트
권한 부여 설명을 저장하고 권한 부여 프로필 페이지에서 테스트를 클릭하면 권한 부여 정의를 테스트할 수 있습니다. 테스트를 클릭하면, 권한 부여 테스트 대화창이 나타납니다.  기본 권한 부여를 사용한 권한 부여 테스트 설정 방법
기본 권한 부여를 사용한 권한 부여 테스트 설정 방법
- 권한 부여 확인 URL 필드에서 권한 부여 설정을 테스트하려는 URL을 확인하거나 입력합니다.
- 봇이 하위 도메인을 사용하는 경우 테넌시 필드가 표시되고 테넌트를 지정해야 합니다.
- 웹 서비스의 사용자 이름 및 암호를 입력합니다.
- Content-Type 필드에서 URL에 예상되는 콘텐츠 유형을 선택합니다.
- URL을 테스트하려는 경우 메소드 필드는 읽기 전용이며 GET으로 설정됩니다.
- 테스트를 클릭하여 권한 부여 테스트를 시작합니다.
권한 부여 유효성 검증이 완료되면 권한 부여 테스트 대화창이 닫히고 성공 또는 실패 검증 결과가 화면 오른쪽 상단 코너에 표시됩니다. 권한 부여가 실패하면 헤더 및 응답 탭과 함께 권한 부여 테스트 실패 메시지가 표시됩니다.
작동 원리
봇에 기본 권한 부여가 사용될 때 Kore.ai 애플리케이션은 다음 그림과 같이 사용자에게 웹 애플리케이션 또는 웹 서비스에 액세스하려면 로그인 자격 증명을 입력하라는 메시지를 자동으로 표시합니다. 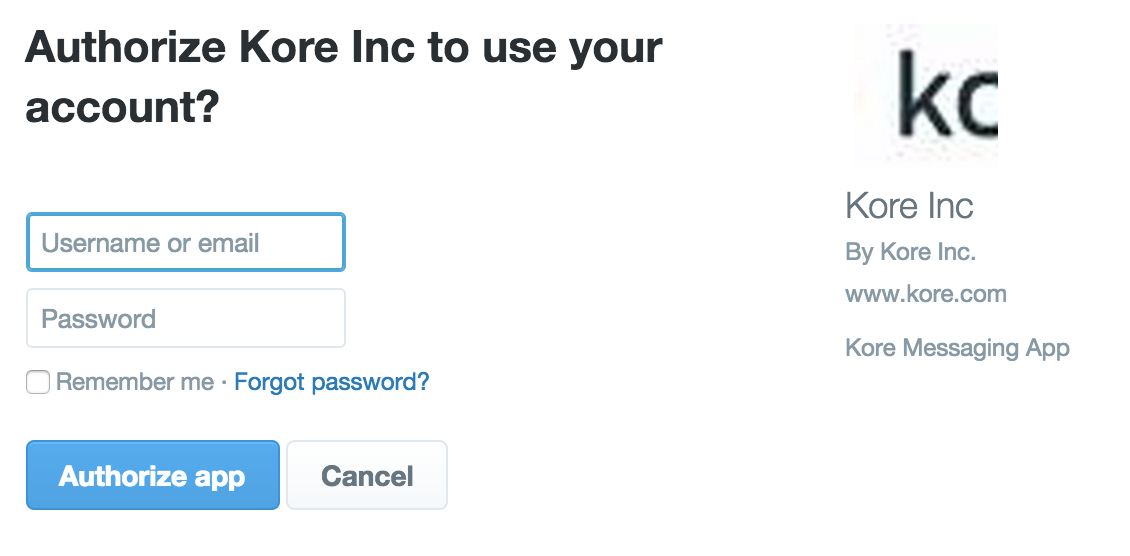 최종 사용자에게 권한이 부여된 후 설정은 다음 명명 구문을 사용하여 저장됩니다.
최종 사용자에게 권한이 부여된 후 설정은 다음 명명 구문을 사용하여 저장됩니다.
{{ First Name }} {{ Last Name }} {{ Bot Name }} {{ Account # }} {{ Sequence # }}
예: John Smith의 Twitter 계정 #1. Kore.ai 애플리케이션은 이 계정을 사용하여 향후 모든 봇 요청을 위해 웹 애플리케이션 또는 웹 서비스에 액세스할 수 있습니다. 또한 최종 사용자는 동일한 봇의 다른 작업을 위해 계정을 재사용할 수 있습니다.
フォーム フィールドの追加
デフォルトのユーザー名とパスワードのフィールドが承認入力のニーズを満たしていない場合は、承認IDPフォームフィールドを追加することで、エンドユーザーに表示されるカスタムフィールドを追加できます。これらのフォームフィールドを使用することができます。たとえば、ユーザー名やパスワードのフォームフィールドに加えて、認証プロセスでPINコードが必要な場合などです。

以下のテーブルは認証IDPフォームフィールドの定義に使用するフィールドの説明です。
| フィールド名 | 説明 |
|---|---|
| フィールド タイトル | 承認ダイアログでエンドユーザー表示するフィールド名を指定します。 |
| フィールドキー | 認証サービスにエンドユーザーが入力する値を示す値。 |
| ヘルプのヒント | フィールドに表示されるヘルプ文字はフィールドに入力すべくものを説明しています。 |
| フィールドタイプ |
上級オプションと選択した場合、エンドユーザーインターフェイスに表示されるフィールドのタイプを指定して、ユーザー入力の割り当てたフィールドキー値として収集します、以下のうちの一つ:
|
| 必須 | 上級オプションと選択した場合、認証を完了するためにエンドユーザーがこのフィールドを定義する必要があるかどうかを選択します。 |
| データタイプ | 上級オプションと選択した場合、エンドユーザーからの入力と予想するデータタイプを指定してください。例えば、文字列。 |
| 可視性 | 詳細オプション を選択した場合、承認フィールドを表示、非表示、または読み取り専用のいずれにするかを指定します。 |
認証フィールドの追加
デフォルトでは、認証フィールドとはボットリクエストのメッセージのヘッダーの一部として調整されたものです。ボットのリクエストに追加の認証フィールドが必要、または想定される認証がヘッダーの一部ではない場合(例:ソーシャルセキュリティ番号やPINなど)、認証フィールドの追加をクリックして必要なフィールドを定義します。 
- フィールドタイプフィールドに、以下のうちの一つを選択することができます。 必須のボットリクエストメッセージの位置および認証フィールドのタイプの次第です。
- ヘッダー―ボットは、リクエストヘッダーで認証フィールドを探します。
- ペイロード―ボットは、リクエスト本文のコンテンツで認証フィールドを探します。
- クエリ文字列―ボットは、リクエスト本文のクエリとして認証フィールドを探します。
- パスパラメータ―ボットは、リクエストURLパスで認証フィールドを探します。
- フィールドキーフィールドに、選択済のフィールドタイプフィールド名を入力してください。
- フィールド値フィールドに、フィールドキーの指定された値を入力してください。
- 追加をクリックします。新規の認証フィールドは認証フィールドのセクションに追加されました。
認証フィールドを追加する場合、認証フィールドセクションの追加をクリックしてください。
認証チェックURL
認証チェックURLフィールドで、認証メカニズムでボットを展開する前にボットビルダー から認証設定をテストするために使用できるURLを定義します。ダイナミックフィールド、パスパラメータフィールド、クエリフィールドなどを使用して、テストURLを定義することができます。(例:https://kore.someCompany.com/sap/opu/odata/sap/{{authfield1}}/?$format=jsonまたはhttps://{tenant}.service-now.com/api/now/v1/table/incident)詳細については、タスクのセッション変数とコンテキスト変数を使用を参照してください。
コネクタを使用してアクセス
コネクタでアクセスのセクションで、はいを選択するとKore.aiコネクタエージェントでKore.aiボットへのアクセスをできるようにします。Kore.aiコネクタエージェントを使用して、クラウドベースのKore.aiボットとオンプレミスのボットアプリケーション間の安全なデータ接続を確立および維持できます。オンプレミスのボットアプリケーションでは、イントラネット内のユーザーやシステムを制限したり、特定のデータ交換のために特定のチャネルを設定したりすることで、通信のセキュリティを確保しています。
もしご使用のドメインは定義済の活動的なKore.aiコネクタではない場合、警告メッセージは表示され、ボットのアドミンコンソールのシステムアドミニストレータに連絡します。詳細については、ボット管理コンソールのドキュメントのKore.aiコネクタの使用をご確認ください。
保存をクリックして保存認証を保存して新規認証メカニズムのダイアログを閉めます。
認証のテスト
認証設定を保存した後、認証プロファイルページからテストをクリックすると、認証の定義をテストすることができます。テストをクリックすると、テスト認証ダイアログ。

テスト認証の設定 – 基本認証
- 認証チェックURLフィールドに、実証やURLをテスト認証調整に入力してください。
- ボットはサブドメインを使用する場合、テンナンシーフィールドは表示されて、必ずテナントを指定してください。
- ウェブサービスのユーザー名とパスワードを入力します。
- URLとして求めるコンテンツ タイプは、コンテンツ タイプフィールドで選択します。
- URLのテストの場合、方法フィールドはリードオンリーそしてGETと設定されました。
- テストをクリックすると認証テストを開始します。
認証の検証が完了すると、テスト認証ダイアログが閉じ、画面右上に検証結果(成功または失敗)が表示されます。認証失敗の場合、認証テスト失敗のメッセージがヘッダーおよびレスポンスのタブとともに表示されます。
仕組みについて
ボットに基本認証を使用する場合、下記の図の通り、Kore.aiアプリケーションは自動的にユーザーをプロンプトしてクレデンシャルのロクインでウェブアプリケーションやウェブサービスへのアクセスへ進めます。

エンドユーザーが承認された後、以下のシンタックスを使用して設定が保存されます。
{{ First Name }} {{ Last Name }} {{ Bot Name }} {{ Account # }} {{ Sequence # }}
たとえば、ジョン・スミスのツイッター アカウント#1。Kore.aiアプリケーションは、このアカウントを使用して、将来のすべてのボットリクエストに対して、WebアプリケーションまたはWebサービスにアクセスすることができます。その他、エンドユーザーはアカウントを他のタスクに同じボットで再使用することができます。
To define Basic Authorization for your bot, follow these steps:
- Open the bot for which you want to configure the Basic Authorization profile.
- Select the Build tab from the top menu.
- From the left menus, click Configurations -> Authorization Profile
- Click Add. The New Authorization Mechanism dialog opens.
- In the Authorization Type drop-down list, select Basic Auth.
- In the Name field, enter the name for your Basic Auth type.

Defining Tenancy
If required, in the Subdomain section, select Yes if the base URL for a web application or user interface uses a tenant name in the URL. For example, kore is the tenant organization for a web service using tenants as www.kore.someCompany.com.
In the following example configuration, the tenancy URL contains the {tenant} organization placeholder.

Adding Form Fields
If the default username and password fields do not meet your needs for authorization input, you can add custom fields displayed to the end-user by adding authorization IDP form fields. You can use these form fields. For example, if PIN code is required in the authorization process, in addition to the Username and Password form fields.

The following table describes the fields used to define an authorization IDP form field.
| FIELD NAME | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|
| Field Title | Specify the name of the field displayed to the end-user in the authorization dialog. |
| Field Key | The value that represents the end-user input value to the authorizing service. |
| Help Hint | The help text displayed in the field to describe what should be entered into the field. |
| Field Type | When Advanced Options is selected, specify the type of field displayed in the end-user interface to collect the user input assigned as the value for the Field Key, one of:
|
| Mandatory | When Advanced Options is selected, select if the end-user must define this field to complete the authorization. |
| Data Type | When Advanced Options is selected, specify the type of data expected as input from the end-user, for example, String. |
| Visibility | When Advanced Options is selected, specify if the authorization field should be visible, hidden, or displayed as read-only. |
Adding Authorization Fields
By default, authorization fields are configured as part of the header of the Bot request message. If your Bot request requires additional authorization fields or the expected authorization is not part of the header, for example, social security number or PIN, click Add in the Authorization Fields section and then define the required fields.
- In the Field Type field, you can select one of the following depending on where in the Bot request message and the type of authorization fields that are required.
- Header – The bot looks for the authorization fields in the request header.
- Payload – The bot looks for the authorization fields in the request body content.
- Query String – The bot looks for the authorization fields as a query in the request body.
- Path Param – The book looks for the authorization fields in the request URL path.
- In the Field Key field, enter the name of the field for the selected Field Type.
- In the Field Value field, enter the value for the Field Key specified.
- Click Add. The new authorization field is added in the Authorization Fields section.
To add additional authorization fields, click Add in the Authorization Fields section.
Authorization Check URL
In the Authorization Check URL field, optionally define a URL that can be used to test the authorization settings from Bot Builder before you deploy the Bot with the authorization mechanism. You can use dynamic fields, path parameter fields, query fields, and so forth, to define the test URL.
For example
https://kore.someCompany.com/sap/opu/odata/sap/{{authfield1}}/?$format=json
or
https://{tenant}.service-now.com/api/now/v1/table/incident
For more information, see Using Session and Context Variables in Tasks.
Access Using a Connector
In the Access Using a Connector section, select Yes to enable access for Kore.ai Bots using the Kore.ai Connector Agent.
The Kore.ai Connector Agent can be used to establish and maintain secure data connectivity between cloud-based Kore.ai Bots and your on-premises Bots application. Using an on-premise Bots application, communications security is maintained by restricting users and systems within the company intranet or by configuring specific channels for specific data exchange.
If your domain does not have any active Kore.ai Connectors defined, a warning message is displayed to contact the Bots Admin Console system, administrator. For more information, see Using the Kore.ai Connector in the Bots Admin Console documentation.
Click Save to save the authorization settings and close the New Authorization Mechanism dialog.
Testing the Authorization
Once you save the authorization settings, you can test your authorization definition when you click Test from the Authorization Profile page.
When you click Test, the Test Authorization dialog.
To configure the Test Authorization – Basic Auth
- In the Auth Check URL field, verify or enter the URL to test the authorization configuration.
- If your bot uses subdomains, the Tenancy field is displayed and you must specify the tenant.
- Enter your User Name and Password for the web service.
- Select the content type expected for the URL in the Content-Type field.
- For testing the URL, the Method field is read-only and set to GET.
- Click Test to begin the authorization test.
When the validation of authorization is complete, the Test Authorization dialog closes and you can see the results of the validation, either success or failure, on the top-right corner of the screen.
If the authorization fails, the Auth Test Failed message is displayed along with the Headers and Response tabs.
How it all Works
When basic authorization is used for a Bot, the Kore.ai application automatically prompts the user for login credentials to access the web application or web service as shown in the following illustration.

After the end-user authorizes, the settings are saved using the following naming syntax:
{{ First Name }} {{ Last Name }} {{ Bot Name }} {{ Account # }} {{ Sequence # }}
For example, John Smith’s Twitter Account #1.
The Kore.ai application can access the web application or web service for all future Bot requests using this account. In addition, the end-user can reuse the account for other tasks for the same Bot.