Business Rules allows you to define rules to personalize and fine-tune the search results based on contexts. Rules can also be used for merchandising and promotions. Rules are set based on user context, search context, page context, or a combination of multiple contexts. Rules define the promotion or filtering of a set of results. For example, in an eCommerce site, based on the geographical location some products may not be available, or if the user is logged in from a mobile device the number of search results displayed needs to be reduced due to limited screen space.
SearchAssist lets you define two aspects of Business Rules:
- Condition – Using conditions you can define when the trigger takes place, based on the context and parameter values.
- Context can be:
- Search context is based on the user search history and has pre-defined attributes such as Recent Searches, Current Search, Trait, Entity, Keyword, Semantic.
- Page context can be based on pre-defined attributes such as Browser, Current page, Recent pages, and Location and other required attributes of a page can be passed from the website through the SDK.
- User Context can be based on user information that a website can pass through SDK.
- Parameters include setting the above context to contain/not contain/equals/not equals to a keyword.
- Context can be:
- Outcome – Using Outcome, you can define what happens when the condition mentioned in the condition matches.
- Action can be one of the following:
- Boost a particular response set – This is used to promote the results to display at the top
- Lower a particular response set – This is used to demote the results from displaying at the top
- Hide a particular response set – This is used to hide certain results from showing to the search user
- Filter a particular response set – This is used to filter certain search results by default to show to the search user.
- Response on which the above actions need to be applied can be specified by a field value containing/being equal to a static keyword or a dynamic keyword from the context.
- Action can be one of the following:
The following are some scenarios where you can apply business rules:
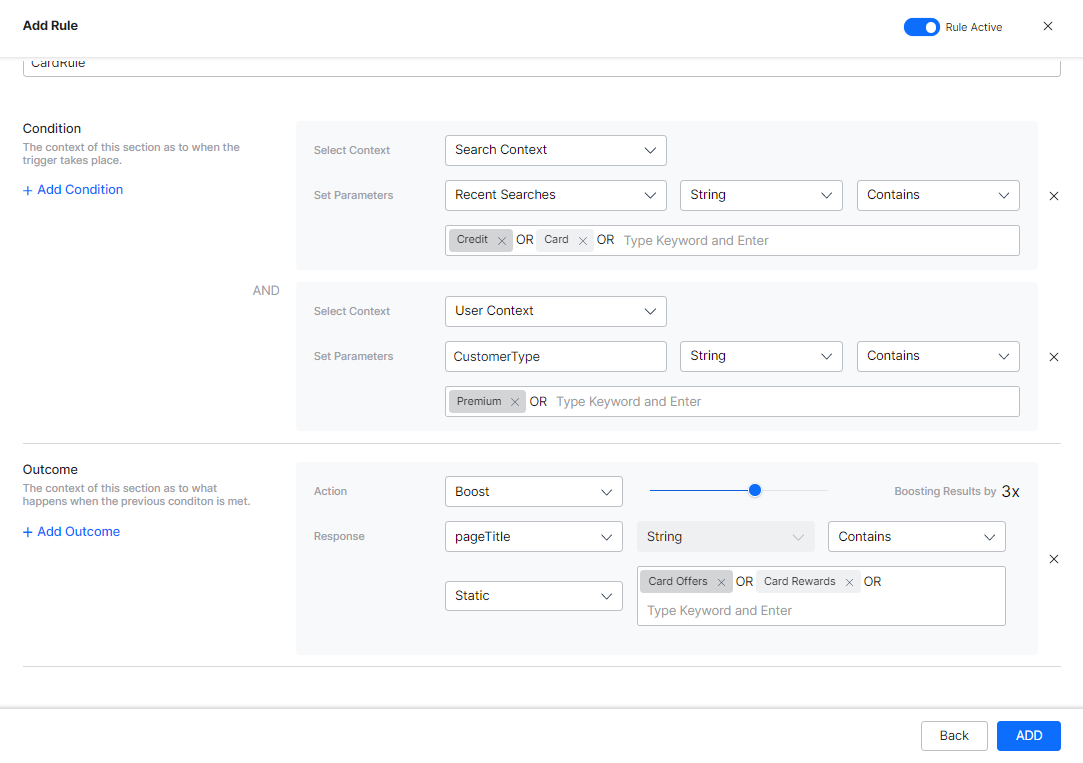
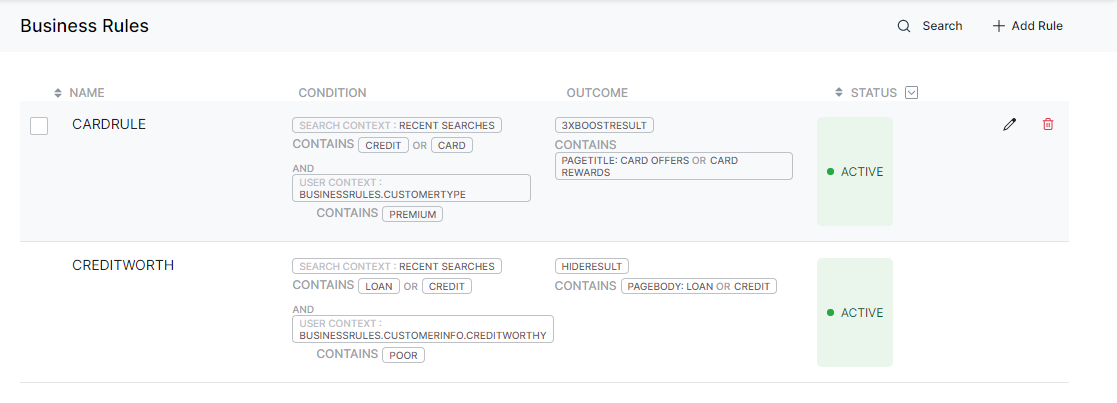
- Say, in a banking scenario, you want to present to your premium customers some credit card related offers, then you can define a rule as follows:
CONDITION: “Search Context: RecentSearches” Contains “Credit” OR “Card”
AND “User Context: CustomerType” Contains “Premium”
OUTCOME: “Boost Results” Containing “Title: Card Offers” OR “Title: Card Rewards” - If the user is proven to be not creditworthy, then you do not want to show them any loan offers, then you can define a business rule as follows:
CONDITION: “Search Context: RecentSearches” Contains “Loan” OR “Credit”
AND “User Context.CustomerInfo.CreditWorthy” Contains “Poor”
OUTCOME: “Hide Results” Containing “Loans: Loan” OR “Loans: Credit” - If the user has only a savings account and is searching for account-related information, you do not want to show them information related to other types of accounts like checking accounts. In such a scenario, then you can define a business rule as follows:
CONDITION: “User Context.AccountType” Contains “Savings”
AND “User Context: AccountType” Doesn’t Contain “Checking”
AND “Page Context: PageName” Contains “Account” OR “Banking”
AND “Search Context: CurrentSearch” Contains “Information” OR “Details”
OUTCOME: “Filter Results” Containing “Title: Savings”
Add Rule
To add a business rule, follow the below steps:
- Click the Indices tab on the top.
- On the left pane, under the Search Configuration section, click Business Rules.
- On the Business Rules page, click Add Rule on the top-right.
- On the Add Rule dialog box, enter a name in the Rule Name field.
- Under the Conditions section,
- Select a context from the Select Context drop-down list:
- Search Context – It is used to optimize search results based on the context provided by the user. For example, context-based on a recent search, current search, traits, etc.
- Page Context – It is the data that is specifically assigned to a page. For example, context-based on the current page, recent page, browser, device, etc.
- User Context – It is the data that is specifically assigned to a search user. For example, context based on the User Type (Premium User, Normal User, User Profile, Age).
- Configure the parameters as follows:
- Select the parameters available for the corresponding context from the Set Parameters drop-down lists.
- Set the Data Type expected for the parameter.
- Set the condition to Contains/Does not Contain/Equals to/Not Equals to.
- Set the keyword to be compared with, add multiple keywords by hitting enter after each entry.
- To add more conditions, click + Add Condition.
- Select a context from the Select Context drop-down list:
- Under the Outcome section,
- Select an action from the Action drop-down list:
- Boost – It boosts the results by X times (max 5X times).
- Lower – It lowers the results by X times (max 5X times).
- Hide – It hides the results based on the above conditions.
- Filter – It filters the results based on the above conditions.
- Select the parameters from the Response drop-down lists.
- Field that needs to be considered for the response.
- Data Type for the field, auto-populated by the application.
- Set the condition to Contains/Does not Contain/Equals to/Not Equals to.
- Static keyword or a dynamic keyword based on the context values.
- Set the keyword to be compared with, add multiple keywords by hitting enter after each entry.
- To add more outcomes, click + Add Outcome.
- Select an action from the Action drop-down list:
- Click Proceed.
Actions
Once added, you can perform the following actions on the rules:
- Search for a given business rule by name.
- Edit or Delete a business rule using the edit/delete icons. You can also delete business rules in bulk with the Bulk Select option.
- Using the handlebar against each business rule, you can specify the order in which the business rules should be applied.