Kore.ai 가상 비서 플랫폼을 사용하여 대화형 AI 가상 비서를 구축할 수 있습니다. 대화형 AI는 기계가 사용자와 자연스러운 대화를 할 수 있도록 하는 것입니다. 대화형 봇이 인간 상호 작용을 이해하는 비결은 사용자의 의도를 파악하고(의도 감지), 대화에서 유용한 정보를 추출하고(엔티티 추출), 이를 관련 조치 또는 작업에 매핑하는(대화 작업 실행) 능력에 있습니다. 여기서 중요한 용어는 자연어 이해하기입니다. NLP(자연어 처리)는 자연스러운 대화에서 의도와 관련 정보를 추론하는 기술입니다. Kore.ai 가상 비서의 대화 흐름은 다양한 NLU 엔진과 대화 엔진을 거쳐 조치와 대응을 결정합니다.
이 문서의 목표는 Kore.ai 가상 비서 내의 NLP 흐름의 개요를 제공하고 개발자로서 이 기능을 활용하여 효율적이고 정확한 봇 응답을 통해 사용자 경험을 개선하는 방법을 제공하는 것입니다.
NLP Approach
The Kore.ai Bots platform employs a multi-pronged approach to natural language, which combines the following three models for optimal outcomes:
- Fundamental Meaning: A computational linguistics approach that is built on ChatScript. The model analyzes the structure of a user’s utterance to identify each word by meaning, position, conjugation, capitalization, plurality, and other factors.
- Custom Machine Learning (ML): Kore.ai uses state-of-the-art NLP algorithms and models for machine learning.
- Ontology-based Knowledge Graph Engine (KG): Kore.ai Knowledge Graph helps you turn your static FAQ text into an intelligent and personalized conversational experience.
With its three-fold approach, the Kore.ai Bots platform enables you to accelerate the NLU performance of the virtual assistant and achieve optimal NLU accuracy with relatively less training data. It automatically enables the NLP capabilities to all built-in and custom bots, and powers the way chatbots communicate, understand, and respond to a user request.
Kore.ai NLP 구성 요소
Kore.ai 가상 비서가 사용자 발화를 수신하면 사용자 의도를 식별하고 추가 정보를 추출한 다음 작업 실행을 통해 사용자에게 응답하도록 처리됩니다. NLP는 첫 두 가지, 즉, 의도 감지와 엔티티 추출과 주로 관련이 있습니다. 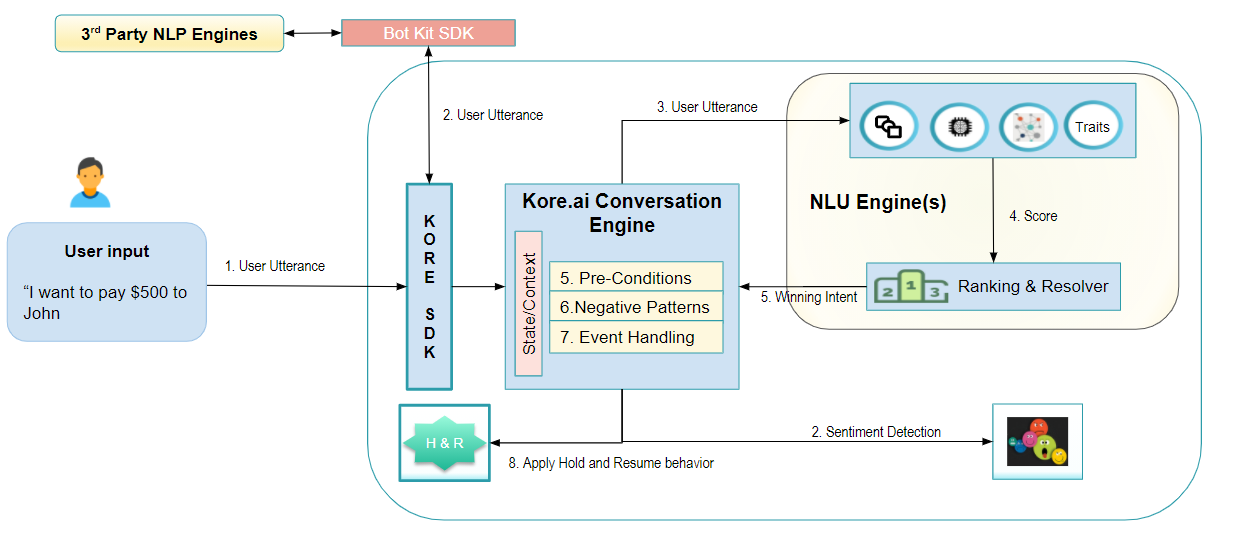 대화형 흐름의 단계:
대화형 흐름의 단계:
- 사용자 발화는 엔티티 추출과 의도 감지를 위해 일련의 NLU 엔진을 거칩니다. Kore.ai 플랫폼이 제공하는 다양한 NLU 엔진은 다음과 같습니다.
- 문법 구조에 따라 발화를 분해하는 Fundamental Meaning Engine,
- 예시 기반 자동 학습 과정을 기반으로 발화에서 개별 단어를 분류하는 기계 학습 엔진,
- 주로 FAQ 유형의 사용자 질의를 처리하고 사용자 질의에 대한 응답으로 작업을 실행하도록 설정할 수 있는 지식 컬렉션 엔진,
- 다중 클래스 분류기로서 사용자 발화에서 여러 카테고리를 식별할 수 있어서 사용자 의도 감지 개선에 도움이 되는 특성 엔진,
- 대화에 인간미를 더하기 위한 스몰 토크 엔진,
- 위의 엔진에서 얻은 결과에 점수를 매기고 설정된 비즈니스 규칙에 따라 순위를 매기는 순위와 해결.
- 위의 기본 NLU 기능을 확장하여 나만의 NLU 엔진을 사용할 수 있습니다. Bot Kit SDK를 설치하고 가상 비서를 타사 NLP 엔진과 쉽게 통합할 수 있습니다. 타사 NLP 엔진의 출력은 Kore.ai NLU 엔진의 출력을 보완하여 엔진의 효율성과 정확도를 높입니다.
- 추출된 엔티티와 함께 최상의 의도는 실제 작업 실행을 위해 대화 엔진을 거칩니다. 이 엔진은 사용자 세부 정보, 사용자가 요청한 이전 의도, 비즈니스 규칙에 따라 태그된 기타 정보를 사용하여 대화의 상태 또는 컨텍스트를 유지하여 인간에 가까운 대화 경험을 제공합니다. 대화 엔진은 다음 조건과 함께 이러한 상태 정보를 사용하여 NLU 엔진이 식별한 의도를 수락하거나 거부합니다.
- 사전 조건 – 의도에 일련의 사전 정의된 조건이 설정되어 있고 이러한 조건 중 하나라도 충족되지 않으면 최상의 의도는 거부됩니다. 예를 들어, 청구서 지불 의도에는 사용 가능한 수취인 세부 정보가 있어야 합니다.
- 네거티브 패턴 – 특정 의도를 식별하지 않아야 하는 패턴의 존재를 캡처합니다. 예를 들어 “카드를 분실했습니다. 새 카드를 신청하려면 어떻게 해야 합니까”에서 “카드를 분실했습니다”라는 문구가 존재하므로 “카드 신청” 의도를 실행하는 대신 현재 카드를 비활성화하고 사기성 행위를 신고해야 합니다
- 이벤트 처리 – 환영 메시지, 감정 분석 등에 대해 정의된 이벤트
- 중단 설정(진행 중인 작업 과정에서 다른 의도가 식별되는 상황 처리) 또는 감정 분석 설정(사용자가 화난 것 같으므로 상담사로 전환이 필요함)과 같은 다른 조건도 수행해야 할 조치에 중요합니다.
- 상호 작용 채널을 기준으로 응답이 생성되어 사용자에게 표시됩니다. 응답은 성공 메시지, 사용자가 요청한 정보 또는 누락된 정보를 요청하는 프롬프트일 수 있습니다.
NLP 학습
이전 섹션에서 Kore.ai 가상 비서의 NLP 프로세스를 살펴보았지만, 귀사의 요구 사항에 따라 프로세스가 진행되도록 하려면 귀사 쪽에서도 학습이 필요합니다. 그렇다면 완전한 기능을 갖춘 봇을 학습시켜 최상의 결과를 얻는 방법은 무엇일까요? 위의 기능을 최대한 활용하는 방법은 무엇일까요?
이 섹션에서 NLP 학습의 몇 가지 기본 지침을 먼저 확인한 후 각 NLU 엔진의 세부 사항을 살펴보겠습니다.
범위
NLP 학습의 첫 번째 단계는 봇의 범위를 정의하는 것이며, 봇이 해결해야 할 문제를 좁히면, 다양한 학습 뉘앙스를 설정하는 데 도움이 됩니다. SME/BA, 대화 경험 디자이너, 봇 개발자, NLP 분석가/데이터 엔지니어, NLP 트레이너, 테스터와 같은 다양한 이해 관계자와의 브레인스토밍 세션을 포함합니다. 다음은 봇 범위를 지정하는 동안 추천된 기본 지침입니다.
- 해결해야 할 문제부터 시작하세요 – 봇이 완수해야 할 작업을 명확히 이해하세요. 비즈니스 분석가와 봇 개발자와 상담하여 봇의 요구 사항과 실제 기능을 이해하세요.
- 사용 사례에 대한 의도 목록을 생성하세요 – 전체 프로세스가 간소화됩니다.
- 각 의도에 대해 봇이 수행하고자 하는 핵심 결과를 식별하세요.
- 플랫폼 요구 사항이 아니라 사용자 요구 사항에 집중해야 합니다.
- 예시 대화를 자세히 설명하세요 – 발화 및 응답 모두
- 방에 있는 사람의 이상적인 결과는 무엇입니까
- 극단적인 경우와 후속 조치 그리고 질문 명확화를 검토하세요
- 이를 위해 플랫폼의 스토리보드 기능을 활용할 수 있습니다. 봇 개발 단계에서 아직 사용하지 않은 경우, 지금 사용할 수 있습니다
- 조치를 달성하기 위해 사람들이 어떤 질문을 할 수 있을지 물어보세요 – 모든 의도의 대체 발화가 됩니다. 관용 표현 및 속어 사용법도 포함하세요.
어떤 엔진일까요?
Kore.ai 플랫폼이 NLU를 위한 세 가지 주요 엔진을 제공하는 것을 위에서 확인했습니다
- 기계 학습(ML)
- Fundamental Meaning(FM)
- 지식 컬렉션(KG)
어떤 엔진을 언제 사용할까요? 각 엔진에는 설정과 구성이 있습니다. 이러한 내용은 다른 곳에서 자세히 다룹니다(자세한 내용은 여기를 참조하세요). 어떤 엔진을 언제 사용해야 하는지에 대한 광범위한 지침이 여기에 있습니다.
기계 학습 엔진
ML은 봇 학습을 위해 권장되는 엔진입니다. 바로 유연성과 자동 학습 기능 때문입니다. 몇 가지 예를 들자면 엔진은 유사한 새로운 발화를 학습하고 이해할 수 있습니다.
그리고 학습 발화는 완전한 문장일 필요가 없으며, ML은 문구에서도 학습할 수 있습니다. 구현하려는 각 의도에 대해 대규모 말뭉치가 있는 경우 기계 학습을 선택하세요. 말뭉치가 없다면 말뭉치를 하나 개발하는 것이 좋습니다. 장기적으로 볼 때 시간이 덜 걸리고 쉬운 다른 옵션을 선택하는 것보다 대규모 말뭉치를 구축하고 ML을 사용하는 데 시간을 할애하는 것이 더 좋습니다. 대규모 말뭉치의 정의는 의도에 따라 다를 수 있습니다.
예를 들어, 의도가 공통점이 전혀 없고 서로 매우 다르지만 “잔고 가져오기” 및 “송금“과 같은 샘플 데이터를 사용하여 이해할 수 있는 경우, 각 의도별로 200-300개의 말뭉치로 충분합니다. 그러나 의도가 송금 및 청구서 결제와 같이 서로 비슷한 경우(“지불하고 싶습니다….”라는 매우 유사한 발화로 보통 시작합니다), 말뭉치는 수천 개여야 합니다.
마찬가지로, Deep Neural Networks를 사용하려는 경우 이러한 네트워크는 데이터가 많이 필요하기 때문에 참 긍정 및 참 부정 모두를 더 잘 예측하기 위해 더 많은 수의 샘플이 필요합니다.
지식 컬렉션 엔진
귀하의 의도가 본질적으로 거래 작업보다 질의와 유사하거나 콘텐츠가 문서에 있고 봇이 문서로부터 사용자 질의에 응답하도록 하려면 지식 컬렉션을 선택합니다. 지식 컬렉션은 사용자 질의에 대한 응답으로 대화 작업을 실행하는 데 사용할 수도 있으므로 양날의 검으로 작동합니다.
의도는 많고 대체 발화를 준비할 시간이 없지만 일부 중요한 용어에 수동으로 주석을 달 수 있는 경우 지식 컬렉션을 선택합니다. 그러나 KG의 주석은 ML의 자동 학습 프로세스와 유사한 방식으로 작동하기 때문에 말뭉치를 구축하고 ML을 선택하는 데 시간을 할애하는 것이 좋습니다.
Fundamental Meaning Engine
사용자가 관용적인 문장이나 명령어와 같은 문장을 사용하거나 너무 엄격하지 않고 일부 긍정 오류를 감수할 수 있는 경우 FM 엔진을 선택하세요.
Kore.aiバーチャルアシスタントプラットフォームを使用すると、会話型AIバーチャルアシスタントを構築できます。会話型AIとは、機械がユーザーと自然に会話できるようにすることです。会話型ボットが人間との相互作用を理解するための鍵は、ユーザーの意図を識別し(インテント検出)、発話から有用な情報を抽出し(エンティティ抽出)、関連するアクション又はタスクにマッピングする(ダイアログタスクの実行)能力にあります。ここで重要な条件は、自然言語を理解することです。NLP(自然言語処理)は、自然な会話から意図と関連情報を推測するサイエンスです。Kore.aiバーチャルアシスタントの会話フローは、アクションと応答を決定する前に、さまざまなNLUエンジンと会話エンジンを通過します。
このドキュメントは、Kore.aiバーチャルアシスタント内のNLPフローの概要の提供と、開発者としてその機能を活用して効率的で正確なボット応答を実現し、ユーザーエクスペリエンスを向上させる方法を提供することを目的としています。
NLP Approach
The Kore.ai Bots platform employs a multi-pronged approach to natural language, which combines the following three models for optimal outcomes:
- Fundamental Meaning: A computational linguistics approach that is built on ChatScript. The model analyzes the structure of a user’s utterance to identify each word by meaning, position, conjugation, capitalization, plurality, and other factors.
- Custom Machine Learning (ML): Kore.ai uses state-of-the-art NLP algorithms and models for machine learning.
- Ontology-based Knowledge Graph Engine (KG): Kore.ai Knowledge Graph helps you turn your static FAQ text into an intelligent and personalized conversational experience.
With its three-fold approach, the Kore.ai Bots platform enables you to accelerate the NLU performance of the virtual assistant and achieve optimal NLU accuracy with relatively less training data. It automatically enables the NLP capabilities to all built-in and custom bots, and powers the way chatbots communicate, understand, and respond to a user request.
Kore.aiNLPビルディングブロック
Kore.aiバーチャルアシスタントがユーザーの発話を受信すると、ユーザーのインテントを識別し、追加情報を抽出して処理され、タスクの実行を介してユーザーに応答します。NLPは、主に最初の2つ-インテント検出とエンティティ抽出に関係しています。 会話フローにおけるステップ:
会話フローにおけるステップ:
- ユーザーの発話は、エンティティの抽出とインテントの検出のために一連のNLUエンジンを通過します。Kore.aiプラットフォームが提供するさまざまなNLUエンジンは次のとおりです:
- 文法構成に基づいて発話を分割するファンダメンタル ミーニング エンジン
- 例に基づく自動学習トレーニングプロセスに沿って、発話内の個々の単語を分類する機械学習エンジン
- 主にFAQタイプのユーザー問い合わせを処理するナレッジコレクションエンジンで、ユーザー問い合わせに応答してタスクをトリガーするように構成することもできます
- マルチクラス分類が可能であり、ユーザーの発話の複数のカテゴリを識別できるため、ユーザーのインテントの検出を改善するのに役立つ示唆エンジン
- 会話に人間味を加えるためのスモールトークエンジン
- 上記のエンジンからの結果をスコアリングし、設定されたビジネスルールに従ってランク付けするためのランキングおよび解決。
- 上記のすぐに使用できるNLU機能を拡張して、独自のNLUエンジンを使用できます。ボットキットSDKをインストールして、バーチャルアシスタントをサードパーティのNLPエンジンと簡単に統合できます。サードパーティのNLPエンジンからの出力は、Kore.ai NLUエンジンからの出力を補完するため、エンジンの効率と精度が向上します。
- 識別されたインテントは、抽出されたエンティティとともに、実際のタスク実行のために会話エンジンに移行します。このエンジンは、ユーザーの詳細、以前ユーザーが要求したインテント、および人間に近い会話体験を提供するのに役立つビジネスルールによってタグ付けされたその他の情報などを使用して、会話の状態またはコンテキストを維持します。会話エンジンは、この状態情報と次の条件を使用して、NLUエンジンによって識別されたインテントを受け入れるか拒否を判断します。
- 前提条件-インテントに事前定義された条件のセットが構成されていて、これらの条件のいずれかが満たされていない場合、識別されたインテントは拒否されます。たとえば、請求書の支払いインテントでは、受取人の詳細が必要になります。
- ネガティブパターン-特定のインテントを特定してはならないパターンの存在をキャプチャします。たとえば、「カードを紛失しました。新しいカードを申請するにはどうすればよいですか」は、「カードを申請」インテントをトリガーする代わりに、まず現在のカードを無効にして、「カードを紛失した」というフレーズが存在するために不正行為を報告する必要があります。
- イベント処理-ウェルカムメッセージ、感情分析などのために定義されたイベント
- 割り込み設定(進行中のタスクの過程で別のインテントが識別された状況を処理するため)や感情分析設定(ユーザーが怒っているように聞こえるので、エージェントに転送する必要がある)などの他の条件も、実行するアクションとして重要です。
- インタラクションのチャネルに基づいて、レスポンスが生成され、ユーザーに提示されます。レスポンスは、成功メッセージ、ユーザーが要求した情報、又は不足している情報のプロンプトである可能性があります。
NLPトレーニング
前のセクションでは、Kore.aiバーチャルアシスタントのNLPプロセスについて説明しましたが、プロセスが要求どおりに進行するようにするには、トレーニングが必要です。では、最高の結果を達成するためにボットを完全に機能するようにトレーニングする方法は?上記の機能を最大限に活用する方法は?各NLUエンジンの詳細に入る前に、このセクションでNLPトレーニングのいくつかの基本的なガイドラインを見て行きます。
スコープ
NLPトレーニングの最初のステップは、ボットの範囲を定義することで、ボットが解決する必要のある問題を絞り込むことで、さまざまなトレーニングのニュアンスを構成するのに役立ちます。これには、SME / BA、会話エクスペリエンスデザイナー、ボット開発者、NLPアナリスト/データエンジニア、NLPトレーナー、テスターなどのさまざまな利害関係者とのブレインストーミングセッションが含まれます。ボットのスコーピング中に提案される基本的なガイドラインは次のとおりです;
- 解決すべき問題から始めます-ボットが何を達成することになっているのかを明確に把握します。ボットの要件と実際の機能を理解するには、ビジネスアナリストとボット開発者に相談してください。
- ユースケースのインテントのリストを作成します-これにより、全体のプロセスが合理化されます
- インテントごとに、ボットが達成しようとしている主要な結果を特定します
- プラットフォームの要件ではなく、ユーザーのニーズに焦点を当てる必要があります
- 会話の例を詳しく説明する-発話とレスポンスの両方
- 部屋の結果の理想的な人は何ですか
- エッジケース、フォローアップ、質問の明確化について考えます
- このために、プラットフォームのストーリーボード機能を活用できます。それはボット開発フェーズでまだ使用されていない場合は、今すぐ使用できます
- アクションを達成する一環として人が何を尋ねるかを自問します-これらはすべてのインテントの代替発話になります。慣用句や俗語の使用も含めるようにしてください。
どのエンジン?
Kore.aiプラットフォームがNLU用に3つのメインエンジンを提供することをこれまで見てきました
- 機械学習(ML)
- ファンダメンタルミーニング(FM)
- ナレッジ収集(KG)
どのエンジンをいつ使用しますか?これらの各エンジンには、設定と構成があります。これらは他の場所で詳細に扱われます(詳細についてはここを参照)。ここでは、どのエンジンをいつ使用するかについての幅広いガイドラインを上げます。機械学習エンジンMLは、ボットのトレーニングに推奨されるエンジンです。理由は、その柔軟性と自動学習機能です。いくつかの例を挙げれば、エンジンは似たような新しい発話を学習し、理解することができます。又、トレーニングの発話は完全な文章である必要はありません。MLはフレーズからも学習できます。実装を計画しているインテントごとに大きな言語集がある場合は、機械学習に進みます。言語集がない場合でも、それをを開発することをお勧めします。長期的には、時間のかからない簡単な他のオプションを選択するよりも、大規模な言語集の構築に時間を費やしてMLを使用する方が適切です。大きな言語集の定義は、インテントによって異なる場合があります。たとえば、インテントが共通性を持たずに互いに大きく異なり、「バランスを入手」や「資金を移動」などのサンプルデータを使用して理解できる場合は、インテントごとに200〜300の言語集で十分です。但し、[資金を移動]と[請求書を支払う]のように意図が互いに近い場合(通常、「支払いたい…」という非常によく似た発話で始まります)、言語集は1000位になります。同様に、ディープニューラルネットワークの使用を計画している場合、これらのネットワークはデータを大量に消費するため、真のポジティブと真のネガティブの両方をより正確に予測するには、より多くのサンプルが必要です。ナレッジ収集エンジン-インテントがトランザクションタスクよりも本質的に問い合わせに似ている場合、またはコンテンツがドキュメント内にあり、ボットがドキュメントからユーザー問い合わせに応答するようにしたい場合は、ナレッジコレクションに進みます。ナレッジ収集は、ユーザーの問い合わせに応じてダイアログタスクをトリガーするためにも使用できるため、両刃の剣として機能します。インテントがたくさんあるが、別の発話を準備する時間がなく、いくつかの重要な用語に手動で注釈を付けることができる場合は、ナレッジコレクションにアクセスしてください。但し、KGでの注釈は、MLの自動学習プロセスと同じように機能するため、言語集の構築とMLの取得に時間をかけることをお勧めします。ファンダメンタルミーニングエンジン-ユーザーが慣用的な文やコマンドのような文を使用できる場合、又は厳密すぎず、誤検知が発生する可能性がある場合は、FMエンジンを使用してください。
Conversational AI is all about enabling a machine to have natural conversations with users. The key for a conversational bot to understand human interactions lies in its ability to identify the intention of the user (Intent Detection), extract useful information from their utterance (Entity Extraction), and map them to relevant actions or tasks (Dialog Task execution). The crucial idea here is understanding the natural language.
Natural Language Processing(NLP) is the science of deducing the intention and related information from natural conversations. The conversation flow in Kore.ai virtual assistants passes through various NLU engines and conversation engines before deciding upon action and response.
This document aims at providing an overview of the NLP flow within a Kore.ai virtual assistant and how you, as a developer, can leverage its features for an efficient and accurate VA response thus improving the user experience.
NLP Approach
The Kore.ai XO platform employs a multi-pronged approach to natural language, which combines the following three models for optimal outcomes:
- Fundamental Meaning: A computational linguistics approach that is built on ChatScript. The model analyzes the structure of a user’s utterance to identify each word by meaning, position, conjugation, capitalization, plurality, and other factors.
- Custom Machine Learning (ML): Kore.ai uses state-of-the-art NLP algorithms and models for machine learning.
- Ontology-based Knowledge Graph Engine (KG): Kore.ai Knowledge Graph helps you turn your static FAQ text into an intelligent and personalized conversational experience.
With its three-fold approach, the Kore.ai XO platform enables you to accelerate the NLU performance of the virtual assistant and achieve optimal NLU accuracy with relatively less training data. It automatically enables the NLP capabilities to all built-in and custom VAs, and powers the way virtual assistants communicate, understand and respond to a user request.
Kore.ai NLP Building Blocks
When the Kore.ai Virtual Assistant receives a user utterance, it is processed to identify the user intent, extract any additional information, and then answer the user via a task execution. NLP is mostly concerned with the first two – intent detection and entity extraction.
Steps in a conversation flow:
-
The user utterance goes through a series of NLU engines for entity extraction and intent detection. The various NLU engines provided by the Kore.ai platform are as follows:
- Fundamental Meaning Engine which breaks up the utterances based on the grammar constructs;
- Machine Learning Engine which classifies individual words in the utterance/ based on an example-based auto-learning training process;
- Knowledge Collection Engine which mostly deals with FAQ type user queries can also be configured to trigger tasks in response to the user query;
- Traits Engine which is a multiclass classifier and can identify multiple categories in user utterances thus aiding in refining user intent detection;
- Small Talk Engine which adds human flavor to the conversations;
- Ranking and Resolver scores the results from the above engines and ranks them according to the set business rules.
-
You can extend the above out-of-the-box NLU functionality to use your own NLU engine. You can install the Bot Kit SDK and easily integrate the virtual assistant with any 3rd party NLP engine. The output from the 3rd party NLP engine complements the outputs from the Kore.ai NLU engines thus adding to the efficiency and accuracy of the engine.
-
The winning intent along with the entities extracted then passes through the conversation engine for the actual task execution. This engine maintains the state or context of the conversation with information like user details, the previous intents requested by the user, and any other information as tagged by the business rules which would aid in providing a near-human conversation experience. The conversation engine uses this state information along with the following conditions to accept or reject the intent identified by the NLU engines
-
Pre-conditions – if an intent has a set of predefined conditions configured and if any of these conditions are not satisfied then the winning intent is rejected. For example, bill payment intent should have the payee details available.
-
Negative patterns – to capture the presence of a pattern that should not identify a particular intent. For example “I lost my card, how do I apply for a new card” should, instead of triggering “Apply Card” intent, attempt to disable the current card and report fraudulent activity due to the presence of the phrase “lost my card”
-
Event handling – events defined for a welcome message, sentiment analysis, etc
-
- Other conditions like Interruption settings (to handle situations where another intent is identified during the course of an ongoing task) or Sentiment Analysis settings (user sounds angry and hence should be transferred to an agent) also are crucial to the action to be taken.
- A response is generated and presented to the user based on the channel of interaction. The response could be a success message, information as requested by the user, or a prompt for missing information.
NLP Training
In the previous section, we have seen the NLP process of the Kore.ai virtual assistant, but it needs some training on your part to ensure that the process proceeds as per your requirements. So, how to train a fully functional bot to achieve the best results? How to make maximum use of the above features?
We will see some basic guidelines in NLP training in this section, before going into the details of each of the NLU engines.
Scoping
The first step in NLP training would be to define the scope of the bot, narrowing down the problem the bot will need to solve helps in configuring the various training nuances. This involves brainstorming sessions with various stakeholders like SMEs/BAs, Conversation Experience Designers, Bot Developers, NLP Analysts/Data Engineers, NLP Trainers, and Testers.
Following are the basic guidelines suggested while scoping the bot:
- Start with a problem to solve – get a clear idea of what the bot is supposed to accomplish. Talk to the business analyst and the bot developers to understand the requirements and the actual functionality of the bot.
- Create a list of Intents for the use cases – this would streamline the entire process
- For each intent, identify the key results that the bot is aiming to accomplish
- The focus should be on the needs of the user and not the platform requirements
- Detail out example conversations – both utterances and responses
- What is the ideal Person in the room result
- Think through edge cases, follow-ups, clarifying questions
- You can leverage the Storyboard feature of the platform for this. If it has not been already used for the bot development phase, you can use it now
- Ask what a person might ask as a part of achieving the actions – these would be the alternate utterances for every intent. Try to include idiomatic and slang usage also.
Which Engine?
We have seen above that the Kore.ai platform offers three main engines for NLU
- Machine Learning (ML)
- Fundamental Meaning (FM)
- Knowledge Collection (KG)
Which engine to use when? Each of these engines has settings and configurations. These are dealt with in detail elsewhere (see here for details). Here we will list out broad guidelines as to which engine to use when.
Machine Learning Engine
ML is the recommended engine for training a bot. The reason for this is its flexibility and auto-learn feature. Given a few examples, the engine learns and is capable of understanding similar new utterances. And the training utterances need not be full sentences, ML can learn from phrases too.
If you have a large corpus for each intent that you are planning to implement, then go for Machine Learning. Even if you don’t have a corpus it would be a good idea to develop one. In the long run, it is better to spend time building a large corpus and use ML rather than going for the other less time-consuming, easier options.
Definition of large corpus could differ depending on the intents. For example, if the intents are very different from each other without any commonality and can be understood using their sample data like “Get Balance” and “Transfer Funds“, then a corpus of 200-300 for each intent is sufficient. However, if intents are closer to each other like Transfer funds and Pay bill (they usually start with a very similar utterance “I want to pay….”), then the corpus should be in 1000s.
Similarly, if you are planning to use Deep Neural Networks, you need a higher number of samples for better predictions of both True Positives and True Negatives, as these networks are data-hungry.
Knowledge Collection Engine
If your intents are more query-like in nature than transactional tasks or if the content is in documents and you want the bot to answer user queries from documents, then go for Knowledge Collection. Knowledge Collection can also be used to trigger dialog tasks in response to user queries thus works as a double-edged sword.
If you have a lot of Intents but do not have time to prepare alternate utterances, but you can manually annotate some important terms, go for Knowledge Collection. But it is advisable to spend some time in building a corpus and going for ML since annotation in KG works in a similar way to ML’s auto-learning process.
Fundamental Meaning Engine
If you have cases where users could use idiomatic sentences or command-like sentences or if you are not too strict and can live with some false positives then go for FM engine.